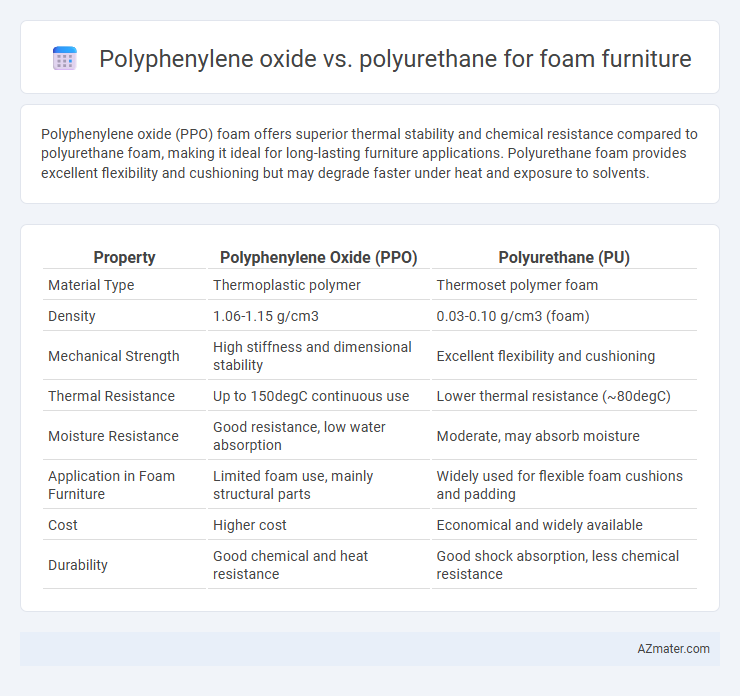
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) foam offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polyurethane foam, making it ideal for long-lasting furniture applications. Polyurethane foam provides excellent flexibility and cushioning but may degrade faster under heat and exposure to solvents.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoset polymer foam |
| Density | 1.06-1.15 g/cm3 | 0.03-0.10 g/cm3 (foam) |
| Mechanical Strength | High stiffness and dimensional stability | Excellent flexibility and cushioning |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 150degC continuous use | Lower thermal resistance (~80degC) |
| Moisture Resistance | Good resistance, low water absorption | Moderate, may absorb moisture |
| Application in Foam Furniture | Limited foam use, mainly structural parts | Widely used for flexible foam cushions and padding |
| Cost | Higher cost | Economical and widely available |
| Durability | Good chemical and heat resistance | Good shock absorption, less chemical resistance |
Introduction to Polyphenylene Oxide and Polyurethane
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for durable foam applications in furniture. Polyurethane (PU) foam is widely used in furniture for its versatile cushioning properties, superior comfort, and ability to be formulated in varying densities and firmness levels. Comparing PPO and polyurethane highlights PPO's strength in structural rigidity and resistance to heat, while polyurethane excels in flexibility and softness for foam furniture comfort.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) features a rigid aromatic polymer backbone with ether linkages, providing excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength ideal for durable foam furniture. Polyurethane (PU) is a versatile polymer formed by the reaction of polyols and diisocyanates, resulting in a flexible, resilient foam structure with customizable density and softness. The chemical composition of PPO leads to higher dimensional stability and resistance to solvents, while polyurethane's structure allows for enhanced cushioning and energy absorption in foam applications.
Manufacturing Processes
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) foam manufacturing involves high-temperature polymerization and precise control of molecular weight to achieve superior thermal stability and rigidity, typically using injection molding or extrusion techniques. Polyurethane foam is produced through a chemical reaction between polyols and isocyanates, commonly via a batch mixing or continuous lamination process that allows for versatile density and cushioning properties. The manufacturing process of polyurethane foam enables customization of foam characteristics, while PPO foams require more stringent processing conditions to maintain structural integrity.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits higher thermal stability, excellent dimensional stability, and superior resistance to moisture and chemicals compared to polyurethane, making it ideal for long-lasting foam furniture applications. Polyurethane foam offers greater flexibility, higher compressive strength, and better cushioning properties, providing enhanced comfort and shock absorption in furniture design. Both materials have distinct physical characteristics, with PPO prioritizing durability and rigidity, while polyurethane emphasizes softness and resilience.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior thermal stability compared to polyurethane, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures above 150degC, which enhances foam furniture durability in high-heat environments. Polyurethane foam, while offering excellent cushioning and flexibility, tends to degrade faster under elevated temperatures, leading to loss of shape and performance over time. The higher heat resistance and dimensional stability of PPO-based foams make them a preferred choice for furniture applications requiring long-term thermal performance and resistance to deformation.
Durability and Longevity
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) foam offers superior durability and resistance to degradation from heat, chemicals, and moisture, making it ideal for long-lasting furniture applications. Polyurethane foam, while more flexible and cost-effective, tends to compress and break down faster under repeated use and exposure to environmental factors. For furniture requiring extended lifespan and structural integrity, PPO foam provides significantly enhanced longevity over polyurethane alternatives.
Comfort and Ergonomic Qualities
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) foam in furniture offers superior breathability and resilience, enhancing comfort through consistent support and temperature regulation. Polyurethane foam is known for its adaptive cushioning and variety of firmness options, providing ergonomic benefits by conforming closely to body contours and relieving pressure points. While PPO excels in durability and maintaining shape over time, polyurethane's versatility often results in more personalized comfort and improved posture support.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) foam furniture offers superior environmental benefits due to its recyclable nature and lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions compared to polyurethane (PU) foam, which often relies on petrochemical-based raw materials and releases harmful substances during production and decomposition. PPO foams exhibit higher thermal stability and durability, reducing the frequency of replacement and waste generation, which aligns with sustainable furniture practices. Choosing PPO over PU contributes to a reduced carbon footprint and supports circular economy initiatives within the furniture industry.
Cost Considerations and Market Availability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) foam typically incurs higher production costs compared to polyurethane foam due to its complex polymer structure and specialized manufacturing processes. Polyurethane foam dominates the furniture market with widespread availability, diverse density options, and lower price points, making it a cost-effective choice for mass production. Market accessibility heavily favors polyurethane, as PPO foam remains niche, limiting suppliers and driving up costs for large-scale furniture applications.
Applications in Foam Furniture Industry
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers exceptional dimensional stability and thermal resistance, making it suitable for high-performance foam furniture components that require durability and shape retention. Polyurethane foam is widely preferred for its superior cushioning properties, flexibility, and adaptability in upholstered furniture, providing comfort and resilience. In the foam furniture industry, PPO is typically used in structural parts and casings, while polyurethane serves as the primary material for foam cushions and padding.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polyurethane for Foam furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com