Polyethylene offers excellent chemical resistance and durability for shoe soles, while Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) provides superior cushioning, flexibility, and lightweight comfort. EVA is preferred in athletic footwear due to its shock absorption and softness, whereas polyethylene is often used in more rigid, wear-resistant soles.
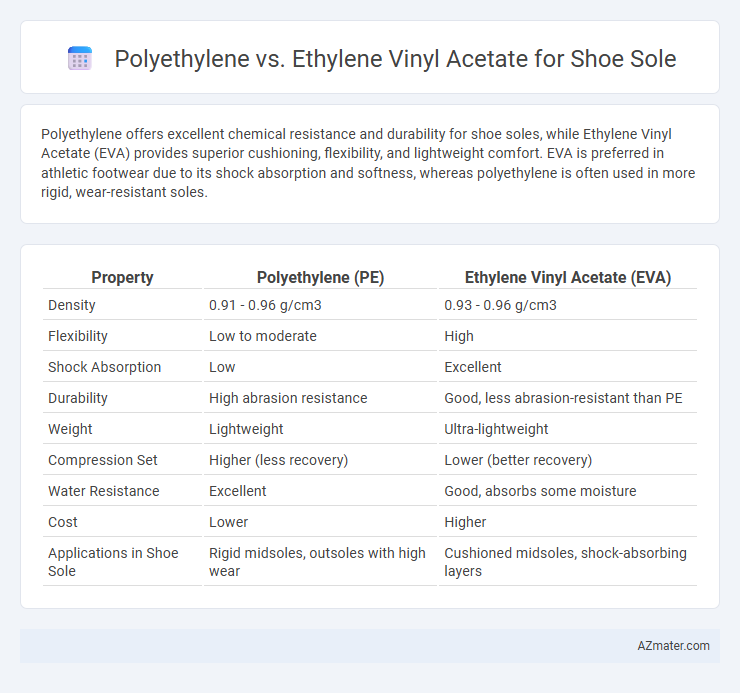
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.91 - 0.96 g/cm3 | 0.93 - 0.96 g/cm3 |
| Flexibility | Low to moderate | High |
| Shock Absorption | Low | Excellent |
| Durability | High abrasion resistance | Good, less abrasion-resistant than PE |
| Weight | Lightweight | Ultra-lightweight |
| Compression Set | Higher (less recovery) | Lower (better recovery) |
| Water Resistance | Excellent | Good, absorbs some moisture |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Applications in Shoe Sole | Rigid midsoles, outsoles with high wear | Cushioned midsoles, shock-absorbing layers |
Introduction to Shoe Sole Materials
Polyethylene and Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) are key materials in shoe sole manufacturing, each offering distinct performance characteristics. Polyethylene provides high durability and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for heavy-duty footwear applications. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate offers superior cushioning, flexibility, and lightweight properties, commonly used in athletic and casual shoe soles for enhanced comfort and shock absorption.
What is Polyethylene (PE)?
Polyethylene (PE) is a versatile thermoplastic polymer characterized by its high durability, chemical resistance, and low moisture absorption, making it ideal for robust shoe soles. It features a semi-crystalline structure that provides excellent impact strength and flexibility, crucial for footwear performance. Compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), PE offers superior abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, enhancing the longevity of shoe soles under heavy usage.
What is Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)?
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a soft, flexible copolymer made from ethylene and vinyl acetate, widely used for shoe soles due to its excellent cushioning, lightweight nature, and durability. EVA offers superior shock absorption and resilience compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for athletic and casual footwear that requires comfort and flexibility. Its closed-cell foam structure provides water resistance and thermal insulation, enhancing overall shoe performance.
Key Physical Properties of PE vs EVA
Polyethylene (PE) exhibits high density and rigidity, offering excellent abrasion resistance and chemical stability, ideal for durable shoe soles requiring toughness and wear resistance. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) provides superior flexibility, cushioning, and shock absorption due to its low density and softer texture, enhancing comfort and impact protection in footwear. While PE boasts higher tensile strength, EVA excels in cushioning and elasticity, making each material suited for different functional shoe sole applications.
Comfort and Cushioning: PE vs EVA
Polyethylene (PE) offers moderate cushioning and rigidity, making it suitable for shoe soles requiring durability but less emphasis on comfort. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) provides superior cushioning and flexibility due to its lightweight, shock-absorbing properties, enhancing overall foot comfort during prolonged wear. EVA's enhanced energy return and softness make it the preferred choice for athletic and casual footwear focused on comfort and impact protection.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Polyethylene shoe soles offer high durability with excellent resistance to abrasion and impact, making them suitable for heavy-duty use. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) soles provide superior flexibility and cushioning, enhancing comfort but may wear out faster under intense conditions. For longevity, polyethylene generally outperforms EVA in toughness, while EVA prioritizes shock absorption at the expense of long-term wear resistance.
Flexibility and Weight Differences
Polyethylene offers higher rigidity and durability but tends to be heavier, impacting overall shoe weight and reducing flexibility. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) provides superior flexibility and lightweight properties, enhancing comfort and shock absorption in shoe soles. Choosing EVA improves cushioning and reduces fatigue, making it ideal for athletic and casual footwear.
Performance in Various Weather Conditions
Polyethylene shoe soles offer exceptional durability and chemical resistance but tend to become rigid and less flexible in cold weather, reducing comfort and performance. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) soles maintain excellent cushioning and flexibility across a wide temperature range, providing superior shock absorption and resilience in both hot and cold conditions. EVA's lightweight and water-resistant properties make it a preferred choice for footwear requiring consistent performance in varying weather environments.
Cost Comparison: PE vs EVA
Polyethylene (PE) offers a lower cost alternative to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) for shoe sole manufacturing due to its inexpensive raw materials and simpler production process. EVA, while more costly, provides enhanced cushioning and flexibility, justifying its higher price in performance-focused applications. The cost difference between PE and EVA soles typically ranges from 15% to 40%, influencing manufacturers' material selection based on budget constraints and desired product quality.
Which Material is Best for Shoe Soles?
Polyethylene offers high rigidity and chemical resistance, making it suitable for durable, rigid shoe soles that require long-lasting wear. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) provides superior flexibility, lightweight cushioning, and shock absorption, ideal for athletic and comfort-focused footwear. For the best shoe soles, EVA is preferred in performance and casual shoes due to its comfort and resilience, while polyethylene suits applications demanding structural toughness.
Infographic: Polyethylene vs Ethylene Vinyl Acetate for Shoe Sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com