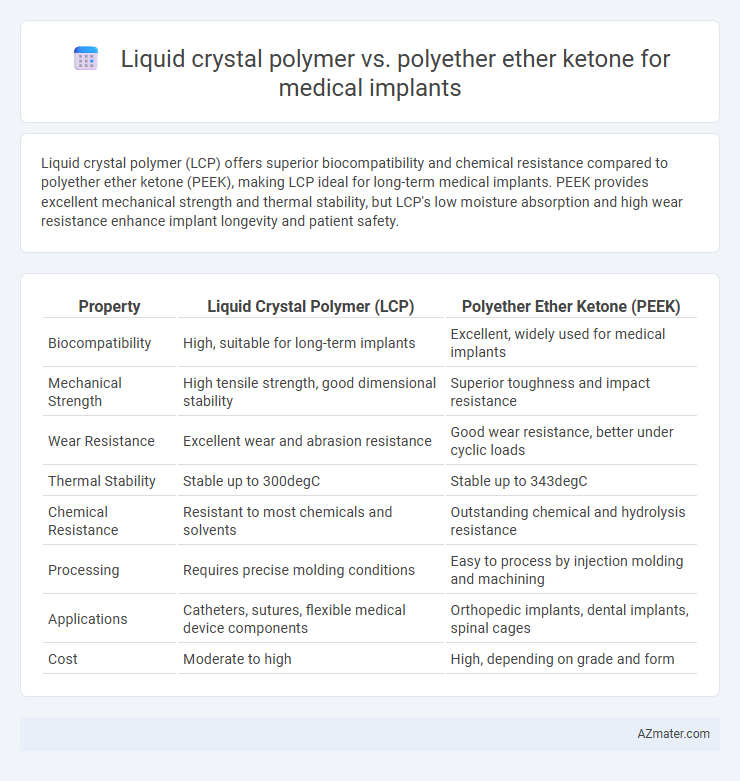
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior biocompatibility and chemical resistance compared to polyether ether ketone (PEEK), making LCP ideal for long-term medical implants. PEEK provides excellent mechanical strength and thermal stability, but LCP's low moisture absorption and high wear resistance enhance implant longevity and patient safety.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) | Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) |
|---|---|---|
| Biocompatibility | High, suitable for long-term implants | Excellent, widely used for medical implants |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, good dimensional stability | Superior toughness and impact resistance |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent wear and abrasion resistance | Good wear resistance, better under cyclic loads |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to 300degC | Stable up to 343degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to most chemicals and solvents | Outstanding chemical and hydrolysis resistance |
| Processing | Requires precise molding conditions | Easy to process by injection molding and machining |
| Applications | Catheters, sutures, flexible medical device components | Orthopedic implants, dental implants, spinal cages |
| Cost | Moderate to high | High, depending on grade and form |
Introduction to Liquid Crystal Polymer and Polyether Ether Ketone
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) is a class of thermoplastic polymers known for their exceptional mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and biocompatibility, making them suitable for medical implant applications requiring durability and precision. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is a high-performance polymer characterized by its excellent thermal stability, radiolucency, and resistance to wear and sterilization processes, widely used in spinal, orthopedic, and dental implants. Both LCP and PEEK offer unique advantages in medical devices, with LCP offering superior stiffness and chemical stability, while PEEK provides enhanced toughness and long-term in vivo performance.
Key Properties of Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP)
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) exhibits exceptional chemical resistance, high tensile strength, and outstanding biocompatibility, making it highly suitable for medical implants requiring durability and inertness. Its low moisture absorption combined with excellent dimensional stability ensures reliable performance in sterilization processes and long-term bodily exposure. Compared to Polyether ether ketone (PEEK), LCP offers superior stiffness and lower density, which can enhance implant integration and patient comfort.
Key Properties of Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK)
Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) offers exceptional chemical resistance, high tensile strength, and outstanding biocompatibility, making it a preferred material for medical implants. Its excellent wear resistance and ability to withstand sterilization processes without degradation ensure long-term performance within the human body. Compared to Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP), PEEK provides superior mechanical stability and durability crucial for load-bearing orthopedic and spinal implants.
Mechanical Strength Comparison: LCP vs PEEK
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits superior tensile strength and stiffness compared to polyether ether ketone (PEEK), making it highly suitable for load-bearing medical implants requiring enhanced mechanical performance. LCP typically demonstrates tensile strengths exceeding 500 MPa and a modulus of elasticity around 10-20 GPa, whereas PEEK shows tensile strength near 90-100 MPa with a modulus approximately 3-4 GPa, emphasizing LCP's advantage in high-strength implant applications. The combination of LCP's excellent fatigue resistance and lower creep rates further distinguishes it from PEEK, ensuring longer-term structural integrity in demanding biomedical environments.
Biocompatibility in Medical Implants
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) exhibits excellent biocompatibility characteristics, including low toxicity, chemical inertness, and resistance to bodily fluids, making it suitable for long-term medical implants. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is renowned for its high biocompatibility, mechanical strength, and bioinertness, with extensive FDA approval for orthopedic and spinal implants. Both materials demonstrate superior biostability, but PEEK's proven track record in load-bearing applications often positions it as the preferred choice for implants requiring high mechanical performance combined with biocompatibility.
Sterilization Resistance and Chemical Stability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior sterilization resistance and chemical stability compared to polyether ether ketone (PEEK), making it highly suitable for medical implants exposed to repetitive sterilization cycles such as autoclaving and gamma irradiation. LCP maintains mechanical integrity and resists degradation when exposed to aggressive sterilization methods and bodily fluids, whereas PEEK, although chemically stable, may exhibit slight property changes under harsh sterilization conditions. The excellent chemical inertness and resistance to high-temperature sterilization processes position LCP as a preferable material for long-term implantable medical devices requiring consistent performance and biocompatibility.
Processing and Fabrication Techniques
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers superior dimensional stability and ease of injection molding compared to polyether ether ketone (PEEK), enabling precise fabrication of complex medical implant geometries. PEEK requires higher processing temperatures and specialized extrusion or compression molding techniques, which extend cycle times but provide excellent mechanical strength and biocompatibility for load-bearing implants. Both materials support advanced fabrication methods like additive manufacturing; however, LCP's lower melting point facilitates faster production while PEEK's thermal resistance ensures long-term implant durability.
Cost Considerations for Medical Applications
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) tends to have a higher upfront cost compared to polyether ether ketone (PEEK) due to complex manufacturing and limited supplier availability, impacting the overall budget for medical implants. PEEK offers a more cost-effective solution with its established supply chain and ease of processing, making it favorable for large-scale implant production. Budget-sensitive medical applications often prioritize PEEK for its balance of performance and affordability, while LCP is selected when specialized properties justify the premium expense.
Common Medical Implant Applications
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) and polyether ether ketone (PEEK) are widely used in medical implant applications due to their excellent biocompatibility and mechanical properties. LCP is favored for microscale implants and flexible electronics in cardiovascular devices, while PEEK is commonly used in orthopedic implants such as spinal cages and dental implants for its high strength and chemical resistance. Both materials offer radiolucency and sterilization compatibility, making them suitable for long-term medical implant solutions.
Selecting the Right Polymer: LCP or PEEK?
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) offers exceptional chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and excellent dimensional stability, making it suitable for precise, high-performance medical implants requiring minimal deformation. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) provides superior mechanical strength, biocompatibility, and radiolucency, ideal for load-bearing orthopedic implants and long-term durability within the human body. Selecting between LCP and PEEK depends on the implant's functional requirements, such as flexibility versus rigidity, chemical exposure, and the need for imaging compatibility during post-operative assessments.
Infographic: Liquid crystal polymer vs Polyether ether ketone for Medical implant
 azmater.com
azmater.com