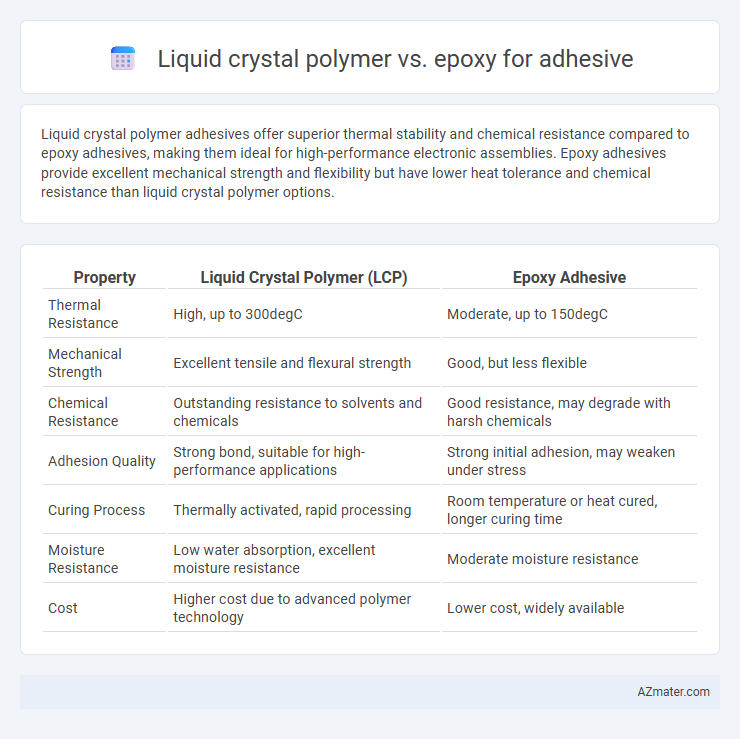
Liquid crystal polymer adhesives offer superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to epoxy adhesives, making them ideal for high-performance electronic assemblies. Epoxy adhesives provide excellent mechanical strength and flexibility but have lower heat tolerance and chemical resistance than liquid crystal polymer options.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) | Epoxy Adhesive |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | High, up to 300degC | Moderate, up to 150degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent tensile and flexural strength | Good, but less flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Outstanding resistance to solvents and chemicals | Good resistance, may degrade with harsh chemicals |
| Adhesion Quality | Strong bond, suitable for high-performance applications | Strong initial adhesion, may weaken under stress |
| Curing Process | Thermally activated, rapid processing | Room temperature or heat cured, longer curing time |
| Moisture Resistance | Low water absorption, excellent moisture resistance | Moderate moisture resistance |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced polymer technology | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Adhesive Materials
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) adhesives exhibit exceptional thermal resistance, chemical stability, and mechanical strength, making them suitable for high-performance electronic and aerospace applications. Epoxy adhesives offer strong bonding, excellent adhesion to various substrates, and good electrical insulation, commonly used in industrial and consumer goods. The choice between LCP and epoxy depends on specific requirements like temperature tolerance, flexibility, and environmental exposure.
Understanding Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP)
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) adhesives exhibit exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to traditional epoxy adhesives, making them ideal for high-performance electronic and aerospace applications. LCPs possess a unique molecular structure that aligns during curing, resulting in superior mechanical strength, low moisture absorption, and excellent dimensional stability. These properties enable LCP adhesives to maintain integrity under extreme temperatures and harsh environmental conditions, significantly outperforming conventional epoxy in demanding scenarios.
Overview of Epoxy Adhesives
Epoxy adhesives are widely recognized for their exceptional mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and adhesion to a variety of substrates, including metals, ceramics, and composites. Their thermosetting properties allow for strong, durable bonds that maintain performance under high stress and temperature conditions. Epoxies are commonly used in electronics, aerospace, and automotive industries due to their versatility and reliability compared to Liquid Crystal Polymer adhesives.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) adhesives exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to epoxy adhesives, especially in high-stress and high-temperature environments, due to their molecular alignment and crystalline structure. LCP adhesives offer enhanced tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexibility, making them ideal for advanced electronics and aerospace applications where durability and thermal stability are critical. Epoxy adhesives, while strong and rigid, generally possess lower impact resistance and are more prone to brittleness under mechanical stress.
Thermal Performance Differences
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) adhesives exhibit superior thermal performance compared to epoxy adhesives, maintaining stability and mechanical integrity at temperatures exceeding 300degC. LCP adhesives demonstrate low thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity, enabling efficient heat dissipation in high-temperature applications. Epoxy adhesives typically degrade above 150degC, leading to reduced adhesion strength and potential material failure under prolonged thermal stress.
Chemical Resistance Analysis
Liquid crystal polymers exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to epoxy adhesives, particularly against solvents, acids, and alkalis, making them ideal for harsh environmental conditions. Epoxy adhesives offer good chemical resistance but tend to degrade under prolonged exposure to aggressive chemicals, especially strong acids and bases. The molecular alignment in liquid crystal polymers provides enhanced barrier properties, reducing permeation and chemical attack, whereas epoxy networks are more susceptible to hydrolytic and oxidative degradation.
Flexibility and Durability
Liquid crystal polymer adhesives offer superior flexibility due to their unique molecular alignment, allowing them to withstand repeated bending and thermal cycling without cracking. Epoxy adhesives provide exceptional durability with high mechanical strength and chemical resistance but tend to be more rigid and prone to brittleness under continuous stress. Comparing both materials, liquid crystal polymer adhesives excel in applications requiring dynamic flexibility, while epoxies are preferred for static structural bonds demanding long-term stability.
Processing and Application Methods
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) adhesives offer superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, enabling precision application methods such as screen printing and dispensing for electronic components and high-performance bonding. Epoxy adhesives provide versatile curing options including room temperature, heat, or UV curing, making them suitable for structural bonding in automotive, aerospace, and general assembly processes. The high viscosity of epoxy allows for manual or automated application with ease, whereas LCP demands controlled processing environments due to its anisotropic melting behavior and crystalline phase transitions.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) adhesives typically exhibit higher material costs compared to epoxy adhesives due to their specialized properties and manufacturing processes. Epoxy adhesives are widely available and cost-effective, making them the preferred choice for general bonding applications and large-scale production. The cost-effectiveness of epoxy adhesives is enhanced by their versatility and extensive availability in various formulations and quantities.
Choosing Between LCP and Epoxy for Adhesive Needs
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) adhesives offer superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength compared to traditional epoxy adhesives, making them ideal for high-performance electronics and automotive applications. Epoxy adhesives excel in providing strong bonding with ease of use and cost-effectiveness, suitable for general-purpose bonding where extreme conditions are not a factor. Choosing between LCP and epoxy depends on application-specific requirements such as operating temperature range, exposure to chemicals, and mechanical stress tolerance.
Infographic: Liquid crystal polymer vs Epoxy for Adhesive
 azmater.com
azmater.com