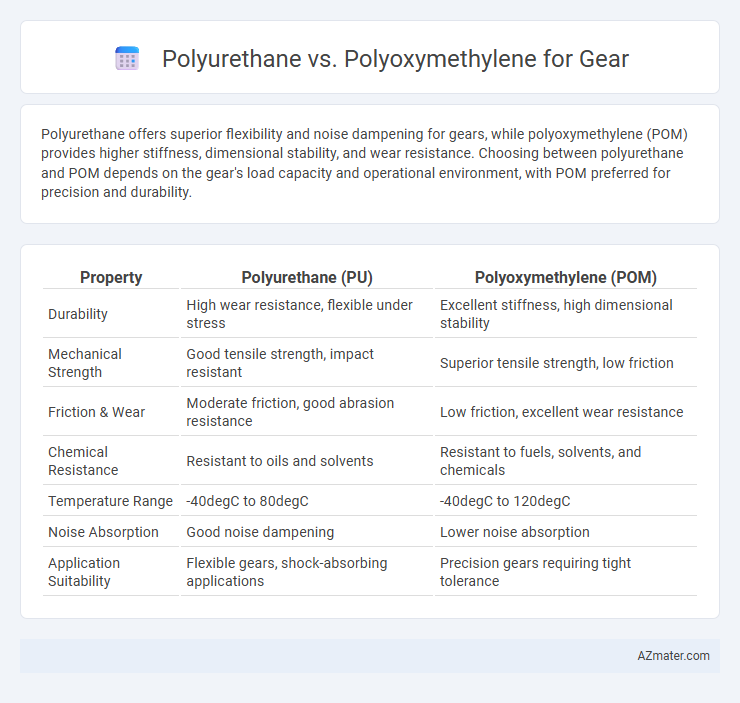
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and noise dampening for gears, while polyoxymethylene (POM) provides higher stiffness, dimensional stability, and wear resistance. Choosing between polyurethane and POM depends on the gear's load capacity and operational environment, with POM preferred for precision and durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) | Polyoxymethylene (POM) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High wear resistance, flexible under stress | Excellent stiffness, high dimensional stability |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength, impact resistant | Superior tensile strength, low friction |
| Friction & Wear | Moderate friction, good abrasion resistance | Low friction, excellent wear resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils and solvents | Resistant to fuels, solvents, and chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 80degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Noise Absorption | Good noise dampening | Lower noise absorption |
| Application Suitability | Flexible gears, shock-absorbing applications | Precision gears requiring tight tolerance |
Introduction to Gear Material Selection
Polyurethane offers high abrasion resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for gears subjected to shock loads and requiring noise reduction. Polyoxymethylene (POM), known for its excellent dimensional stability and low friction, excels in precision gear applications with continuous operation. Selecting between polyurethane and polyoxymethylene depends on factors such as load conditions, wear resistance, and environmental exposure to optimize gear performance and longevity.
Overview of Polyurethane (PU) and Polyoxymethylene (POM)
Polyurethane (PU) is a versatile polymer known for its excellent elasticity, abrasion resistance, and impact strength, making it ideal for gears requiring cushioning and noise reduction. Polyoxymethylene (POM), also called acetal, is a high-stiffness, low-friction engineering plastic with exceptional dimensional stability and resistance to wear and chemicals, suitable for precise and high-load gear applications. The choice between PU and POM gears depends on the balance of flexibility, durability, and operational environment specific to the mechanical demands.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyurethane exhibits high elasticity and excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for gears requiring shock absorption and noise reduction, with a typical tensile strength range of 35-70 MPa and elongation at break up to 500%. Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, offers superior dimensional stability, low friction coefficient (0.2), and higher hardness (typically 80-90 Shore D), resulting in enhanced wear resistance and mechanical strength useful for precision gears. The choice between polyurethane and polyoxymethylene depends on application-specific demands, with polyurethane preferred for flexibility and impact resistance, and POM favored for rigidity and consistent performance under high load conditions.
Wear Resistance and Durability
Polyoxymethylene (POM) outperforms polyurethane in wear resistance due to its low friction coefficient and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for precision gears under high load conditions. Polyurethane offers superior shock absorption and flexibility, which enhances durability in applications involving dynamic or impact stresses but tends to wear faster under continuous friction. For gears demanding long-term wear resistance and consistent performance, polyoxymethylene provides greater reliability, whereas polyurethane is preferred when elasticity and noise reduction are critical.
Noise and Vibration Dampening
Polyurethane gears excel in noise and vibration dampening due to their inherent flexibility and high energy absorption capacity, reducing operational sound significantly compared to polyoxymethylene (POM). Polyoxymethylene, a rigid thermoplastic, offers superior dimensional stability and wear resistance but transmits more noise and vibration under load. Choosing polyurethane for gears prioritizes quieter performance in applications with dynamic motion and impact loads, while POM suits precision and low-friction requirements with less noise attenuation.
Chemical and Temperature Resistance
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polyurethane, maintaining stability against solvents, oils, and fuels without degradation, making it ideal for harsh chemical environments. Polyurethane offers moderate chemical resistance but excels in flexibility and abrasion resistance, though it may degrade faster when exposed to strong acids or bases. In terms of temperature resistance, POM withstands continuous operating temperatures up to 100degC to 120degC, whereas polyurethane typically tolerates ranges from -40degC to 80degC, limiting its use in high-temperature gear applications.
Machinability and Manufacturing Processes
Polyurethane offers superior machinability for gears, enabling faster cutting and reduced tool wear due to its elastomeric nature. Polyoxymethylene (POM), known as acetal, provides excellent dimensional stability and low friction but requires precise machining parameters to avoid material melting or deformation. Manufacturing processes for polyurethane gears often involve molding and post-machining, while POM gears benefit from CNC machining and injection molding for achieving tight tolerances and smooth surface finishes.
Cost Effectiveness and Availability
Polyurethane gears offer superior wear resistance and flexibility, making them cost-effective for applications requiring shock absorption and noise reduction, with wide availability in various hardness grades. Polyoxymethylene (POM) gears provide high stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability, often costing more upfront but delivering long-term performance benefits in precision gear systems. Both materials are readily available, but polyurethane's lower initial cost and versatility often make it the preferred choice for budget-sensitive projects with moderate load requirements.
Ideal Applications for PU and POM Gears
Polyurethane (PU) gears excel in applications requiring high elasticity, wear resistance, and noise reduction, making them ideal for machinery with shock absorption and vibration damping needs such as conveyors and printing presses. Polyoxymethylene (POM) gears offer superior stiffness, dimensional stability, and low friction, which is essential for precision instruments, automotive components, and high-speed gear transmissions. Selecting PU gears suits environments with frequent impact and flexibility demands, while POM gears perform best where high load capacity and mechanical accuracy are critical.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Your Gears
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior dimensional stability, low friction, and excellent wear resistance, making it ideal for precision gears with high load requirements. Polyurethane provides better vibration damping and impact resistance, suitable for gears operating under fluctuating loads and noise-sensitive environments. Selecting the right material depends on the gear's operational demands: choose POM for durability and precision, and polyurethane for flexibility and shock absorption.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Polyoxymethylene for Gear
 azmater.com
azmater.com