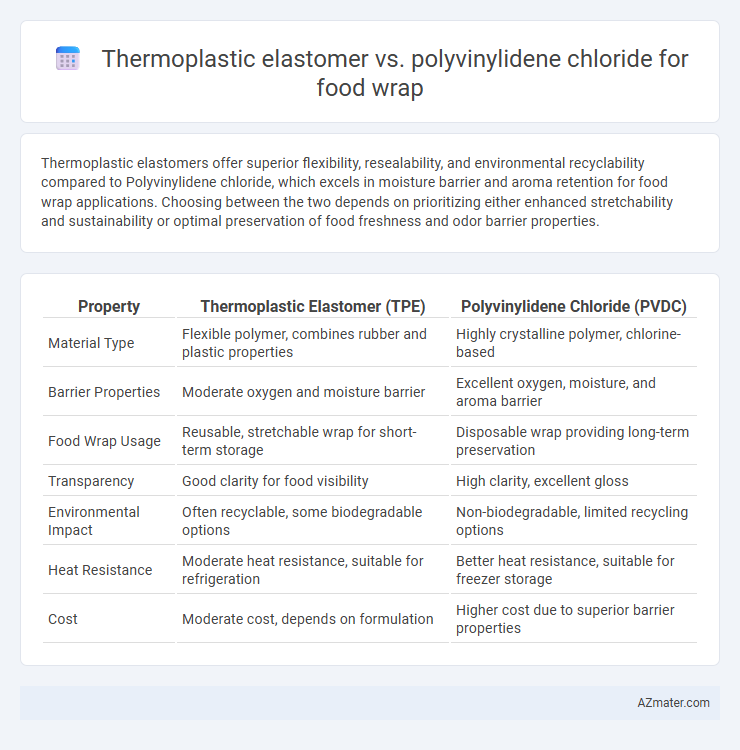
Thermoplastic elastomers offer superior flexibility, resealability, and environmental recyclability compared to Polyvinylidene chloride, which excels in moisture barrier and aroma retention for food wrap applications. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing either enhanced stretchability and sustainability or optimal preservation of food freshness and odor barrier properties.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) | Polyvinylidene Chloride (PVDC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Flexible polymer, combines rubber and plastic properties | Highly crystalline polymer, chlorine-based |
| Barrier Properties | Moderate oxygen and moisture barrier | Excellent oxygen, moisture, and aroma barrier |
| Food Wrap Usage | Reusable, stretchable wrap for short-term storage | Disposable wrap providing long-term preservation |
| Transparency | Good clarity for food visibility | High clarity, excellent gloss |
| Environmental Impact | Often recyclable, some biodegradable options | Non-biodegradable, limited recycling options |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat resistance, suitable for refrigeration | Better heat resistance, suitable for freezer storage |
| Cost | Moderate cost, depends on formulation | Higher cost due to superior barrier properties |
Introduction to Food Wrap Materials
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer flexibility, durability, and excellent sealing properties, making them suitable for food wrap applications where stretchability and reusability are important. Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) provides superior barrier performance against oxygen, moisture, and odors, which enhances food preservation and extends shelf life. Selecting between TPE and PVDC depends on the specific food wrap requirements for flexibility, barrier protection, and environmental impact.
Overview of Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE)
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer a flexible, durable, and recyclable alternative to traditional food wrap materials like polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC). TPEs combine the elastic properties of rubber with the processability of plastics, providing excellent stretchability and resistance to tearing, making them suitable for sealing and protecting perishable food items. Their non-toxic and reusable nature enhances food safety and environmental sustainability compared to PVDC, which is known for its barrier properties but limited recyclability and potential environmental concerns.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Chloride (PVDC)
Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) is a high-performance polymer widely used in food wrap due to its exceptional barrier properties against oxygen, moisture, and aromas, significantly extending food shelf life. Its chemical resistance and low permeability make PVDC an ideal material for preserving freshness and preventing contamination. Compared to thermoplastic elastomers, PVDC offers superior cling and durability, essential for maintaining food quality in packaging applications.
Barrier Properties: TPE vs PVDC
Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) offers superior oxygen and moisture barrier properties compared to thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), making it highly effective for food wrap applications that require extended shelf life and preservation of freshness. TPEs, while flexible and recyclable, generally exhibit higher permeability to gases and water vapor, limiting their effectiveness in preventing food spoilage. The enhanced barrier characteristics of PVDC result from its dense, crystalline structure, which significantly reduces gas transmission rates compared to the more permeable, elastomeric matrix of TPEs.
Food Safety and Chemical Migration
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) used in food wrap offer superior flexibility and lower chemical migration compared to polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC), enhancing food safety by reducing potential contaminant transfer. PVDC exhibits excellent oxygen and moisture barrier properties but may release harmful chlorinated compounds under certain conditions, posing risks of chemical migration into food. Regulatory assessments favor TPE for minimizing exposure to toxic substances, ensuring safer packaging that complies with stringent food contact material standards.
Flexibility and Cling Performance
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior flexibility compared to polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC), allowing food wrap to contour tightly around irregularly shaped items. TPE-based wraps exhibit excellent cling performance due to their inherent elastic properties, ensuring a secure seal without the need for additional adhesives. In contrast, PVDC provides good barrier properties but has less stretchability and cling, making it less adaptable for flexible wrapping applications.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) offer improved environmental impact over polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) by being more easily recyclable and often free of chlorine, reducing toxic emissions during disposal. PVDC, commonly used in food wrap due to its excellent barrier properties, poses significant environmental concerns due to its chlorine content, which can release harmful dioxins when incinerated. The superior recyclability of TPEs supports circular economy initiatives in the food packaging industry, making them a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious applications.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) generally offer a cost-effective alternative to polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) in food wrap applications, with lower raw material expenses and simpler processing requirements contributing to reduced overall production costs. Market availability of TPE-based wraps is increasing rapidly due to growing demand for recyclable and environmentally friendly packaging solutions, whereas PVDC remains widely used but faces limitations from environmental regulations and higher production expenses. The balance between affordability and eco-conscious compliance continues to drive the shift toward TPE in global food wrap markets.
Applications in Food Packaging
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer excellent flexibility, resealability, and puncture resistance, making them ideal for wrapping fresh produce, meats, and cheeses that require repeated access and protection. Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) provides superior barrier properties against oxygen, moisture, and odors, extending the shelf life of packaged products such as processed meats, baked goods, and ready-to-eat meals. Both materials are widely used in food packaging, with TPE favored for stretchable wrap applications and PVDC for coatings or multilayer films requiring enhanced preservation performance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Food Wrap
Thermoplastic elastomers offer superior flexibility, stretchability, and recyclability, making them ideal for versatile and sustainable food wrapping solutions. Polyvinylidene chloride excels in providing excellent barrier properties against moisture and oxygen, ensuring extended food freshness but with lower environmental friendliness. Selecting the right material depends on prioritizing either environmental impact and flexibility with thermoplastic elastomers or maximum preservation and shelf life with polyvinylidene chloride.
Infographic: Thermoplastic elastomer vs Polyvinylidene chloride for Food wrap
 azmater.com
azmater.com