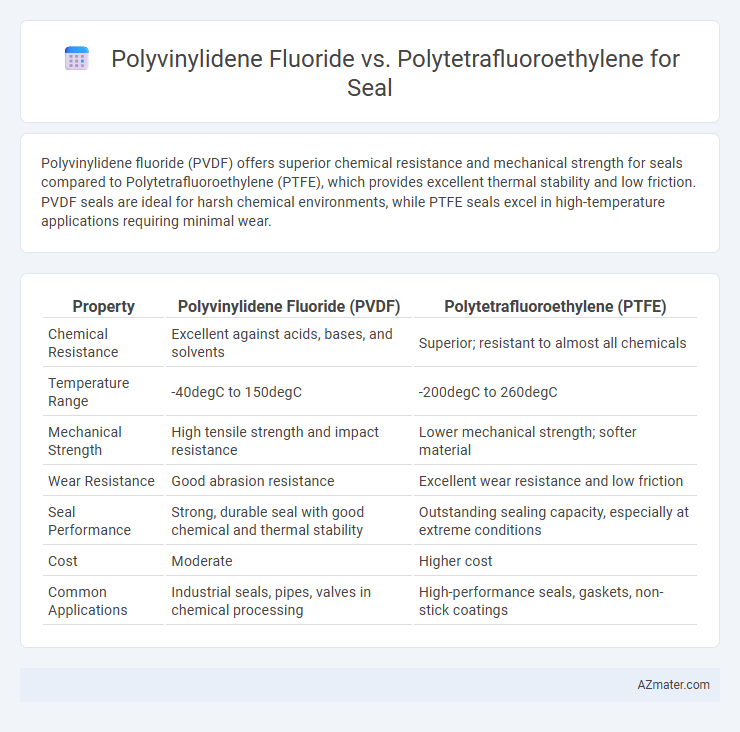
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and mechanical strength for seals compared to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which provides excellent thermal stability and low friction. PVDF seals are ideal for harsh chemical environments, while PTFE seals excel in high-temperature applications requiring minimal wear.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids, bases, and solvents | Superior; resistant to almost all chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -200degC to 260degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and impact resistance | Lower mechanical strength; softer material |
| Wear Resistance | Good abrasion resistance | Excellent wear resistance and low friction |
| Seal Performance | Strong, durable seal with good chemical and thermal stability | Outstanding sealing capacity, especially at extreme conditions |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher cost |
| Common Applications | Industrial seals, pipes, valves in chemical processing | High-performance seals, gaskets, non-stick coatings |
Introduction: PVDF vs PTFE Seals
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are widely used materials for seals in chemical and industrial applications due to their chemical resistance and durability. PVDF seals offer higher tensile strength and better resistance to UV radiation compared to PTFE, making them suitable for applications requiring mechanical robustness and outdoor exposure. PTFE seals provide exceptional non-stick properties and superior chemical inertness across a broad temperature range, ideal for sealing aggressive chemicals and extreme thermal environments.
Chemical Structure and Properties
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) features a semi-crystalline polymer structure with repeating units of -(CH2-CF2)-, providing high chemical resistance and strong mechanical properties ideal for seals in aggressive environments. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), composed of -(CF2-CF2)- repeating units, exhibits exceptional chemical inertness and a low coefficient of friction, making it suitable for seals exposed to extreme temperatures and corrosive chemicals. PVDF offers better tensile strength and stiffness compared to the more flexible and slippery PTFE, influencing the selection based on sealing performance requirements and chemical exposure.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), making it more suitable for high-stress seal applications. PTFE exhibits excellent chemical resistance and low friction but has lower mechanical strength and is more prone to deformation under load. PVDF seals maintain structural integrity better under mechanical stress, ensuring longer durability in dynamic sealing environments.
Temperature Resistance Capabilities
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers temperature resistance up to approximately 150degC, making it suitable for moderately high-temperature seal applications. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits superior thermal stability with temperature resistance ranging from -200degC to 260degC, excelling in extreme temperature environments. PTFE's broader temperature range and excellent chemical resistance make it the preferred choice for seals exposed to fluctuating or high-temperature conditions.
Chemical Compatibility and Resistance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers excellent chemical compatibility with a wide range of acids, bases, and solvents, making it ideal for seals exposed to aggressive chemicals. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides superior resistance to almost all chemicals, including strong oxidizers and hydrocarbons, due to its highly inert molecular structure. PTFE seals exhibit better long-term durability in extreme chemical environments, while PVDF seals balance chemical resistance with higher mechanical strength and temperature tolerance.
Permeability and Seal Integrity
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits lower permeability to gases and liquids compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), making PVDF seals more effective in preventing fluid leakage. The molecular structure of PVDF provides superior chemical resistance and enhanced seal integrity under high pressure and temperature conditions. PTFE, while also chemically inert, tends to have higher permeability and may require additional design considerations to maintain long-term seal integrity in demanding applications.
Wear and Abrasion Resistance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers excellent wear resistance due to its high mechanical strength and chemical stability, making it suitable for seals exposed to abrasive environments. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), known for its exceptional low friction and broad chemical resistance, provides superior abrasion resistance but tends to have lower mechanical strength compared to PVDF. In sealing applications where wear and abrasion are critical, PVDF is preferred for its durability under mechanical stress, while PTFE is ideal when minimizing friction and chemical corrosion is paramount.
Cost Considerations
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) seals typically offer a cost advantage over Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) due to lower raw material prices and simpler manufacturing processes. PTFE, known for its exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance, often commands a premium price in sealing applications. When budget constraints are critical, PVDF provides a balance of performance and affordability, making it a cost-effective choice for many industrial sealing solutions.
Typical Applications in Sealing
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is highly valued in sealing applications for its excellent chemical resistance and durability in aggressive environments such as chemical processing and pharmaceutical industries. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers superior non-stick properties and operates effectively in extreme temperatures, making it ideal for seals in food processing and high-temperature chemical reactors. Both materials provide exceptional resistance to corrosion and wear, but PVDF is preferred for mechanical strength while PTFE excels in lubrication and thermal stability.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Seal
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers excellent chemical resistance, higher mechanical strength, and better temperature tolerance up to 150degC, making it ideal for seals in aggressive chemical environments. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) excels in low friction, superior thermal stability up to 260degC, and outstanding non-stick properties, suitable for high-temperature seals with minimal wear. Choosing the right material depends on operating temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress requirements to ensure optimal seal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com