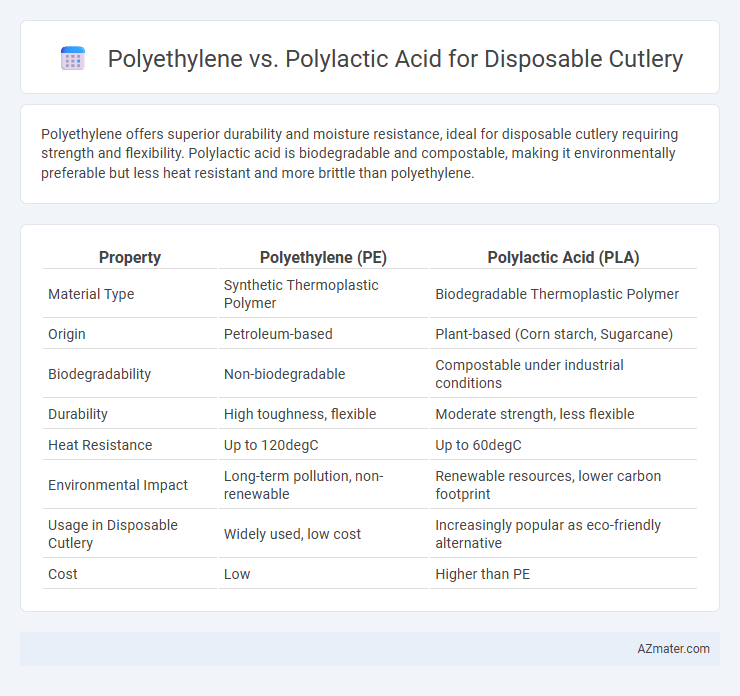
Polyethylene offers superior durability and moisture resistance, ideal for disposable cutlery requiring strength and flexibility. Polylactic acid is biodegradable and compostable, making it environmentally preferable but less heat resistant and more brittle than polyethylene.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Polylactic Acid (PLA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic Thermoplastic Polymer | Biodegradable Thermoplastic Polymer |
| Origin | Petroleum-based | Plant-based (Corn starch, Sugarcane) |
| Biodegradability | Non-biodegradable | Compostable under industrial conditions |
| Durability | High toughness, flexible | Moderate strength, less flexible |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 120degC | Up to 60degC |
| Environmental Impact | Long-term pollution, non-renewable | Renewable resources, lower carbon footprint |
| Usage in Disposable Cutlery | Widely used, low cost | Increasingly popular as eco-friendly alternative |
| Cost | Low | Higher than PE |
Introduction to Disposable Cutlery Materials
Polyethylene (PE) and Polylactic Acid (PLA) are prominent materials used for disposable cutlery, each offering distinct environmental and functional characteristics. Polyethylene, derived from petroleum, provides exceptional durability, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it a staple in mass-produced plastic utensils. Polylactic Acid, a biodegradable biopolymer made from fermented plant starches like corn, presents an eco-friendly alternative by offering compostability under industrial conditions while maintaining adequate strength for everyday use.
What is Polyethylene?
Polyethylene is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its durability, flexibility, and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for disposable cutlery production. Its chemical structure consists of long chains of ethylene monomers, providing strength and lightweight characteristics essential for single-use utensils. Polyethylene's low cost and easy moldability enable mass production, though its non-biodegradable nature raises environmental concerns compared to alternatives like polylactic acid.
What is Polylactic Acid (PLA)?
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, widely used for manufacturing eco-friendly disposable cutlery. Unlike conventional polyethylene, PLA decomposes under industrial composting conditions, reducing long-term environmental impact. Its biocompatibility and lower carbon footprint make PLA a sustainable alternative in single-use food service items.
Production Processes: Polyethylene vs PLA
Polyethylene production relies on the polymerization of ethylene derived from petroleum or natural gas through processes like high-pressure or catalytic polymerization, resulting in a highly durable and flexible plastic used in disposable cutlery. Polylactic Acid (PLA) is produced via the fermentation of renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane into lactic acid, followed by polymerization into a biodegradable thermoplastic with lower environmental impact. While polyethylene offers efficient large-scale manufacturing with stable output, PLA's production emphasizes sustainability but involves more complex processing conditions and sensitivity to moisture during extrusion.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Polyethylene (PE) disposable cutlery is derived from fossil fuels and exhibits low biodegradability, leading to persistent environmental pollution and microplastic accumulation. Polylactic Acid (PLA) cutlery, sourced from renewable resources like cornstarch, offers compostability under industrial conditions, significantly reducing landfill waste and carbon footprint. However, PLA's degradation depends on proper composting infrastructure, while PE's resistance to natural decomposition contributes to long-term environmental harm.
Biodegradability and Compostability
Polyethylene (PE) cutlery is derived from petroleum-based polymers, making it non-biodegradable and resistant to composting processes, resulting in long persistence in landfills and environmental pollution. Polylactic Acid (PLA) cutlery, sourced from renewable plant materials like corn starch, demonstrates biodegradability and industrial compostability under controlled conditions within 60 to 90 days. The choice between PE and PLA for disposable cutlery significantly impacts waste management strategies, with PLA offering environmentally sustainable alternatives aligned with circular economy principles.
Performance: Strength and Durability
Polyethylene disposable cutlery exhibits superior strength and durability, making it resistant to bending and breaking during use. Polylactic acid (PLA) cutlery generally offers moderate strength but tends to be more brittle, especially in warm conditions, which limits its durability. The choice between polyethylene and PLA hinges on performance needs, with polyethylene favored for robust applications and PLA preferred for compostability despite its lower mechanical resilience.
Cost and Market Availability
Polyethylene (PE) cutlery remains significantly more cost-effective than polylactic acid (PLA) alternatives due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses, making PE the dominant choice in budget-sensitive markets. PLA cutlery, derived from renewable resources such as corn starch, faces higher production costs and limited large-scale manufacturing facilities, impacting its market availability and price competitiveness. Despite growing demand for eco-friendly options, PE products maintain widespread distribution and stronger supply chain networks, reinforcing their market dominance in disposable cutlery.
Regulatory and Certification Standards
Polyethylene (PE) disposable cutlery must comply with FDA 21 CFR 177.1520 and EU Regulation No 10/2011 for food contact materials, ensuring safety for direct food use. Polylactic Acid (PLA) cutlery requires certification under ASTM D6400 or EN 13432 standards, verifying compostability and biodegradability alongside food safety compliance. Both materials must meet heavy metal migration limits and overall migration limits set by regulatory agencies to ensure consumer protection.
Choosing the Best Material for Disposable Cutlery
Polyethylene offers exceptional durability and moisture resistance, making it a cost-effective choice for disposable cutlery ideal for hot and cold foods. Polylactic Acid (PLA), derived from renewable resources like corn starch, provides biodegradability and compostability, aligning with eco-friendly and sustainable packaging goals. Selecting the best material depends on balancing performance needs such as strength and temperature tolerance with environmental impact considerations and regulatory compliance for single-use utensils.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Polylactic Acid for Disposable Cutlery
 azmater.com
azmater.com