Fluoropolymer food containers offer superior chemical resistance and non-stick properties compared to polystyrene, ensuring enhanced durability and safety for food storage. Polystyrene containers are more prone to cracking and leaching harmful chemicals, making fluoropolymer a more reliable choice for long-term food contact.
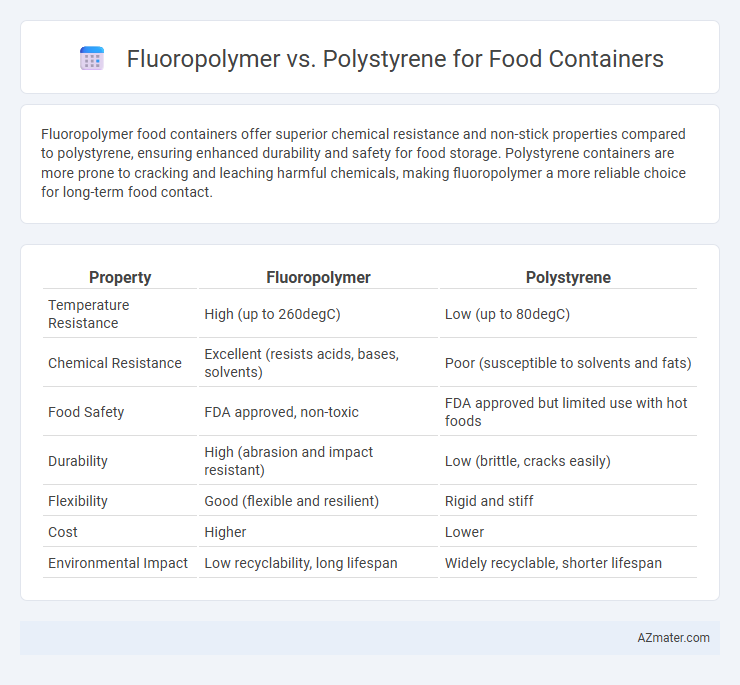
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluoropolymer | Polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | High (up to 260degC) | Low (up to 80degC) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (resists acids, bases, solvents) | Poor (susceptible to solvents and fats) |
| Food Safety | FDA approved, non-toxic | FDA approved but limited use with hot foods |
| Durability | High (abrasion and impact resistant) | Low (brittle, cracks easily) |
| Flexibility | Good (flexible and resilient) | Rigid and stiff |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Environmental Impact | Low recyclability, long lifespan | Widely recyclable, shorter lifespan |
Introduction to Food Container Materials
Fluoropolymers and polystyrene represent distinct categories of food container materials, each offering unique properties tailored to food safety and durability. Fluoropolymers provide exceptional chemical resistance, non-stick surfaces, and thermal stability, making them ideal for high-temperature and acidic food applications. Polystyrene, characterized by its lightweight, rigidity, and cost-effectiveness, is commonly used for disposable food containers but lacks the heat resistance and chemical inertness found in fluoropolymers.
Overview of Fluoropolymers
Fluoropolymers are high-performance polymers characterized by their exceptional chemical resistance, low surface energy, and thermal stability, making them ideal for food container applications where safety and durability are critical. Unlike polystyrene, fluoropolymers do not leach harmful substances and maintain integrity under extreme temperatures, ensuring food safety during storage and heating. Their non-stick and anti-corrosive properties also contribute to extended product lifespan and improved hygiene in food packaging.
Overview of Polystyrene
Polystyrene is a widely used thermoplastic polymer in food containers due to its rigidity, low cost, and excellent clarity, making it ideal for packaging fresh foods and disposable utensils. It offers good thermal insulation but has limited heat resistance and can leach styrene monomers under high temperatures, raising potential health concerns. Unlike fluoropolymers, polystyrene lacks chemical resistance and durability, which restricts its use to short-term food storage and single-use applications.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Fluoropolymer food containers exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to polystyrene, effectively withstanding exposure to strong acids, bases, and organic solvents without degradation. Polystyrene tends to absorb or swell when in contact with certain oils and solvents, leading to potential contamination and reduced durability. This chemical inertness of fluoropolymers ensures safer storage of a wider range of food substances, maintaining container integrity under harsh chemical exposure.
Temperature Tolerance and Durability
Fluoropolymers offer superior temperature tolerance, withstanding extreme heat up to 260degC (500degF) and resisting chemical degradation, making them ideal for food containers exposed to high temperatures. Polystyrene, while inexpensive and lightweight, typically tolerates only up to 90degC (194degF) and can become brittle or deform when exposed to heat for extended periods. The durability of fluoropolymer containers also surpasses polystyrene due to their resistance to cracking, UV radiation, and chemical corrosion, supporting long-term reuse and safety.
Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Fluoropolymer food containers provide superior chemical resistance and non-reactivity, reducing the risk of food contamination and ensuring compliance with FDA and EFSA regulations. Polystyrene, while widely used, can leach styrene monomers under heat, posing potential health risks and stricter regulatory scrutiny. Fluoropolymer materials meet stringent food safety standards such as FDA 21 CFR 177.1550, offering enhanced protection for storing acidic or oily foods compared to conventional polystyrene containers.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fluoropolymer food containers offer superior chemical resistance and durability but pose environmental challenges due to their persistence and difficulty in recycling, leading to long-term pollution concerns. Polystyrene containers, although lightweight and cost-effective, contribute significantly to plastic pollution because of their low biodegradability and limited recycling infrastructure. Choosing sustainable packaging requires evaluating the lifecycle impacts, with emerging biodegradable alternatives and improved recycling technologies offering potential mitigation pathways.
Cost Analysis: Fluoropolymer vs Polystyrene
Fluoropolymer food containers typically incur higher production costs due to expensive raw materials and complex manufacturing processes compared to polystyrene, which benefits from lower material costs and widespread industrial use. Polystyrene offers a more economical option for single-use packaging, while fluoropolymers provide durability and chemical resistance that justify their premium pricing in specialized applications. Cost efficiency analysis reveals polystyrene as the preferred choice for mass-market food packaging, whereas fluoropolymer containers serve niche markets demanding superior performance despite increased expenses.
Common Food Container Applications
Fluoropolymer containers are preferred for applications requiring superior chemical resistance and non-stick properties, such as storing acidic or oily foods, making them ideal for long-term food storage and microwave heating. Polystyrene containers dominate in disposable food packaging like takeout boxes and bakery trays due to their lightweight, low cost, and excellent clarity for product visibility. Both materials are commonly used in food service, but fluoropolymers offer enhanced durability and temperature resistance, while polystyrene is favored for convenience and cost-effectiveness in short-term use.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Material
Fluoropolymer offers superior chemical resistance, non-stick properties, and heat tolerance, making it ideal for food containers requiring durability and safety. Polystyrene is cost-effective and lightweight but lacks the thermal and chemical robustness of fluoropolymers, limiting its suitability for long-term or high-temperature food storage. Choosing the best material depends on prioritizing factors like thermal endurance, chemical inertness, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Fluoropolymer vs Polystyrene for Food Container
 azmater.com
azmater.com