Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and ease of molding for electrical connectors, while Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) provides superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability in high-performance electrical applications. PPS connectors perform better in environments requiring high heat tolerance and chemical exposure, making them ideal for demanding electronic and automotive uses.
Table of Comparison
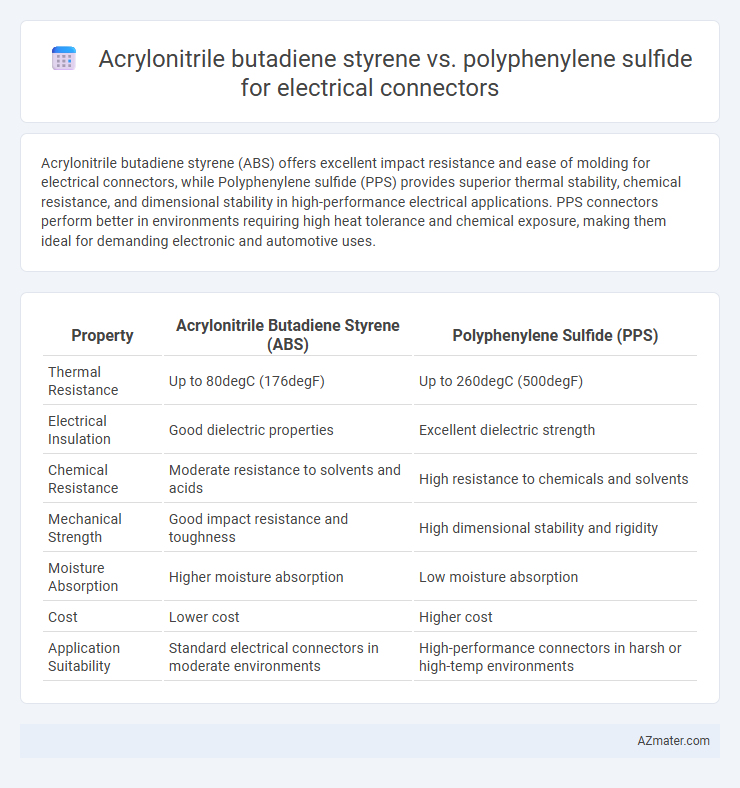
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 80degC (176degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Electrical Insulation | Good dielectric properties | Excellent dielectric strength |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to solvents and acids | High resistance to chemicals and solvents |
| Mechanical Strength | Good impact resistance and toughness | High dimensional stability and rigidity |
| Moisture Absorption | Higher moisture absorption | Low moisture absorption |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Application Suitability | Standard electrical connectors in moderate environments | High-performance connectors in harsh or high-temp environments |
Introduction to ABS and PPS in Electrical Connectors
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) are key materials in electrical connectors, chosen for their distinct thermal and mechanical properties. ABS offers excellent impact resistance and ease of processing, making it suitable for connectors with moderate temperature requirements. PPS provides superior chemical resistance, high heat tolerance up to 260degC, and dimensional stability, ideal for high-performance electrical connectors exposed to demanding environments.
Material Properties: ABS vs PPS
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance, ease of processing, and good electrical insulation suitable for standard electrical connectors, but it has moderate thermal stability, typically up to 80-100degC. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) provides superior chemical resistance, high thermal stability exceeding 200degC, and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for connectors operating in harsh environments or high-temperature applications. The choice between ABS and PPS depends on requirements for thermal endurance, mechanical stress, and environmental exposure in electrical connector design.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate mechanical strength with good impact resistance, suitable for general electrical connector housings requiring durability against physical stress. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) exhibits superior mechanical strength and excellent dimensional stability under high-temperature conditions, making it ideal for connectors exposed to harsh environments and continuous mechanical load. PPS outperforms ABS in tensile strength, flexural modulus, and resistance to creep, ensuring longer lifespan and reliability in demanding electrical applications.
Thermal Resistance: Performance Under Heat
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits moderate thermal resistance with a maximum continuous use temperature around 80-100degC, making it suitable for standard electrical connectors but limiting its application in high-heat environments. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) offers superior thermal resistance, maintaining structural integrity at continuous operating temperatures up to 260degC, ideal for electrical connectors exposed to extreme thermal stress. The enhanced thermal stability of PPS ensures reliable performance and longevity in demanding electrical applications where heat resistance is critical.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) offers good electrical insulation with a dielectric strength around 16-20 kV/mm, making it suitable for standard electrical connectors. Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) demonstrates superior electrical insulation properties, with dielectric strength typically exceeding 25 kV/mm and excellent resistance to high temperatures and chemicals. PPS is preferred in high-performance electrical connectors where enhanced dielectric reliability and thermal stability are critical.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate chemical resistance, particularly against acids and alkalis, but tends to degrade when exposed to strong solvents and UV radiation, limiting its durability in harsh environmental conditions. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) excels in chemical resistance, with outstanding stability against aggressive chemicals, high temperatures up to 260degC, and excellent resistance to hydrolysis and flame, making it ideal for electrical connectors in demanding applications. PPS also provides superior environmental resistance, including excellent moisture and UV resistance, ensuring long-term performance and reliability compared to ABS in electrical connector manufacturing.
Cost Analysis: ABS vs PPS
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers a lower initial material cost compared to Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), making ABS a budget-friendly option for electrical connectors in large-volume production. PPS provides superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, but these enhanced properties come with a higher unit price that can significantly impact overall project expenses. Cost analysis of ABS versus PPS must consider not only material price but also long-term durability and performance requirements in harsh electrical environments.
Processing and Manufacturing Considerations
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent moldability and rapid cycle times, making it suitable for high-volume electrical connector production with cost-effective injection molding. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) requires higher processing temperatures and more precise control due to its semi-crystalline structure, which enhances thermal stability and chemical resistance but increases manufacturing complexity. PPS's superior dimensional stability under heat and resistance to solvents are critical for connectors subjected to harsh environments, offsetting the elevated tooling and processing costs.
Typical Applications and Industry Use Cases
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is widely used in electrical connectors for consumer electronics and automotive interiors due to its excellent impact resistance and ease of molding. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) is favored in high-performance electrical connectors within aerospace, automotive under-the-hood, and industrial machinery applications, thanks to its superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability. Both materials address distinct industry needs, with ABS preferred for cost-effective, general-purpose connectors and PPS chosen for demanding environments requiring high heat and chemical exposure resistance.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Material for Electrical Connectors
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and ease of molding, making it suitable for general electrical connector housings requiring moderate thermal and chemical stability. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) provides superior heat resistance, dimensional stability, and chemical inertness, ideal for high-performance electrical connectors exposed to harsh environments or elevated temperatures above 200degC. Selecting the right material depends on the specific application demands, with ABS favoring cost-effective, versatile use and PPS recommended for critical, high-temperature, and chemically aggressive electrical connector applications.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polyphenylene sulfide for Electrical connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com