Polypropylene offers lightweight, moisture-wicking, and high durability benefits ideal for activewear, while Polytrimethylene Terephthalate (PTT) provides superior elasticity, softness, and wrinkle resistance, enhancing comfort and resilience in textile fibers. Choosing between Polypropylene and PTT depends on specific performance needs like breathability or stretchability in fabric applications.
Table of Comparison
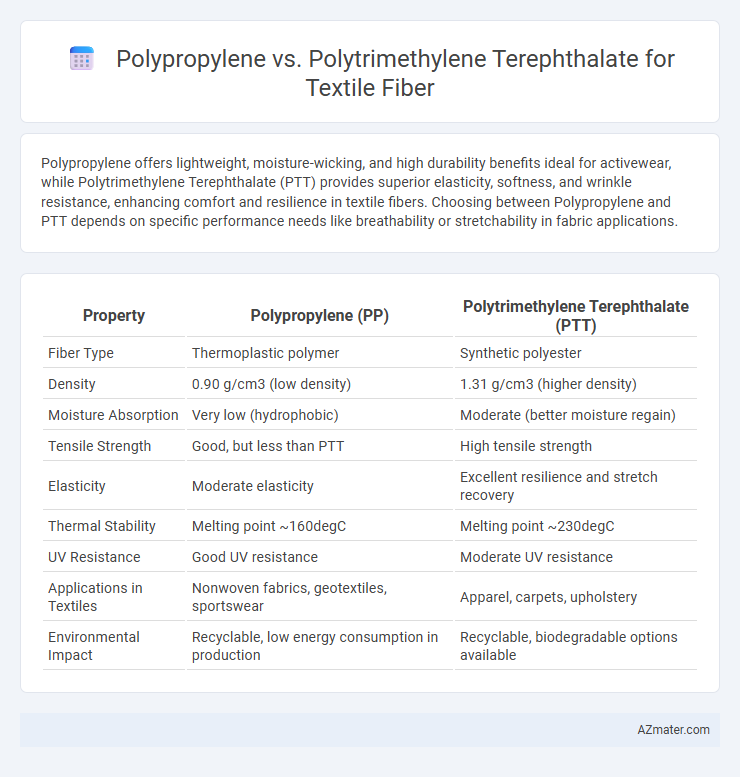
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Polytrimethylene Terephthalate (PTT) |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Synthetic polyester |
| Density | 0.90 g/cm3 (low density) | 1.31 g/cm3 (higher density) |
| Moisture Absorption | Very low (hydrophobic) | Moderate (better moisture regain) |
| Tensile Strength | Good, but less than PTT | High tensile strength |
| Elasticity | Moderate elasticity | Excellent resilience and stretch recovery |
| Thermal Stability | Melting point ~160degC | Melting point ~230degC |
| UV Resistance | Good UV resistance | Moderate UV resistance |
| Applications in Textiles | Nonwoven fabrics, geotextiles, sportswear | Apparel, carpets, upholstery |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, low energy consumption in production | Recyclable, biodegradable options available |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Polytrimethylene Terephthalate
Polypropylene is a lightweight, thermoplastic polymer widely used in textile fibers due to its excellent chemical resistance, moisture-wicking properties, and high tensile strength. Polytrimethylene terephthalate (PTT) is a polyester fiber characterized by its superior elasticity, resilience, and soft hand feel, making it highly suitable for apparel and carpet applications. Both polymers offer distinct advantages in textile manufacturing, with polypropylene excelling in durability and stain resistance, while PTT provides enhanced comfort and stretchability.
Molecular Structure and Chemical Composition
Polypropylene (PP) is a polyolefin composed of repeating propylene monomers with a simple hydrocarbon chain, featuring methyl groups attached to a carbon backbone, which results in hydrophobic properties and high chemical resistance. Polytrimethylene terephthalate (PTT) is a semi-aromatic polyester synthesized from 1,3-propanediol and terephthalic acid, characterized by ester linkages and aromatic rings that provide elasticity, resilience, and enhanced dyeability. The molecular structure of PP contributes to its lightweight and moisture-wicking abilities, while PTT's chemical composition imparts superior softness, durability, and stain resistance in textile applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polypropylene fibers exhibit high tensile strength and excellent elasticity, making them suitable for applications requiring durability and flexibility, while Polytrimethylene Terephthalate (PTT) fibers demonstrate superior abrasion resistance and resilience, offering enhanced recovery and softness ideal for wearable textiles. PTT fibers typically provide better dimensional stability and resistance to wrinkling compared to polypropylene, contributing to prolonged fabric lifespan under mechanical stress. The choice between polypropylene and PTT fibers depends on the specific mechanical performance requirements such as tensile modulus, elongation at break, and fatigue resistance in textile manufacturing.
Moisture Absorption and Wicking Performance
Polytrimethylene terephthalate (PTT) exhibits superior moisture absorption and wicking performance compared to polypropylene (PP), enhancing wearer comfort by efficiently managing sweat and humidity. PTT fibers absorb up to 3-4% moisture, promoting quick-drying properties, whereas polypropylene's hydrophobic nature results in moisture absorption below 0.01%, leading to limited sweat management. These differences make PTT a preferred choice for performance textiles requiring enhanced hydration control and breathability.
Dyeability and Color Fastness
Polytrimethylene terephthalate (PTT) exhibits superior dyeability compared to polypropylene (PP) due to its polar molecular structure, which allows better interaction with hydrophilic dyes and vibrant color uptake. Polypropylene's hydrophobic nature limits its dye affinity, requiring specialized dyeing techniques such as solution or mass dyeing to achieve acceptable color intensity and uniformity. In terms of color fastness, PTT fibers demonstrate enhanced resistance to washing, light, and abrasion, maintaining color integrity longer than polypropylene, which is prone to color fading and diminished fastness under similar conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polypropylene (PP) fibers feature low energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions during production but face challenges in biodegradability and microplastic pollution. Polytrimethylene Terephthalate (PTT) fibers offer improved biodegradability and recyclability, with a lower carbon footprint due to bio-based feedstocks derived from renewable resources such as corn glucose. PTT's enhanced durability and slower degradation rate contribute to longer garment lifespans, reducing overall environmental impact compared to conventional polypropylene fibers.
Cost Considerations and Market Availability
Polypropylene offers a low-cost advantage in textile fiber production due to its inexpensive raw materials and energy-efficient manufacturing process, making it highly accessible in global markets. Polytrimethylene terephthalate (PTT) fibers, derived from renewable sources like corn sugar, incur higher production costs but provide superior elasticity and softness, appealing to premium apparel segments. Market availability of polypropylene is widespread, supported by established supply chains and high-volume production, whereas PTT remains more niche with limited commercial-scale suppliers, influencing its price and accessibility in textile applications.
Typical Textile Applications
Polypropylene fibers are widely used in activewear, geotextiles, and upholstery due to their lightweight, moisture-wicking, and chemical resistance properties. Polytrimethylene terephthalate (PTT) excels in carpet fibers, apparel, and home textiles, offering superior elasticity, resilience, and softness compared to conventional polyester. The choice between polypropylene and PTT fibers depends on the specific performance requirements, with polypropylene favored for durability and cost-effectiveness, while PTT provides enhanced comfort and aesthetic appeal.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Polypropylene offers excellent durability and wear resistance due to its high tensile strength and chemical inertness, making it ideal for textile fibers exposed to abrasive conditions. Polytrimethylene terephthalate (PTT) provides superior elasticity and resilience, enhancing fabric recovery and long-term wear performance under repeated stress. While polypropylene excels in moisture resistance and abrasion durability, PTT outperforms in stretch retention and resistance to pilling, balancing durability with comfort in textile applications.
Future Trends in Textile Fiber Innovations
Polypropylene is gaining traction for sustainable textile fiber use due to its lightweight, moisture-wicking properties, and recyclability, whereas Polytrimethylene Terephthalate (PTT) is favored for its softness, durability, and elasticity, making it ideal for high-performance apparel. Emerging trends highlight bio-based PTT derived from renewable resources, addressing environmental concerns, while advanced polypropylene fibers incorporate nanotechnology for enhanced strength and thermal regulation. Future innovations will likely blend these materials or develop hybrid fibers, maximizing the benefits of both polymers to meet growing demands for eco-friendly, high-performance textiles.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Polytrimethylene Terephthalate for Textile Fiber
 azmater.com
azmater.com