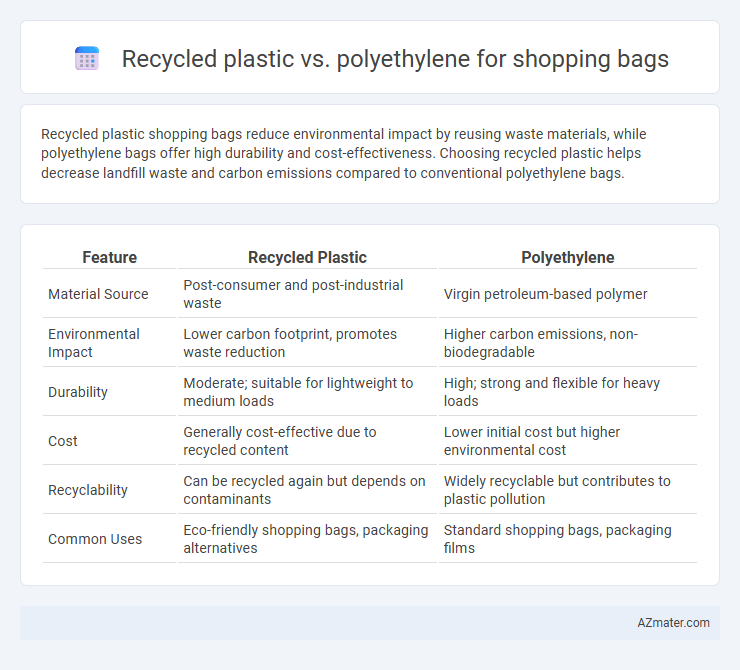
Recycled plastic shopping bags reduce environmental impact by reusing waste materials, while polyethylene bags offer high durability and cost-effectiveness. Choosing recycled plastic helps decrease landfill waste and carbon emissions compared to conventional polyethylene bags.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Plastic | Polyethylene |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Post-consumer and post-industrial waste | Virgin petroleum-based polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, promotes waste reduction | Higher carbon emissions, non-biodegradable |
| Durability | Moderate; suitable for lightweight to medium loads | High; strong and flexible for heavy loads |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective due to recycled content | Lower initial cost but higher environmental cost |
| Recyclability | Can be recycled again but depends on contaminants | Widely recyclable but contributes to plastic pollution |
| Common Uses | Eco-friendly shopping bags, packaging alternatives | Standard shopping bags, packaging films |
Introduction to Shopping Bag Materials
Recycled plastic and polyethylene are two common materials used in shopping bag production, each offering distinct environmental and functional properties. Recycled plastic bags utilize post-consumer or post-industrial waste, reducing landfill waste and conserving resources, while polyethylene bags, typically made from virgin materials, provide durability and flexibility. Understanding the material composition and environmental impact of these bags is crucial for consumers and retailers aiming to make sustainable packaging choices.
Understanding Recycled Plastic Bags
Recycled plastic shopping bags are made from post-consumer or post-industrial plastic waste, significantly reducing environmental impact by diverting materials from landfills and lowering energy consumption compared to virgin polyethylene bags. These bags often contain high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or low-density polyethylene (LDPE), processed to meet durability and flexibility standards similar to traditional polyethylene versions. Understanding recycled plastic bags highlights their contribution to circular economy goals by minimizing carbon footprint and conserving natural resources while maintaining performance for everyday retail use.
What is Polyethylene?
Polyethylene is a widely used thermoplastic polymer made from ethylene monomers, known for its durability, flexibility, and resistance to moisture, making it an ideal choice for manufacturing shopping bags. It exists in various forms such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE), each offering distinct properties suitable for different types of bags. Compared to recycled plastic, polyethylene provides consistent strength and lower production costs but raises environmental concerns due to its non-biodegradable nature unless recycled properly.
Environmental Impact: Recycled Plastic vs Polyethylene
Recycled plastic shopping bags significantly reduce environmental impact by lowering the demand for virgin polyethylene, which is derived from non-renewable fossil fuels. The production of recycled plastic bags consumes less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional polyethylene bags. Furthermore, recycling helps decrease plastic waste in landfills and oceans, enhancing overall sustainability efforts in the packaging industry.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Recycled plastic shopping bags exhibit comparable durability to polyethylene bags but may vary based on the recycling process and material blend, affecting tensile strength and tear resistance. Polyethylene bags, particularly high-density variants, provide superior strength and resistance to punctures, making them highly reliable for heavier loads. Choosing recycled plastic supports environmental sustainability while maintaining reasonable durability, whereas polyethylene offers consistently high performance in terms of structural integrity.
Cost Efficiency Analysis
Recycled plastic shopping bags offer significant cost savings compared to virgin polyethylene bags due to lower raw material expenses and reduced energy consumption during production. Polyethylene bags, while generally cheaper upfront, incur higher environmental compliance costs and disposal fees, impacting overall cost efficiency. Lifecycle assessments reveal recycled plastic bags provide a more economical choice when factoring in long-term sustainability and waste management expenses.
Manufacturing Processes
Manufacturing recycled plastic shopping bags involves sorting, cleaning, and melting used plastics into pellets before extrusion, significantly reducing raw material consumption and energy use compared to virgin polyethylene bags. Polyethylene bags are typically produced through polymerization of ethylene gas derived from crude oil or natural gas, followed by melting and film blowing processes, which require higher fossil fuel inputs and generate more carbon emissions. The use of recycled plastic emphasizes circular economy principles by repurposing waste while maintaining comparable strength and durability to traditional polyethylene bags.
Consumer Perception and Acceptance
Recycled plastic shopping bags are increasingly favored by environmentally conscious consumers who prioritize sustainability and waste reduction, while polyethylene bags, though widely accepted for their durability and low cost, face growing criticism for environmental impact. Consumer acceptance of recycled plastic bags is influenced by perceptions of environmental responsibility and the quality of the material, with many willing to pay a premium for eco-friendly options. Studies show that clear communication about the recyclability and durability of recycled plastic bags enhances consumer trust and encourages broader adoption over traditional polyethylene alternatives.
Regulatory and Sustainability Standards
Recycled plastic shopping bags often meet stringent regulatory standards such as the European Union's Circular Economy Action Plan, which mandates minimum recycled content to reduce environmental impact. Polyethylene bags, primarily made from virgin material, face increasing restrictions due to their carbon footprint and lack of biodegradability, prompting legislation like California's plastic bag ban. Sustainability standards, including ISO 14001 and ASTM D7611 for recycled plastics, emphasize material traceability and lifecycle assessment, favoring recycled plastic bags in markets targeting eco-conscious consumers and compliance-driven retailers.
Choosing the Best Material for Shopping Bags
Recycled plastic offers an eco-friendly alternative by reducing waste and lowering carbon emissions compared to virgin polyethylene, making it a sustainable choice for shopping bags. Polyethylene, particularly low-density polyethylene (LDPE), provides excellent durability, flexibility, and moisture resistance, ensuring strong and reliable bag performance. Evaluating factors such as environmental impact, cost-effectiveness, and material strength is essential when choosing the best material for shopping bags.
Infographic: Recycled plastic vs Polyethylene for Shopping bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com