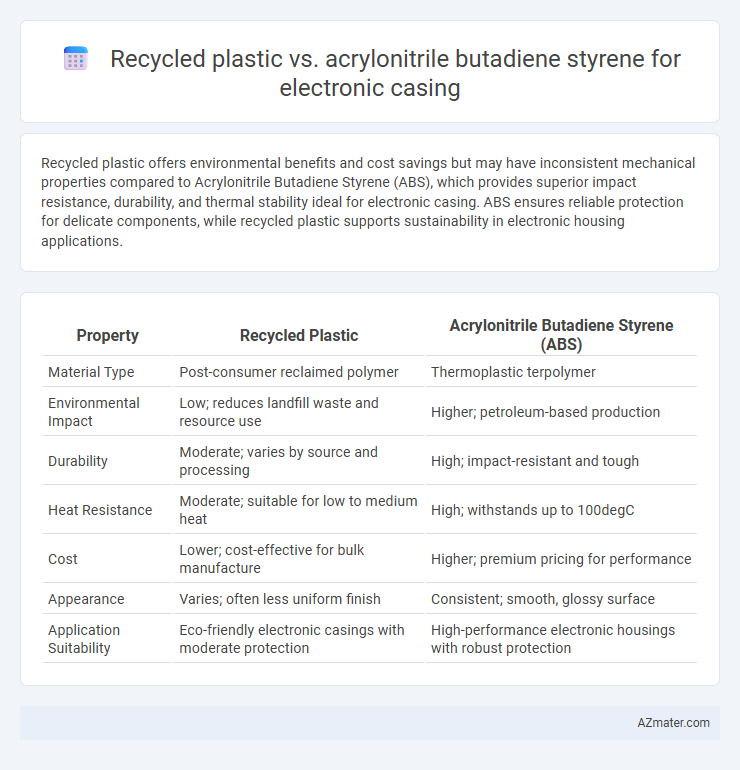
Recycled plastic offers environmental benefits and cost savings but may have inconsistent mechanical properties compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which provides superior impact resistance, durability, and thermal stability ideal for electronic casing. ABS ensures reliable protection for delicate components, while recycled plastic supports sustainability in electronic housing applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Plastic | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Post-consumer reclaimed polymer | Thermoplastic terpolymer |
| Environmental Impact | Low; reduces landfill waste and resource use | Higher; petroleum-based production |
| Durability | Moderate; varies by source and processing | High; impact-resistant and tough |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate; suitable for low to medium heat | High; withstands up to 100degC |
| Cost | Lower; cost-effective for bulk manufacture | Higher; premium pricing for performance |
| Appearance | Varies; often less uniform finish | Consistent; smooth, glossy surface |
| Application Suitability | Eco-friendly electronic casings with moderate protection | High-performance electronic housings with robust protection |
Introduction to Electronic Casing Materials
Electronic casing materials are critical for protecting internal components from physical damage, moisture, and electromagnetic interference. Recycled plastic offers a sustainable option with reduced environmental impact and good mechanical properties, while Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides high strength, heat resistance, and excellent surface finish. Choosing between recycled plastic and ABS involves balancing sustainability with performance requirements for durability and safety in electronic devices.
Overview of Recycled Plastic
Recycled plastic offers an eco-friendly alternative for electronic casing by repurposing post-consumer and post-industrial plastic waste, reducing environmental impact and lowering carbon footprint compared to virgin materials. It provides adequate durability, impact resistance, and insulation properties suitable for many electronic devices while promoting circular economy principles. However, consistency in material quality and mechanical performance can vary based on recycling processes and feedstock sources, requiring careful evaluation for high-precision applications.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Properties and Uses
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance, thermal stability, and dimensional strength compared to recycled plastics, making it ideal for electronic casing applications. Its excellent electrical insulation properties and ease of machining enable precise manufacturing and reliable performance in protecting sensitive electronic components. ABS also resists chemical corrosion and maintains durability under varying environmental conditions, ensuring long-lasting protection for devices.
Material Strength and Durability Comparison
Recycled plastic used for electronic casing offers moderate material strength but generally exhibits lower durability compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which provides superior impact resistance and toughness essential for protecting sensitive electronics. ABS maintains dimensional stability under heat and mechanical stress, making it ideal for long-term use in electronic housings, whereas recycled plastics can vary significantly in quality depending on source and processing methods. Material strength tests show ABS achieves higher tensile strength around 40 MPa and better fatigue resistance, ensuring enhanced durability in demanding applications.
Environmental Impact: Recycled Plastic vs. ABS
Recycled plastic significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering waste in landfills and decreasing the need for virgin polymer production, which minimizes energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), while durable and impact-resistant, is derived from petrochemicals, contributing to higher carbon footprints and non-biodegradability. Choosing recycled plastic for electronic casings offers enhanced sustainability through resource conservation and reduced ecological toxicity compared to conventional ABS materials.
Cost Analysis of Recycled Plastic vs. ABS
Recycled plastic offers a cost advantage over Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) for electronic casing due to lower raw material expenses and reduced processing energy requirements. ABS typically incurs higher costs driven by its superior mechanical properties and impact resistance, which justify the premium in applications demanding durability. Manufacturing with recycled plastic can significantly reduce overall production costs, although it may involve trade-offs in consistency and performance.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Recycled plastic for electronic casing often involves processes like shredding, melting, and remolding, which reduce energy consumption and carbon footprint compared to virgin materials. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) requires polymerization of styrene, acrylonitrile, and butadiene monomers, followed by extrusion and injection molding, resulting in a more energy-intensive and chemically complex manufacturing process. The use of recycled plastic limits resource depletion and supports circular economy goals, while ABS offers superior mechanical properties but with higher environmental costs during production.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Appeal
Recycled plastic offers moderate design flexibility and aesthetic appeal, often requiring additional processing to achieve smooth finishes and vibrant colors suitable for electronic casings. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) provides excellent design flexibility with superior impact resistance and can be easily molded into complex shapes with high gloss finishes, enhancing the visual quality of electronic enclosures. ABS's ability to maintain color stability and surface texture under various environmental conditions makes it a preferred choice for premium electronic casing designs.
End-of-Life and Recycling Potential
Recycled plastic offers superior environmental benefits for electronic casing by significantly reducing landfill waste and conserving resources through closed-loop recycling systems, whereas Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) presents challenges due to its limited recyclability and potential for toxic emissions during incineration. ABS casings often require specialized recycling processes that are not widely available, leading to higher end-of-life disposal costs and environmental impacts. Incorporating recycled plastics enhances circular economy principles by enabling more efficient material recovery and reducing carbon footprint in electronic device manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Material for Electronic Casings
Recycled plastic offers an eco-friendly alternative for electronic casings with good durability and cost-effectiveness but may lack the consistent mechanical properties and thermal resistance of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS). ABS provides superior impact resistance, heat tolerance up to 100degC, and ease of fabrication, making it ideal for protecting sensitive electronic components. Choosing the right material depends on balancing environmental considerations, mechanical performance, and thermal stability specific to the device's operational demands.
Infographic: Recycled plastic vs Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene for Electronic casing
 azmater.com
azmater.com