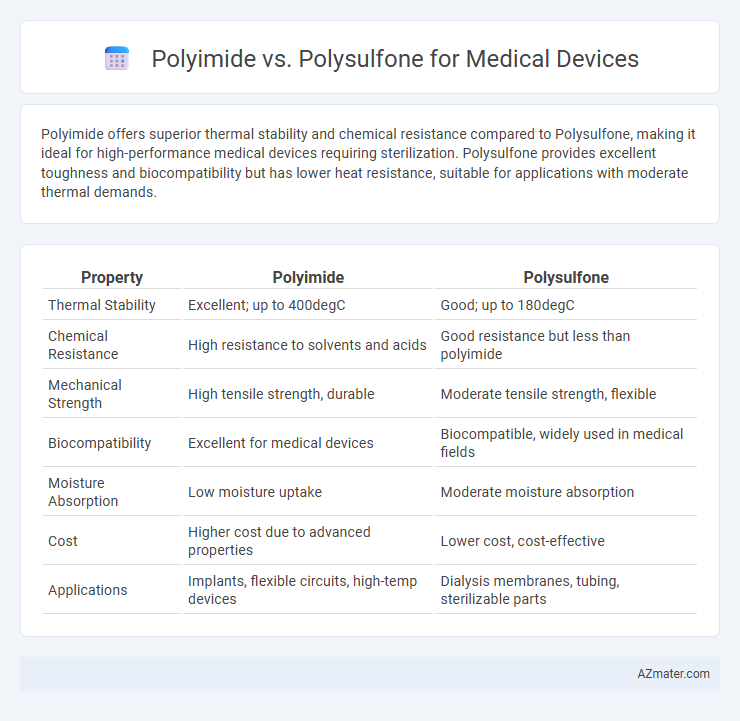
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to Polysulfone, making it ideal for high-performance medical devices requiring sterilization. Polysulfone provides excellent toughness and biocompatibility but has lower heat resistance, suitable for applications with moderate thermal demands.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyimide | Polysulfone |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Excellent; up to 400degC | Good; up to 180degC |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to solvents and acids | Good resistance but less than polyimide |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, durable | Moderate tensile strength, flexible |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent for medical devices | Biocompatible, widely used in medical fields |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture uptake | Moderate moisture absorption |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost, cost-effective |
| Applications | Implants, flexible circuits, high-temp devices | Dialysis membranes, tubing, sterilizable parts |
Introduction to Polyimide and Polysulfone in Medical Devices
Polyimide and polysulfone are high-performance polymers widely used in medical devices due to their excellent thermal stability and biocompatibility. Polyimide offers superior flexibility and chemical resistance, making it ideal for flexible circuits and implantable devices. Polysulfone provides outstanding mechanical strength and hydrolytic stability, commonly used in sterilizable components and fluid handling systems within medical applications.
Chemical Structure and Material Properties Comparison
Polyimide features aromatic imide rings providing exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, ideal for sterilization processes in medical devices. Polysulfone contains sulfone groups within a polymer backbone that ensures high toughness, hydrolytic stability, and clarity, supporting long-term biocompatibility. While polyimide excels in electrical insulation and high-temperature endurance, polysulfone offers superior mechanical strength and transparency for implantable and diagnostic applications.
Biocompatibility and Safety Considerations
Polyimide and polysulfone are both high-performance polymers used in medical devices, with biocompatibility playing a crucial role in their selection. Polyimide offers excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength but may require surface treatments to enhance biocompatibility and reduce cytotoxicity. Polysulfone exhibits superior biocompatibility and chemical resistance, making it more suitable for blood-contacting applications while maintaining safety through sterilization resilience and low leachables.
Sterilization Resistance: Polyimide vs Polysulfone
Polyimide demonstrates superior sterilization resistance compared to polysulfone, maintaining mechanical integrity and chemical stability under repeated steam autoclaving and gamma irradiation processes commonly used in medical device sterilization. Polysulfone, while offering good thermal and chemical resistance, tends to experience degradation and loss of mechanical strength after multiple sterilization cycles. The high glass transition temperature and aromatic imide groups in polyimide contribute to its exceptional durability in harsh sterilization environments, making it preferable for critical medical device components.
Thermal and Mechanical Performance in Medical Applications
Polyimide exhibits superior thermal stability with a high continuous use temperature up to 400degC, making it ideal for sterilization processes in medical devices, while polysulfone offers reliable performance up to 150degC with excellent hydrolytic stability. Polyimide demonstrates exceptional mechanical strength and flexibility, critical for implantable devices requiring durability under cyclic loading, whereas polysulfone provides excellent toughness and dimensional stability for non-implantable components exposed to moist environments. The choice between polyimide and polysulfone depends on specific medical application demands for heat resistance and mechanical resilience during device lifespan.
Flexibility and Durability in Medical Device Design
Polyimide exhibits exceptional flexibility and thermal stability, making it ideal for intricate medical device components that require repeated bending and sterilization cycles. Polysulfone offers superior durability and chemical resistance, ensuring long-term performance in harsh environments and compatibility with various sterilization methods. Balancing polyimide's flexibility and polysulfone's toughness is critical for optimizing medical device designs targeting both patient comfort and device longevity.
Transparency and Optical Properties for Medical Use
Polyimide exhibits limited transparency in the visible spectrum, making it less suitable for applications requiring clear visual inspection within medical devices, whereas polysulfone offers excellent optical clarity and high transparency, essential for diagnostic components and light-guiding elements. Polysulfone's superior UV resistance and minimal coloration ensure consistent optical performance, critical for devices like endoscopes and catheters that rely on precise light transmission. In medical use, polysulfone's combination of mechanical strength and optical properties outweighs polyimide's durability advantages when transparency is a primary requirement.
Processing and Manufacturability Differences
Polyimide offers excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, allowing for high-temperature sterilization processes critical in medical device manufacturing; however, its processing requires precise control due to its high melting point and solvent solubility challenges. Polysulfone provides easier melt processing with lower processing temperatures, enabling faster cycle times and cost-effective manufacturability, but it has comparatively lower thermal resistance and chemical stability than polyimide. These differences influence device design and production scalability, with polyimide preferred for high-performance, heat-resistant components and polysulfone favored for ease of molding and cost efficiency in less demanding applications.
Cost-Effectiveness and Supply Chain Factors
Polyimide and polysulfone exhibit distinct cost-effectiveness and supply chain characteristics critical for medical device manufacturing. Polyimide offers superior thermal and chemical resistance, often commanding higher material costs but providing long-term durability that reduces replacement frequency and maintenance expenses. Polysulfone typically presents lower upfront costs with more stable supply chains due to widespread production, making it a cost-effective option for high-volume medical devices requiring moderate performance standards.
Polyimide vs Polysulfone: Application Suitability and Final Considerations
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-performance medical devices requiring sterilization and harsh chemical exposure, whereas polysulfone provides excellent toughness and dimensional stability suited for long-term implantable devices. Polyimide's flexibility and biocompatibility enable minimally invasive catheter tubing, while polysulfone's transparency and resistance to hydrolysis favor applications like blood oxygenators and dialysis components. Final selection depends on device-specific requirements including mechanical strength, sterilization methods, and environmental exposure, ensuring optimal performance and patient safety.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Polysulfone for Medical Device
 azmater.com
azmater.com