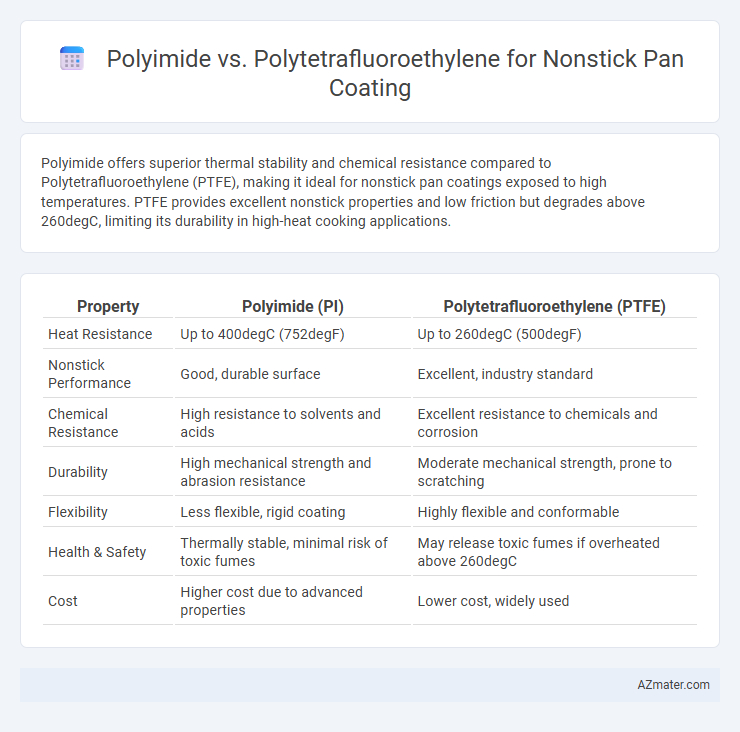
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), making it ideal for nonstick pan coatings exposed to high temperatures. PTFE provides excellent nonstick properties and low friction but degrades above 260degC, limiting its durability in high-heat cooking applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyimide (PI) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 400degC (752degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Nonstick Performance | Good, durable surface | Excellent, industry standard |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to solvents and acids | Excellent resistance to chemicals and corrosion |
| Durability | High mechanical strength and abrasion resistance | Moderate mechanical strength, prone to scratching |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, rigid coating | Highly flexible and conformable |
| Health & Safety | Thermally stable, minimal risk of toxic fumes | May release toxic fumes if overheated above 260degC |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, widely used |
Introduction to Nonstick Pan Coatings
Nonstick pan coatings primarily rely on materials like polyimide and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) due to their excellent heat resistance and low friction properties. PTFE, commonly known by the brand name Teflon, offers superior nonstick performance and chemical inertness, making it a popular choice for cookware surfaces. Polyimide provides enhanced thermal stability and durability, suitable for applications requiring higher temperature tolerance and mechanical resilience in nonstick coatings.
Overview of Polyimide Coating Technology
Polyimide coating technology offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to many other materials, including PTFE, making it ideal for high-temperature applications in nonstick pan coatings. Its unique polymer structure allows it to withstand temperatures up to 400degC, providing a durable, scratch-resistant surface that maintains nonstick properties without degrading. The advanced cross-linking within polyimide films enhances adhesion to metal substrates, ensuring long-lasting performance and reduced risk of flaking or peeling during cooking.
Fundamentals of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Coatings
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) coatings are widely used in nonstick pans due to their exceptional non-reactivity, low coefficient of friction, and high-temperature resistance up to 260degC. The molecular structure of PTFE, consisting of carbon-fluorine bonds, provides excellent chemical inertness and prevents food from adhering during cooking. Compared to polyimide, PTFE offers superior ease of cleaning and enhanced durability for everyday kitchen applications.
Key Differences Between Polyimide and PTFE
Polyimide coatings offer superior thermal stability up to 400degC compared to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which typically withstands temperatures only up to 260degC. While PTFE is well-known for its excellent nonstick properties and chemical resistance, Polyimide exhibits higher mechanical strength and durability under abrasive conditions. Key differences also include Polyimide's better adhesion to metal surfaces, making it ideal for industrial cookware applications, whereas PTFE remains the preferred choice for general nonstick kitchen pans due to its ease of cleaning and widespread availability.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability Comparison
Polyimide exhibits superior heat resistance with a continuous use temperature up to 400degC, outperforming polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which generally withstands temperatures up to 260degC before degradation. The thermal stability of polyimide ensures minimal decomposition at high temperatures, making it ideal for applications requiring prolonged exposure to heat. PTFE, while excellent for nonstick properties, experiences polymer breakdown and reduced performance beyond its thermal limit.
Nonstick Performance: Polyimide vs PTFE
Polyimide coatings offer excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, making them suitable for high-temperature cooking without degrading nonstick performance. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides superior nonstick properties due to its extremely low surface energy, resulting in effortless food release and easy cleanup. While PTFE excels in nonstick performance at typical cooking temperatures, polyimide coatings maintain durability under harsher conditions but may not match PTFE's slickness.
Durability and Longevity in Cooking Applications
Polyimide coatings offer exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, ensuring prolonged durability under high heat and frequent use in nonstick pans. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, provides excellent nonstick properties but tends to degrade faster at temperatures above 260degC, limiting its longevity in rigorous cooking conditions. Polyimide's superior resistance to thermal degradation and mechanical wear makes it a preferred choice for high-performance nonstick cookware demanding extended lifespan.
Safety and Food Contact Compliance
Polyimide exhibits excellent thermal stability and is generally considered safe for food contact applications, meeting FDA and EFSA regulations for nonstick pan coatings. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is widely used due to its superior nonstick properties, but it requires careful temperature control as overheating can release potentially harmful fumes; it is FDA-approved for food contact when used under recommended conditions. Both materials must comply with strict safety standards, but polyimide offers enhanced durability and chemical resistance, making it a safer choice for high-temperature cooking environments.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Polyimide coatings on nonstick pans offer excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, making them easier to clean without degrading over time, whereas polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) requires gentle cleaning to avoid surface damage and maintain its nonstick properties. PTFE-coated pans often demand hand washing with non-abrasive sponges and mild detergents to prevent scratches and prolong their lifespan, while polyimide's robust surface tolerates more rigorous cleaning methods. Regular maintenance for polyimide pans reduces residue buildup and preserves coating integrity, enhancing durability compared to PTFE alternatives.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Coating for Nonstick Pans
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature cooking applications where longevity is essential. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, provides excellent nonstick properties with easy food release and low friction but may degrade at temperatures above 260degC. Selecting the best coating depends on the cooking style: prefer Polyimide for high-heat resistance and industrial-grade cookware, while PTFE remains optimal for everyday home use due to its effective nonstick performance and safety at typical cooking temperatures.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Nonstick Pan Coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com