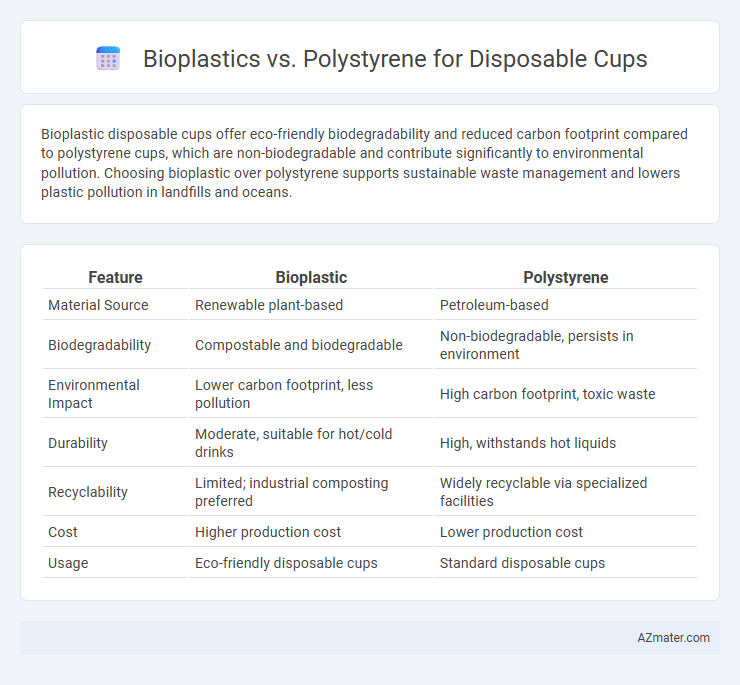
Bioplastic disposable cups offer eco-friendly biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint compared to polystyrene cups, which are non-biodegradable and contribute significantly to environmental pollution. Choosing bioplastic over polystyrene supports sustainable waste management and lowers plastic pollution in landfills and oceans.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bioplastic | Polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Renewable plant-based | Petroleum-based |
| Biodegradability | Compostable and biodegradable | Non-biodegradable, persists in environment |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, less pollution | High carbon footprint, toxic waste |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for hot/cold drinks | High, withstands hot liquids |
| Recyclability | Limited; industrial composting preferred | Widely recyclable via specialized facilities |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost |
| Usage | Eco-friendly disposable cups | Standard disposable cups |
Introduction to Disposable Cup Materials
Disposable cups are commonly made from materials such as polystyrene and bioplastics, each offering distinct environmental and functional properties. Polystyrene, a petroleum-based plastic, provides excellent insulation and durability but contributes significantly to plastic pollution due to its non-biodegradable nature. Bioplastics derived from renewable resources like cornstarch offer a more sustainable alternative with biodegradability and compostability, reducing landfill impact and carbon footprint in single-use cup applications.
What Is Bioplastic?
Bioplastic is a type of biodegradable material derived from renewable biological sources such as corn starch, sugarcane, or cellulose, designed to reduce environmental impact compared to traditional plastics like polystyrene. Unlike polystyrene, which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable, bioplastic decomposes more quickly under industrial composting conditions, making it a more sustainable choice for disposable cups. The use of bioplastic cups helps decrease plastic pollution and reliance on fossil fuels, aligning with eco-friendly and waste reduction goals.
Understanding Polystyrene
Polystyrene is a petroleum-based plastic widely used in disposable cups due to its lightweight, insulating properties, and low manufacturing cost. It is rigid, resistant to moisture and heat, but non-biodegradable, contributing to long-lasting environmental pollution when discarded. Understanding its chemical structure and environmental impact highlights the growing demand for sustainable alternatives like bioplastic in the disposable cup industry.
Production Process Comparison
Bioplastic disposable cups are produced from renewable resources like cornstarch or sugarcane, utilizing fermentation and polymerization processes that reduce carbon emissions and reliance on fossil fuels. In contrast, polystyrene cups are synthesized through the polymerization of styrene monomers derived from petroleum, involving energy-intensive refining and chemical processing steps associated with higher environmental footprints. The production of bioplastic cups typically results in lower greenhouse gas emissions and enhanced biodegradability compared to the conventional, non-biodegradable polystyrene cup manufacturing process.
Environmental Impact of Bioplastic
Bioplastics for disposable cups significantly reduce environmental impact by being derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, leading to lower carbon footprints compared to polystyrene, which relies on fossil fuels. Bioplastics are often biodegradable or compostable, decreasing landfill waste and minimizing long-term pollution problems caused by polystyrene, which can persist for centuries and release harmful chemicals. The shift to bioplastic cups supports circular economy principles by promoting resource efficiency and reducing reliance on non-renewable materials, enhancing sustainability in single-use products.
Environmental Impact of Polystyrene
Polystyrene disposable cups contribute significantly to environmental pollution due to their non-biodegradable nature and persistence in landfills for hundreds of years. The production process of polystyrene releases harmful chemicals such as styrene and benzene, which pose health risks to humans and wildlife. Recycling rates for polystyrene remain low, leading to widespread accumulation in oceans and terrestrial ecosystems, causing detrimental effects on marine life and biodiversity.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Scenarios
Bioplastic disposable cups offer superior biodegradability compared to polystyrene, breaking down naturally within months under industrial composting conditions, whereas polystyrene can persist in the environment for centuries. End-of-life scenarios for bioplastic cups include composting and anaerobic digestion, significantly reducing landfill waste and greenhouse gas emissions. Polystyrene cups often end up in landfills or as litter due to limited recycling infrastructure, contributing to long-term environmental pollution.
Performance and Usability Factors
Bioplastic disposable cups offer superior biodegradability and compostability compared to traditional polystyrene, which can take hundreds of years to decompose and often contributes to environmental pollution. In terms of performance, polystyrene excels in insulation, maintaining beverage temperature longer, while bioplastic cups can sometimes lack the same heat resistance and may soften with hot liquids. Usability factors include bioplastic cups being microwave-safe and compostable, promoting eco-friendly disposal methods, whereas polystyrene cups are typically not microwave-safe and require specialized recycling processes.
Cost Analysis: Bioplastic vs Polystyrene
Bioplastic disposable cups generally have higher production costs compared to polystyrene due to expensive raw materials like cornstarch or sugarcane derivatives. Polystyrene cups benefit from lower manufacturing expenses and established supply chains, making them more cost-effective for large-scale use. However, bioplastic costs may decrease with scale and innovation while offering environmental benefits that could offset initial price differences.
Future Trends and Market Adoption
Bioplastic disposable cups are expected to gain significant market adoption due to increasing consumer demand for sustainable and compostable alternatives, driven by regulatory bans on single-use plastics like polystyrene. Innovations in biopolymer technology are enhancing the durability and cost-effectiveness of bioplastic cups, making them competitive with traditional polystyrene in the foodservice industry. Market trends indicate a rapid growth rate for bioplastics, projected to expand at a CAGR of over 15% by 2030, reflecting a clear shift toward eco-friendly materials in disposable cup production.
Infographic: Bioplastic vs Polystyrene for Disposable Cup
 azmater.com
azmater.com