Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and durability, making it ideal for reusable water bottles with enhanced impact resistance. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) provides excellent clarity and lightweight properties, commonly used for single-use, recyclable water bottles emphasizing safety and cost-efficiency.
Table of Comparison
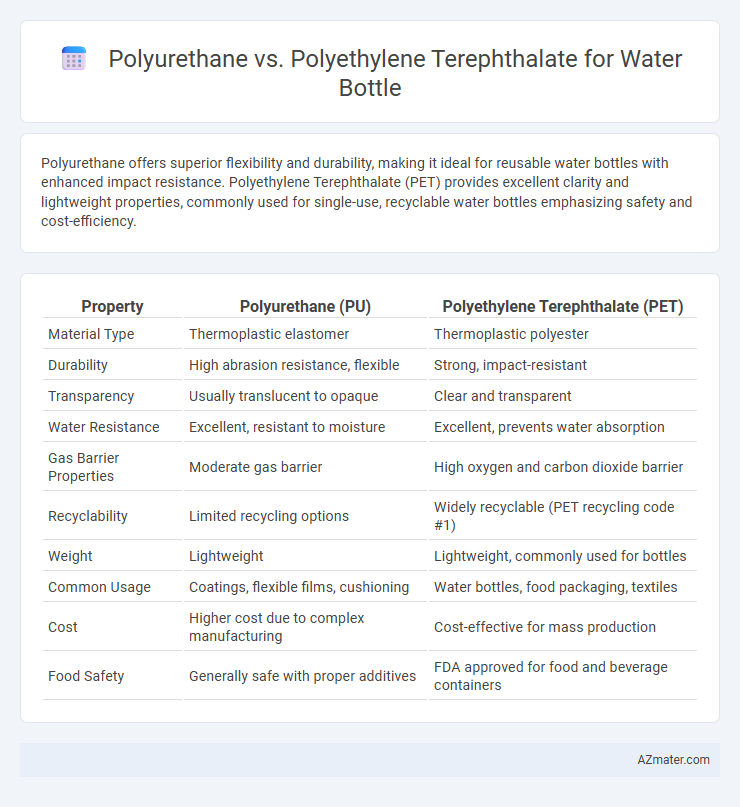
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic elastomer | Thermoplastic polyester |
| Durability | High abrasion resistance, flexible | Strong, impact-resistant |
| Transparency | Usually translucent to opaque | Clear and transparent |
| Water Resistance | Excellent, resistant to moisture | Excellent, prevents water absorption |
| Gas Barrier Properties | Moderate gas barrier | High oxygen and carbon dioxide barrier |
| Recyclability | Limited recycling options | Widely recyclable (PET recycling code #1) |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight, commonly used for bottles |
| Common Usage | Coatings, flexible films, cushioning | Water bottles, food packaging, textiles |
| Cost | Higher cost due to complex manufacturing | Cost-effective for mass production |
| Food Safety | Generally safe with proper additives | FDA approved for food and beverage containers |
Introduction to Polyurethane and Polyethylene Terephthalate
Polyurethane is a versatile polymer known for its flexibility, durability, and resistance to abrasion, commonly used in coatings and foams. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is a strong, lightweight polyester popular in water bottle manufacturing due to its excellent barrier properties and recyclability. Both materials provide distinct advantages in water bottle applications, with PET favored for its clarity and food safety, while polyurethane offers superior impact resistance.
Material Composition and Structure
Polyurethane (PU) water bottles feature a flexible polymer structure formed by reacting diisocyanates with polyols, resulting in a durable, elastic material that resists abrasion and impact. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is a thermoplastic polyester synthesized from terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol, characterized by a semi-crystalline structure offering high tensile strength and excellent barrier properties against moisture and gases. The chemical composition of PU provides superior elasticity and impact resistance, whereas PET's rigid molecular arrangement ensures clarity, strength, and recyclability in water bottle applications.
Durability and Lifespan
Polyurethane offers superior abrasion resistance and flexibility, making it highly durable against impacts and deformation, while polyethylene terephthalate (PET) provides excellent chemical resistance and maintains structural integrity over extended periods. PET's lifespan is typically longer for single-use water bottles due to its resistance to hydrolysis and UV degradation, whereas polyurethane excels in reusable bottle applications where repeated bending and stress occur. Both materials perform well in durability, but PET is favored for long-term storage stability, and polyurethane for resilience under mechanical wear.
Safety and Health Considerations
Polyurethane water bottles often contain chemicals that can leach harmful substances such as isocyanates, raising concerns about toxicity and skin irritation. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely regarded as safe for water storage due to its stable chemical structure and minimal leaching risk, endorsed by regulatory agencies like the FDA and EFSA. For long-term health and safety, PET bottles present fewer hazards compared to polyurethane options, making them a preferred choice in consumer water containers.
Taste and Odor Retention
Polyurethane water bottles typically offer superior taste and odor retention due to their dense polymer structure that resists absorption and leaching of flavors. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), while widely used, is more prone to retaining odors and may impart a slight plastic taste over time, especially when exposed to heat or sunlight. Consumers seeking pure water flavor often prefer polyurethane because it maintains taste integrity without interacting chemically with the liquid.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyurethane water bottles offer higher durability but pose significant challenges for recycling due to their complex chemical structure, often ending up in landfills or incineration. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is widely recycled with an established infrastructure, reducing environmental impact by enabling bottle-to-bottle recycling and minimizing plastic waste in oceans and landfills. The lower carbon footprint and higher recyclability of PET make it the more eco-friendly choice compared to polyurethane in water bottle production.
Manufacturing Cost and Efficiency
Polyurethane water bottles typically exhibit higher manufacturing costs due to complex chemical synthesis and curing processes, whereas polyethylene terephthalate (PET) benefits from cost-effective, scalable blow molding technology. PET's lightweight properties and rapid production cycle enhance efficiency, making it the preferred choice for mass-produced water bottles. Conversely, polyurethane offers superior flexibility and durability, but these advantages come with increased expense and slower manufacturing throughput.
Design Flexibility and Customization
Polyurethane offers superior design flexibility and customization for water bottles due to its elastomeric properties, allowing intricate shapes, varied textures, and enhanced grip options. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), while rigid and transparent, limits design complexity but excels in lightweight, clear bottles with consistent barrier properties. Customization in PET is generally confined to color and label applications, whereas polyurethane enables functional enhancements such as impact resistance and ergonomic contours.
Performance in Varying Temperatures
Polyurethane exhibits excellent flexibility and maintains integrity at low temperatures, making it suitable for water bottles exposed to cold environments, while polyethylene terephthalate (PET) performs well at room temperature but can become brittle in extreme cold. PET offers superior resistance to heat up to around 60degC, retaining structural stability and safety for hot-fill applications, whereas polyurethane may degrade or soften under prolonged heat exposure. Therefore, PET is generally preferred for water bottles requiring broad temperature performance, especially for hot and ambient conditions, while polyurethane excels in maintaining durability in colder climates.
Choosing the Best Option for Water Bottles
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely favored for water bottles due to its superior clarity, lightweight nature, and excellent barrier properties against moisture and gases, ensuring beverage freshness. Polyurethane (PU) offers enhanced flexibility and impact resistance but lacks the rigidity and transparency critical for consumer preference in bottled water applications. Evaluating factors like durability, safety, and recyclability, PET remains the optimal material choice for water bottles in terms of performance and environmental sustainability.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Polyethylene Terephthalate for Water Bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com