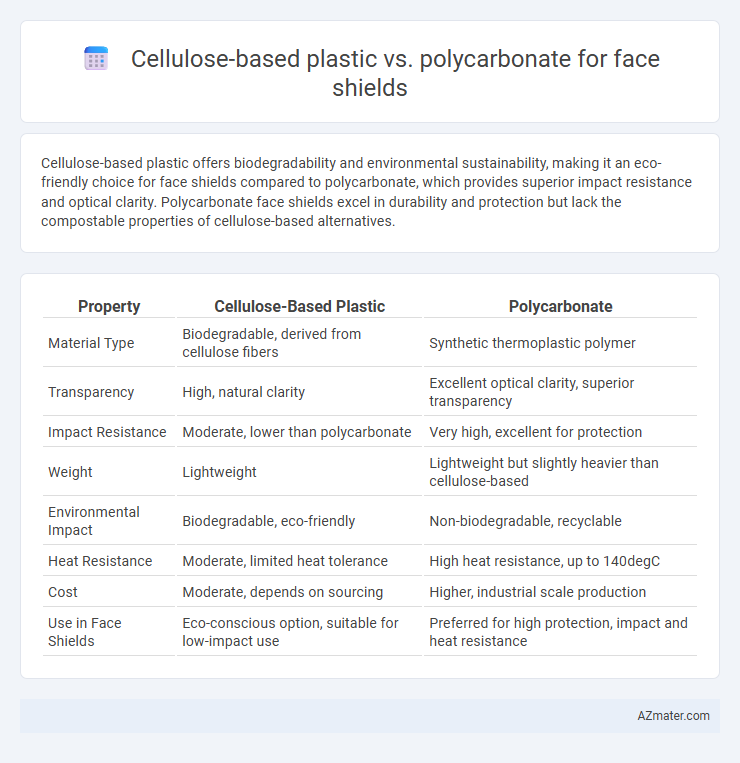
Cellulose-based plastic offers biodegradability and environmental sustainability, making it an eco-friendly choice for face shields compared to polycarbonate, which provides superior impact resistance and optical clarity. Polycarbonate face shields excel in durability and protection but lack the compostable properties of cellulose-based alternatives.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellulose-Based Plastic | Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biodegradable, derived from cellulose fibers | Synthetic thermoplastic polymer |
| Transparency | High, natural clarity | Excellent optical clarity, superior transparency |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate, lower than polycarbonate | Very high, excellent for protection |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight but slightly heavier than cellulose-based |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate, limited heat tolerance | High heat resistance, up to 140degC |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on sourcing | Higher, industrial scale production |
| Use in Face Shields | Eco-conscious option, suitable for low-impact use | Preferred for high protection, impact and heat resistance |
Introduction to Face Shield Materials
Cellulose-based plastics offer a biodegradable and eco-friendly alternative for face shield materials, providing transparency and sufficient mechanical strength for protective use. Polycarbonate is widely utilized in face shields due to its exceptional impact resistance, optical clarity, and lightweight properties, ensuring superior durability and comfort. The selection between cellulose-based plastics and polycarbonate depends on factors such as environmental impact, cost, and performance requirements in personal protective equipment.
Overview of Cellulose-Based Plastics
Cellulose-based plastics are derived from natural polymers found in plant cell walls, offering biodegradability and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional plastics like polycarbonate. These bioplastics exhibit good transparency, decent mechanical strength, and are often compostable, making them suitable for face shields in eco-friendly applications. Although cellulose-based plastics generally have lower impact resistance than polycarbonate, their sustainability credentials and renewable sourcing position them as a promising alternative for protective face shield production.
Polycarbonate: Properties and Uses
Polycarbonate is a highly durable and impact-resistant material ideal for face shields, providing excellent optical clarity and UV protection. Its lightweight and shatterproof properties ensure user safety in medical, industrial, and dental applications. Unlike cellulose-based plastics, polycarbonate resists heat and chemicals, making it suitable for repeated sterilization and prolonged use.
Transparency and Optical Clarity Comparison
Cellulose-based plastics offer moderate transparency with a natural matte finish, reducing glare but limiting optical clarity compared to polycarbonate. Polycarbonate provides superior optical clarity with high light transmission and excellent resistance to yellowing, ensuring clear visibility in face shields. The enhanced transparency of polycarbonate makes it the preferred material for applications demanding precise visual performance.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Cellulose-based plastics offer moderate impact resistance suitable for light protective applications but tend to degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and mechanical stress. Polycarbonate face shields exhibit superior impact resistance with the ability to withstand high-velocity impacts, maintaining durability and clarity over extended use. The inherent toughness and resistance to cracking make polycarbonate the preferred material for industrial and medical face shields requiring consistent performance in demanding environments.
Environmental Sustainability and Biodegradability
Cellulose-based plastics offer superior environmental sustainability compared to polycarbonate due to their renewable sourcing from plant fibers and inherent biodegradability, allowing them to decompose naturally without leaving harmful residues. Polycarbonate, manufactured from petroleum-derived chemicals, presents significant challenges in waste management due to its resistance to biodegradation and potential release of toxic substances during degradation. The eco-friendly profile of cellulose-based materials makes them a preferred choice for face shields in reducing plastic pollution and supporting circular economy initiatives.
Weight and Comfort in Prolonged Use
Cellulose-based plastic face shields offer significantly lower weight compared to polycarbonate, reducing strain during prolonged use. The lightweight nature of cellulose enhances wearer comfort, minimizing pressure on the head and neck over extended periods. Polycarbonate, while durable, tends to be heavier and may cause discomfort during long shifts.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Cellulose-based plastics for face shields offer a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative, benefiting from renewable resources and simpler biodegradability. Polycarbonate requires higher energy input and expense during manufacturing due to its complex polymer structure, but provides superior durability and impact resistance. The choice hinges on balancing cost efficiency and eco-conscious production with the need for long-lasting protection in face shield applications.
Applications in Healthcare and Industry
Cellulose-based plastics offer biodegradability and chemical resistance, making them ideal for disposable face shields in healthcare settings where hygiene and environmental impact are critical. Polycarbonate provides superior impact resistance, optical clarity, and durability, which suits industrial applications requiring reusable face shields with high protection against mechanical hazards. Both materials address specific needs: cellulose-based plastics for eco-friendly, single-use solutions, and polycarbonate for robust, long-term industrial safety gear.
Future Trends in Face Shield Materials
Cellulose-based plastics for face shields offer a sustainable alternative with biodegradability and reduced environmental impact compared to polycarbonate, which remains preferred for its superior clarity, impact resistance, and durability. Future trends in face shield materials emphasize the development of hybrid composites combining bio-based polymers and advanced synthetic materials to enhance performance while minimizing ecological footprint. Innovations in nano-coatings and antimicrobial treatments are also expected to improve hygiene and safety standards in face shield production.
Infographic: Cellulose-based plastic vs Polycarbonate for Face shield
 azmater.com
azmater.com