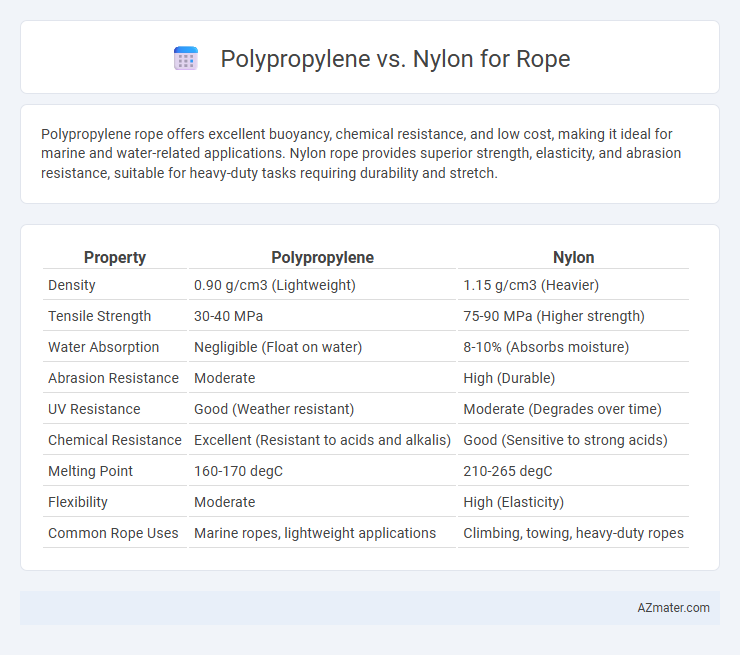
Polypropylene rope offers excellent buoyancy, chemical resistance, and low cost, making it ideal for marine and water-related applications. Nylon rope provides superior strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, suitable for heavy-duty tasks requiring durability and stretch.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene | Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.90 g/cm3 (Lightweight) | 1.15 g/cm3 (Heavier) |
| Tensile Strength | 30-40 MPa | 75-90 MPa (Higher strength) |
| Water Absorption | Negligible (Float on water) | 8-10% (Absorbs moisture) |
| Abrasion Resistance | Moderate | High (Durable) |
| UV Resistance | Good (Weather resistant) | Moderate (Degrades over time) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Resistant to acids and alkalis) | Good (Sensitive to strong acids) |
| Melting Point | 160-170 degC | 210-265 degC |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High (Elasticity) |
| Common Rope Uses | Marine ropes, lightweight applications | Climbing, towing, heavy-duty ropes |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Nylon Ropes
Polypropylene ropes are lightweight, resistant to water absorption, and offer excellent floatation, making them ideal for marine and water-related applications. Nylon ropes provide superior strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, which enhances durability and shock absorption, suitable for heavy-duty and load-bearing tasks. Both materials serve distinct purposes based on their unique physical properties, with polypropylene valued for buoyancy and chemical resistance, while nylon excels in strength and flexibility.
Key Physical Properties Compared
Polypropylene ropes offer excellent buoyancy and resistance to water absorption, making them ideal for marine applications, while nylon ropes excel in tensile strength and elasticity, providing superior shock absorption and durability under load. Polypropylene has a lower melting point around 160degC, whereas nylon withstands higher temperatures up to 260degC, impacting their performance in high-heat environments. Nylon's higher abrasion resistance and UV stability contribute to longer service life compared to polypropylene, which can degrade faster when exposed to sunlight.
Strength and Durability Differences
Polypropylene rope offers moderate tensile strength with excellent resistance to water absorption, making it ideal for marine and wet environments, but it degrades faster under UV exposure and abrasion. Nylon rope boasts superior strength and elasticity, providing remarkable shock absorption and durability against wear, chemicals, and UV damage. Choosing between polypropylene and nylon depends on specific strength requirements and environmental durability needs in rope applications.
Water Resistance and Buoyancy
Polypropylene rope offers superior water resistance and buoyancy compared to nylon, making it ideal for marine applications where floating on water is essential. Nylon absorbs water, which can lead to decreased strength and increased weight, reducing its effectiveness in wet environments. Polypropylene's inherent hydrocarbon-based structure resists water absorption, maintaining its durability and flotation properties over time.
UV Resistance and Weather Performance
Polypropylene ropes exhibit excellent UV resistance, retaining strength and flexibility when exposed to prolonged sunlight, making them ideal for outdoor applications. Nylon ropes, while stronger in tensile strength, tend to degrade faster under UV exposure and can absorb moisture, which affects their weather durability. For environments with intense sunlight and varying weather conditions, polypropylene offers superior longevity and performance compared to nylon.
Flexibility and Handling
Polypropylene rope offers superior flexibility and lightweight handling, making it ideal for applications requiring easy knotting and quick deployment. Nylon rope, while less flexible due to its stronger and more elastic fibers, provides excellent shock absorption and durability under heavy loads. The choice between polypropylene and nylon ropes hinges on the need for supple maneuverability versus robust strength and stretch resilience.
Cost and Availability
Polypropylene ropes typically cost less and are widely available due to their extensive use in marine, industrial, and agricultural applications. Nylon ropes, while generally more expensive, offer higher strength and durability but have more limited availability in basic retail outlets compared to polypropylene. Choosing between the two depends on budget constraints and the specific use case, with polypropylene favored for cost-effectiveness and nylon for performance in demanding environments.
Common Applications for Each Rope Type
Polypropylene ropes are frequently used in marine environments, water sports, and outdoor activities due to their buoyancy, resistance to moisture, and affordability. Nylon ropes excel in heavy-duty applications such as climbing, towing, and industrial lifting because of their high tensile strength, elasticity, and durability under dynamic loads. Both materials serve specific roles based on environmental exposure and mechanical demands, making them ideal for targeted use cases in various industries.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polypropylene rope is lightweight and resistant to water absorption but is derived from non-renewable petroleum, contributing to microplastic pollution when degraded. Nylon offers greater durability and strength with better resistance to UV and abrasion but is also petroleum-based and slower to biodegrade, posing long-term environmental concerns. Sustainable alternatives focus on bio-based or recycled fibers to reduce ecological footprints associated with both polypropylene and nylon ropes.
Choosing the Right Rope: Polypropylene vs Nylon
Polypropylene ropes are lightweight, float on water, and offer excellent resistance to moisture and chemicals, making them ideal for marine and outdoor applications. Nylon ropes provide superior strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, which is essential for heavy-duty tasks requiring shock absorption and durability. Choosing between polypropylene and nylon depends on factors such as load capacity, environmental exposure, and the need for flexibility or buoyancy in specific rope applications.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Nylon for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com