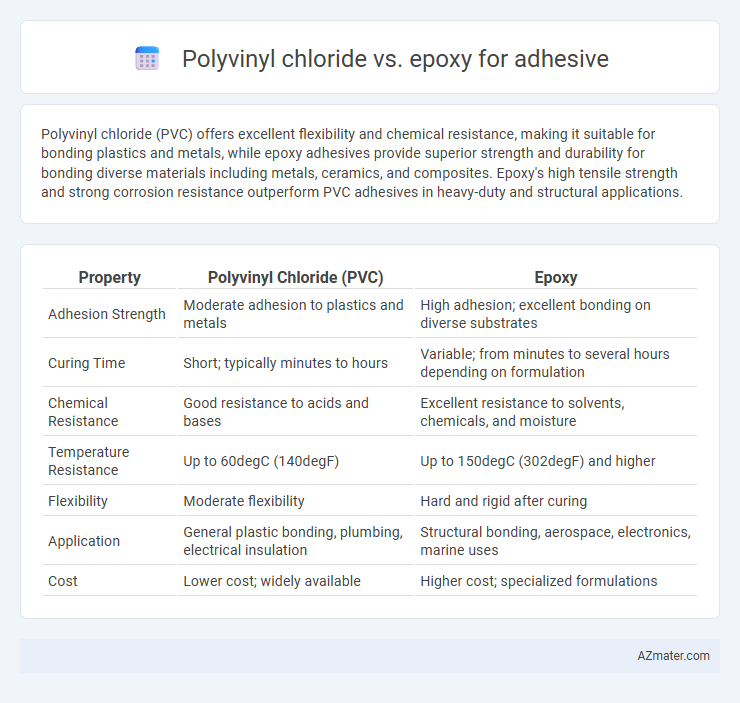
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers excellent flexibility and chemical resistance, making it suitable for bonding plastics and metals, while epoxy adhesives provide superior strength and durability for bonding diverse materials including metals, ceramics, and composites. Epoxy's high tensile strength and strong corrosion resistance outperform PVC adhesives in heavy-duty and structural applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Epoxy |
|---|---|---|
| Adhesion Strength | Moderate adhesion to plastics and metals | High adhesion; excellent bonding on diverse substrates |
| Curing Time | Short; typically minutes to hours | Variable; from minutes to several hours depending on formulation |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and bases | Excellent resistance to solvents, chemicals, and moisture |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 60degC (140degF) | Up to 150degC (302degF) and higher |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | Hard and rigid after curing |
| Application | General plastic bonding, plumbing, electrical insulation | Structural bonding, aerospace, electronics, marine uses |
| Cost | Lower cost; widely available | Higher cost; specialized formulations |
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) and Epoxy Adhesives
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) adhesives are widely used for bonding PVC-based materials due to their excellent compatibility, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals and moisture. Epoxy adhesives offer superior mechanical strength, durability, and strong adhesion to a variety of substrates including metals, plastics, and composites. Both adhesives cater to different industrial needs, with PVC adhesives favored for plastic pipe joining and epoxy adhesives preferred for structural and high-performance applications.
Chemical Composition Differences
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) adhesives primarily consist of vinyl chloride monomers polymerized into a thermoplastic resin, offering flexibility and resistance to environmental factors. Epoxy adhesives are composed of epoxide groups that polymerize with hardeners, creating a highly cross-linked thermosetting polymer known for superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance. The key chemical difference lies in PVC's linear polymer structure versus epoxy's densely cross-linked three-dimensional network, impacting their adhesive bonding properties and thermal stability.
Bonding Strength Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) adhesives exhibit moderate bonding strength suitable for flexible applications but tend to underperform in high-stress environments compared to epoxy adhesives. Epoxy adhesives provide superior bonding strength with excellent resistance to shear and peel forces, making them ideal for structural and heavy-duty uses. Studies show epoxy bonds maintain integrity under thermal cycling and chemical exposure, outperforming PVC-based adhesives in durability and load-bearing capacity.
Applications and Use Cases
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) adhesives are widely used for bonding plastics, especially in plumbing, automotive, and construction industries due to their excellent resistance to chemicals and water. Epoxy adhesives offer superior strength and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications such as aerospace, electronics, and industrial manufacturing where high mechanical stress and temperature resistance are critical. While PVC adhesives excel in flexibility and ease of application on vinyl materials, epoxies provide robust structural bonding for metals, composites, and ceramics.
Surface Preparation Requirements
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) adhesives require thorough surface cleaning and mechanical abrasion to remove contaminants and increase surface roughness for optimal bonding. Epoxy adhesives demand extensive surface preparation, including degreasing, sanding, and sometimes the application of a primer, to ensure maximum adhesion strength and chemical resistance. Both materials benefit significantly from clean, dry surfaces, but epoxy's curing process is more sensitive to surface conditions, necessitating stricter control during preparation.
Curing Time and Process
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) adhesives typically offer faster curing times ranging from 5 to 30 minutes, with a simple solvent-based process that softens the PVC surface for bonding. Epoxy adhesives require longer curing periods, often between 30 minutes to several hours, due to a two-part chemical reaction that produces a strong, durable bond suitable for high-stress applications. The epoxy curing process demands precise mixing of resin and hardener, followed by controlled environmental conditions for optimal adhesion and mechanical strength.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) adhesive offers excellent durability with strong resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV exposure, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial applications. Epoxy adhesive surpasses PVC in environmental resistance due to its superior chemical, heat, and abrasion resistance, ensuring long-lasting bonds in harsh environments such as marine, automotive, and aerospace. While epoxy provides higher mechanical strength and durability under extreme conditions, PVC adhesives remain cost-effective and reliable for less demanding applications.
Flexibility and Rigidity Characteristics
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) adhesives exhibit superior flexibility, allowing for effective bonding in applications requiring movement or vibration resistance, making them ideal for materials prone to expansion and contraction. Epoxy adhesives are characterized by high rigidity and strong mechanical strength, providing durable and stiff bonds suitable for structural components and load-bearing applications. Choosing between PVC and epoxy depends on whether flexibility or rigidity is critical for the adhesive performance in the specific use case.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) adhesives typically offer a lower initial cost compared to epoxy, making them more budget-friendly for large-scale projects or temporary bonds. Epoxy adhesives provide superior strength and durability, reducing long-term maintenance and replacement expenses, which enhances overall cost-effectiveness despite higher upfront prices. Evaluating the total lifecycle cost, including bond performance and environmental resistance, often positions epoxy as the more economically advantageous choice for critical applications.
Safety and Handling Considerations
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) adhesives typically emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that require proper ventilation and protective gloves to avoid respiratory and skin irritation. Epoxy adhesives are generally less volatile but may cause allergic reactions and necessitate the use of gloves and eye protection during handling to prevent skin sensitization and eye damage. Both adhesives demand adherence to safety data sheets and proper storage to minimize exposure and environmental hazards.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride vs Epoxy for Adhesive
 azmater.com
azmater.com