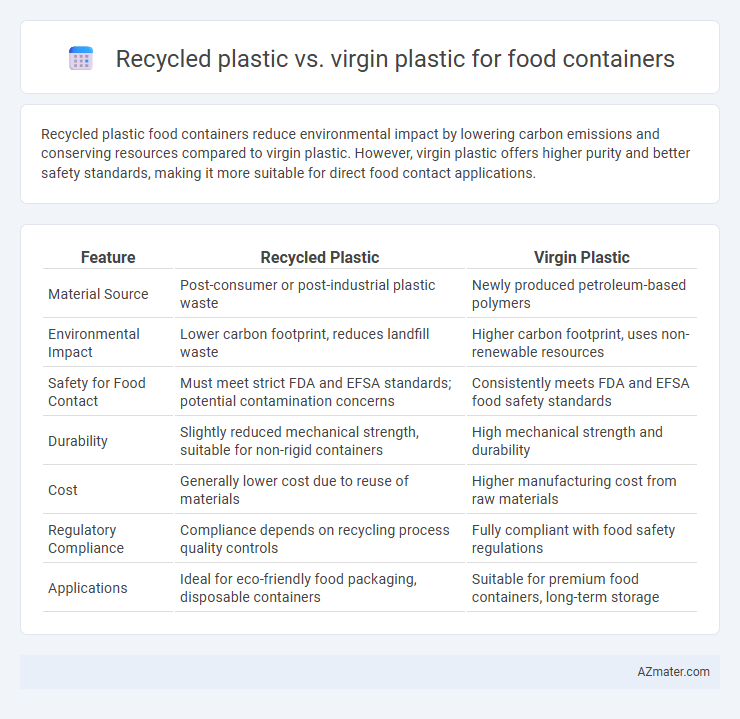
Recycled plastic food containers reduce environmental impact by lowering carbon emissions and conserving resources compared to virgin plastic. However, virgin plastic offers higher purity and better safety standards, making it more suitable for direct food contact applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Plastic | Virgin Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Post-consumer or post-industrial plastic waste | Newly produced petroleum-based polymers |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, reduces landfill waste | Higher carbon footprint, uses non-renewable resources |
| Safety for Food Contact | Must meet strict FDA and EFSA standards; potential contamination concerns | Consistently meets FDA and EFSA food safety standards |
| Durability | Slightly reduced mechanical strength, suitable for non-rigid containers | High mechanical strength and durability |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to reuse of materials | Higher manufacturing cost from raw materials |
| Regulatory Compliance | Compliance depends on recycling process quality controls | Fully compliant with food safety regulations |
| Applications | Ideal for eco-friendly food packaging, disposable containers | Suitable for premium food containers, long-term storage |
Introduction to Plastic Use in Food Containers
Food containers primarily utilize virgin plastic due to its purity, ensuring food safety and preventing contamination. Recycled plastic offers an eco-friendly alternative by reducing plastic waste and conserving resources, but it requires rigorous processing to meet stringent food-grade standards. Innovations in recycling technology are improving the quality and reliability of recycled plastic, expanding its application in food packaging.
Understanding Recycled vs Virgin Plastic
Recycled plastic for food containers originates from processed post-consumer or post-industrial waste, reducing environmental impact by minimizing raw material extraction and lowering carbon emissions. Virgin plastic, derived from freshly sourced petrochemicals, offers consistent purity and performance, essential for stringent food safety standards. Assessing recycled versus virgin plastic requires balancing sustainability goals with regulatory compliance and product quality in the food packaging industry.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Recycled plastic food containers significantly reduce environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to virgin plastic production. The use of recycled plastics decreases landfill waste and the demand for fossil fuels, aiding in resource conservation and pollution reduction. However, recycled plastics may have limitations in purity and durability, influencing their suitability for certain food safety standards.
Safety and Health Considerations
Recycled plastic food containers undergo rigorous testing to meet safety standards, but potential contamination from previous uses may pose health risks if not properly processed. Virgin plastic offers higher purity with fewer chemical additives, reducing concerns about leaching harmful substances into food. Both types comply with FDA regulations, yet consumers should prioritize containers labeled BPA-free and verified for food-grade safety to minimize exposure to toxins.
Durability and Performance
Recycled plastic in food containers often exhibits slightly reduced durability compared to virgin plastic due to potential impurities and polymer degradation during processing. Virgin plastic offers consistent performance with higher tensile strength, better barrier properties, and enhanced resistance to impact and chemicals, ensuring superior food safety and longevity. Advances in recycling technology are narrowing the performance gap, but virgin plastic remains the preferred choice for applications demanding maximum durability and reliability.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Recycled plastic for food containers must meet stringent regulatory standards such as FDA and EFSA guidelines to ensure safety and prevent contamination, often requiring rigorous testing for contaminants and migration limits. Virgin plastic typically exhibits more consistent material properties, simplifying compliance with food contact regulations, but recycled plastics are increasingly engineered to meet these benchmarks through advanced purification technologies. Compliance involves ensuring materials conform to specific migration limits, heavy metal content restrictions, and overall safety standards critical for maintaining food hygiene and consumer health.
Cost Analysis: Recycled vs Virgin Plastic
Recycled plastic food containers generally offer cost savings of 10-30% compared to virgin plastic due to lower raw material expenses and reduced energy consumption during production. Virgin plastic containers provide consistent quality and purity, often justifying their higher costs in sensitive food packaging applications. Market fluctuations in recycled resin availability can impact pricing stability, whereas virgin plastic prices remain more predictable but typically higher.
Consumer Perceptions and Preferences
Consumers increasingly favor recycled plastic food containers due to growing environmental awareness and a desire to reduce plastic waste. However, some express concerns about the safety and durability of recycled plastics compared to virgin plastic, impacting their willingness to switch. Market surveys reveal a preference for clear labeling and certifications that ensure recycled plastics meet food safety standards, influencing purchase decisions.
Innovations in Sustainable Packaging
Innovations in sustainable packaging are advancing the use of recycled plastic for food containers, reducing reliance on virgin plastic derived from fossil fuels. Technologies such as advanced sorting, chemical recycling, and bio-based additives enhance the quality, safety, and durability of recycled plastics, making them more viable for direct food contact. These developments support circular economy goals by minimizing plastic waste and lowering carbon footprints in the food packaging industry.
Future Trends in Food Packaging Materials
Recycled plastic is gaining traction in food containers due to increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand for sustainable packaging, with innovations enhancing barrier properties to ensure food safety and shelf life. Virgin plastic remains prevalent because of its superior purity and performance consistency, but advances in chemical recycling and bio-based additives are narrowing the gap. Future trends indicate a growing shift towards hybrid materials combining recycled content with virgin polymers to meet strict food-grade standards while reducing carbon footprints.
Infographic: Recycled plastic vs Virgin plastic for Food container
 azmater.com
azmater.com