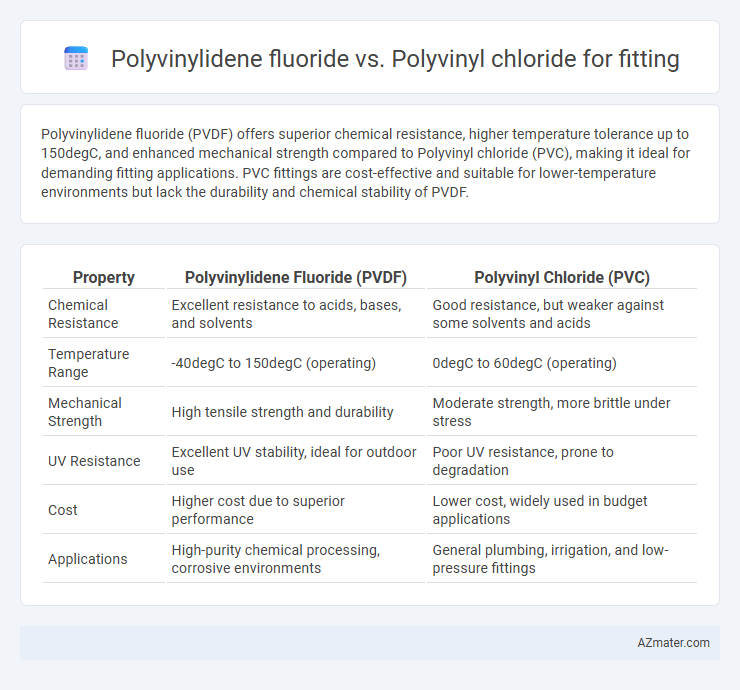
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance, higher temperature tolerance up to 150degC, and enhanced mechanical strength compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for demanding fitting applications. PVC fittings are cost-effective and suitable for lower-temperature environments but lack the durability and chemical stability of PVDF.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and solvents | Good resistance, but weaker against some solvents and acids |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC (operating) | 0degC to 60degC (operating) |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and durability | Moderate strength, more brittle under stress |
| UV Resistance | Excellent UV stability, ideal for outdoor use | Poor UV resistance, prone to degradation |
| Cost | Higher cost due to superior performance | Lower cost, widely used in budget applications |
| Applications | High-purity chemical processing, corrosive environments | General plumbing, irrigation, and low-pressure fittings |
Introduction to PVDF and PVC Fittings
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) fittings are known for their exceptional chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and durability in demanding environments, making them ideal for aggressive fluids and high-purity applications. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) fittings offer cost-effective corrosion resistance and versatility, widely used in water supply, irrigation, and low-pressure chemical transport. The choice between PVDF and PVC fittings depends on factors such as temperature tolerance, chemical compatibility, mechanical strength, and budget constraints.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) features a repeating unit with two fluorine atoms attached to the carbon backbone, providing high chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which consists of vinyl chloride monomers with chlorine atoms bonded to the polymer chain. The fluorine atoms in PVDF create a strong carbon-fluorine bond that enhances its resistance to solvents, acids, and bases, whereas PVC is more susceptible to chemical degradation due to its carbon-chlorine bonds. This fundamental difference in chemical structure makes PVDF fittings more suitable for aggressive chemical environments, while PVC fittings are typically chosen for less demanding applications due to their lower cost and adequate performance.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) fittings exhibit superior mechanical strength and durability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making them ideal for high-stress and chemical-resistant applications. PVDF maintains structural integrity at elevated temperatures up to 150degC, while PVC fittings typically withstand up to 60degC, resulting in less deformation under thermal stress. The enhanced tensile strength and impact resistance of PVDF contribute to longer service life and reduced maintenance in demanding industrial environments.
Thermal Resistance and Temperature Tolerance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), withstanding continuous temperatures up to 150degC while maintaining structural integrity. In contrast, PVC fittings typically endure maximum temperatures around 60-70degC before deformation or degradation occurs. This significant difference makes PVDF fittings more suitable for high-temperature applications requiring enhanced durability and chemical resistance.
Chemical Resistance: Suitability for Various Environments
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it highly suitable for aggressive environments involving acids, bases, and organic solvents. PVDF's stability allows it to withstand high temperatures and harsh chemicals without degrading, which is essential for fittings used in chemical processing and industrial applications. PVC, while cost-effective and resistant to many chemicals, tends to soften or degrade under exposure to strong solvents and elevated temperatures, limiting its use in more demanding environments.
Installation and Fabrication Differences
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) fittings offer superior chemical resistance and higher temperature tolerance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making PVDF ideal for demanding industrial applications. Installation of PVDF fittings requires careful heat fusion techniques due to its higher melting point and flexibility, whereas PVC fittings are easier to install with solvent cement, favoring quick and cost-effective assembly. Fabrication of PVDF involves more precise control and specialized welding equipment to maintain material integrity, while PVC allows for simpler cutting and joining processes suitable for general plumbing and low-pressure systems.
Cost Analysis: PVDF vs PVC Fittings
PVDF fittings demonstrate higher upfront costs compared to PVC fittings due to their superior chemical resistance and temperature tolerance, which enhances durability in demanding applications. PVC fittings offer a more budget-friendly option with widespread availability and adequate performance in less aggressive environments. Evaluating total lifecycle expenses highlights that PVDF fittings can reduce replacement frequency and maintenance costs, proving cost-effective over time despite initial investment differences.
Application Areas and Industry Usage
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) fittings are widely used in chemical processing, pharmaceutical, and food industries due to their superior chemical resistance, UV stability, and high purity compliance. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) fittings dominate water supply, irrigation, and low-pressure plumbing applications because of their cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and good mechanical strength under moderate conditions. PVDF is preferred in harsh environments requiring high temperature and corrosion resistance, while PVC suits general-purpose applications with lower thermal and chemical resistance demands.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior environmental sustainability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) due to its higher chemical resistance and longer lifecycle, reducing the frequency of replacement and waste generation. PVC production and disposal release toxic chlorine-based compounds, contributing to environmental pollution and posing health risks. PVDF's recyclability and lower harmful emissions during manufacturing make it a more eco-friendly option for fittings in sustainable building and industrial applications.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Material for Fittings
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance, UV stability, and higher temperature tolerance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for demanding industrial and outdoor fitting applications. PVC remains a cost-effective option with good mechanical strength and ease of installation, suitable for less aggressive environments and lower temperature ranges. Selecting the right material depends on the specific requirements of the application, balancing durability, chemical compatibility, temperature resistance, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Polyvinyl chloride for Fitting
 azmater.com
azmater.com