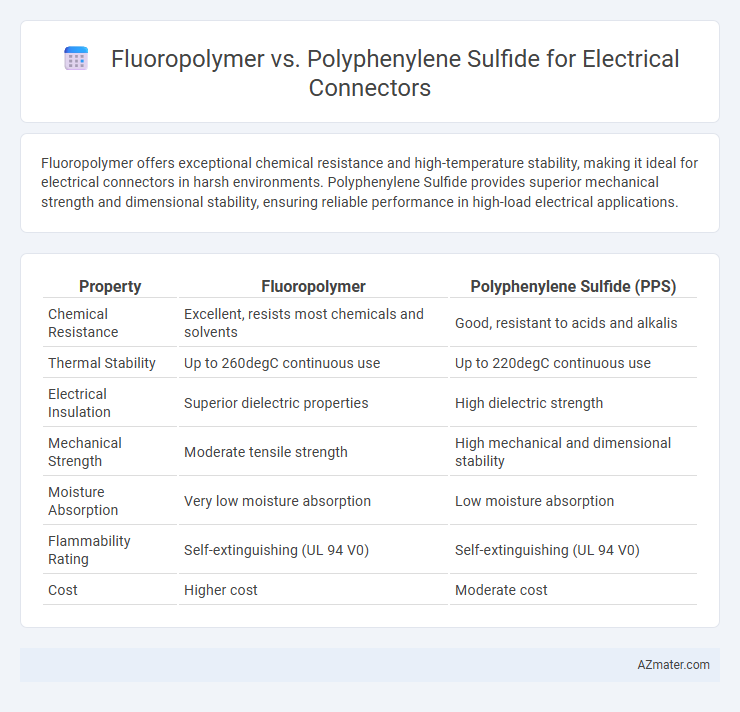
Fluoropolymer offers exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for electrical connectors in harsh environments. Polyphenylene Sulfide provides superior mechanical strength and dimensional stability, ensuring reliable performance in high-load electrical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluoropolymer | Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resists most chemicals and solvents | Good, resistant to acids and alkalis |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 260degC continuous use | Up to 220degC continuous use |
| Electrical Insulation | Superior dielectric properties | High dielectric strength |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High mechanical and dimensional stability |
| Moisture Absorption | Very low moisture absorption | Low moisture absorption |
| Flammability Rating | Self-extinguishing (UL 94 V0) | Self-extinguishing (UL 94 V0) |
| Cost | Higher cost | Moderate cost |
Introduction to Fluoropolymer and Polyphenylene Sulfide
Fluoropolymers, such as PTFE, are high-performance polymers known for exceptional chemical resistance, low dielectric constant, and outstanding thermal stability, making them ideal for electrical connectors requiring high insulation and durability. Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) is a high-temperature thermoplastic with excellent mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and inherent flame retardancy, suitable for connectors exposed to harsh mechanical and thermal environments. Both materials offer unique benefits in electrical connector applications, with fluoropolymers excelling in insulation and chemical resistance, while PPS provides structural integrity and heat resistance.
Key Properties of Fluoropolymer in Electrical Connectors
Fluoropolymers, such as PTFE and FEP, exhibit exceptional electrical insulation properties, including a high dielectric strength exceeding 60 kV/mm, which minimizes signal loss and prevents electrical arcing in connectors. Their excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability up to 260degC ensure reliable performance in harsh environments where polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) may degrade or lose mechanical integrity. Low moisture absorption and a low dielectric constant of around 2.0 make fluoropolymers ideal for maintaining signal integrity and long-term durability in high-frequency electrical connector applications.
Key Properties of Polyphenylene Sulfide in Electrical Connectors
Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) offers exceptional thermal stability up to 260degC, making it ideal for high-temperature electrical connector applications where Fluoropolymers might underperform. PPS exhibits superior mechanical strength and excellent dimensional stability, ensuring reliable performance under mechanical stress and frequent mating cycles. Its inherent chemical resistance and low moisture absorption enhance the durability and longevity of electrical connectors in harsh environments.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Fluoropolymers offer superior thermal stability, maintaining performance in continuous use up to 260degC, while Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) typically withstands temperatures up to 200-220degC. Fluoropolymers exhibit excellent dielectric properties and resistance to thermal degradation, making them ideal for high-temperature electrical connectors in harsh environments. PPS provides good thermal performance with enhanced mechanical strength but may experience thermal oxidation at prolonged exposure near its upper thermal limits.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Fluoropolymers exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), effectively withstanding aggressive solvents, acids, and bases commonly encountered in electrical connector applications. PPS offers good resistance to hydrocarbons and halogenated solvents but is less resilient against strong oxidizing agents and concentrated acids. Selecting fluoropolymers ensures enhanced durability and longevity in harsh chemical environments where electrical connector performance is critical.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Fluoropolymers exhibit exceptional chemical resistance and electrical insulation properties, but their mechanical strength is generally lower compared to polyphenylene sulfide (PPS). PPS offers superior mechanical strength, high dimensional stability, and excellent thermal resistance, making it more durable for demanding electrical connector applications. The stiffness and wear resistance of PPS contribute to longer-lasting connectors in high-stress environments, whereas fluoropolymers are preferred for flexibility and chemical inertness.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Fluoropolymers exhibit superior electrical insulation properties with high dielectric strength and low dielectric constant, making them ideal for electrical connectors exposed to harsh environments and high voltages. Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) offers good electrical insulation but with lower thermal stability and dielectric performance compared to fluoropolymers. The choice between fluoropolymer and PPS depends on the application's voltage requirements, temperature range, and environmental exposure to ensure optimal insulation reliability in electrical connectors.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Fluoropolymers, such as PTFE, offer exceptional chemical resistance and electrical insulation but tend to have higher raw material costs and limited availability compared to polyphenylene sulfide (PPS). PPS provides a cost-efficient alternative with good thermal stability and mechanical strength, commonly available in large volumes at competitive prices, making it suitable for mass-produced electrical connectors. The choice between the two materials depends on balancing premium performance requirements with budget constraints and supply chain access.
Typical Applications in Electrical Connectors
Fluoropolymers are widely used in electrical connectors for high-temperature and chemical-resistant insulation, making them ideal for harsh environments such as aerospace and automotive electronics. Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) offers excellent dimensional stability and electrical insulation properties, suited for connectors in industrial machinery and consumer electronics requiring mechanical strength and thermal endurance. Both materials ensure reliable signal transmission and protect connectors from electrical faults, with fluoropolymers preferred for extreme conditions and PPS for cost-effective, high-performance applications.
Choosing the Right Material: Fluoropolymer vs Polyphenylene Sulfide
Fluoropolymers offer exceptional chemical resistance, low dielectric constant, and high thermal stability, making them ideal for high-performance electrical connectors in harsh environments. Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) provides excellent mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and resistance to heat and flame, suitable for connectors requiring structural integrity and high-temperature endurance. Selecting between fluoropolymer and PPS depends on the specific application's temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical demands, with fluoropolymers favored for extreme chemical resistance and PPS preferred for robust mechanical and thermal performance.
Infographic: Fluoropolymer vs Polyphenylene Sulfide for Electrical Connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com