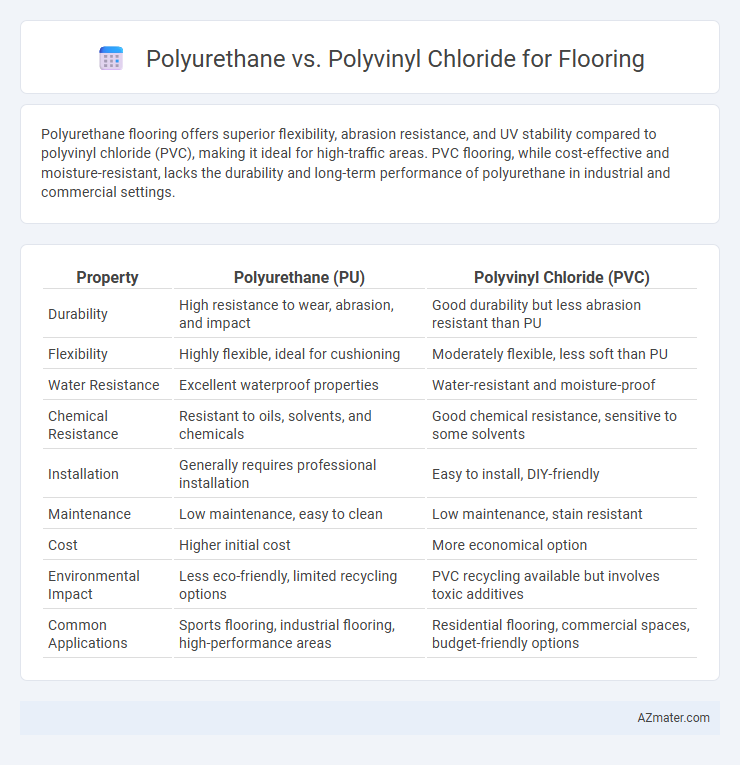
Polyurethane flooring offers superior flexibility, abrasion resistance, and UV stability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for high-traffic areas. PVC flooring, while cost-effective and moisture-resistant, lacks the durability and long-term performance of polyurethane in industrial and commercial settings.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane (PU) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to wear, abrasion, and impact | Good durability but less abrasion resistant than PU |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, ideal for cushioning | Moderately flexible, less soft than PU |
| Water Resistance | Excellent waterproof properties | Water-resistant and moisture-proof |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils, solvents, and chemicals | Good chemical resistance, sensitive to some solvents |
| Installation | Generally requires professional installation | Easy to install, DIY-friendly |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to clean | Low maintenance, stain resistant |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | More economical option |
| Environmental Impact | Less eco-friendly, limited recycling options | PVC recycling available but involves toxic additives |
| Common Applications | Sports flooring, industrial flooring, high-performance areas | Residential flooring, commercial spaces, budget-friendly options |
Introduction to Polyurethane and Polyvinyl Chloride Flooring
Polyurethane flooring offers exceptional durability, flexibility, and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for high-traffic commercial and industrial spaces. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) flooring, known for its water resistance and cost-effectiveness, provides versatility in design with various patterns and textures suitable for residential and commercial use. Both materials deliver distinct benefits: polyurethane excels in longevity and impact absorption, while PVC flooring stands out for maintenance ease and versatility in moisture-prone environments.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Polyurethane flooring is composed of organic polymers derived from isocyanates and polyols, synthesized through a controlled chemical reaction that produces a durable, flexible material resistant to abrasion and chemicals. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) flooring consists of a synthetic plastic polymer made from vinyl chloride monomers polymerized via suspension or emulsion processes, resulting in a rigid or flexible material depending on the plasticizers used. Manufacturing polyurethane involves precise mixing and curing stages to create various forms such as coatings or foams, while PVC production relies on polymerization followed by compounding with additives and extrusion or calendering to form flooring sheets or tiles.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Polyurethane flooring provides superior durability and wear resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for high-traffic areas and industrial environments. Its chemical composition allows polyurethane to resist abrasion, impacts, and staining while maintaining flexibility and preventing cracking over time. PVC floors, although cost-effective and moisture-resistant, are generally less durable and more prone to surface wear and discoloration under heavy use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane flooring offers superior environmental benefits due to its lower toxicity and higher recyclability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which releases harmful dioxins during production and disposal. Polyurethane's biodegradability and reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions contribute to better indoor air quality and reduced ecological footprint, aligning with sustainable building practices. The durability and longer lifespan of polyurethane flooring minimize waste generation, making it a more sustainable choice over PVC, which often requires replacement and contributes to landfill accumulation.
Water and Chemical Resistance
Polyurethane flooring offers superior water and chemical resistance due to its dense polymer structure, making it ideal for environments prone to moisture and harsh chemicals. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) flooring provides moderate water resistance but is less durable against strong chemicals, resulting in potential surface degradation over time. In industrial and commercial settings, polyurethane's enhanced resistance ensures longer-lasting performance and reduced maintenance compared to PVC alternatives.
Comfort and Acoustic Performance
Polyurethane flooring offers superior comfort due to its flexible and shock-absorbing properties, reducing foot fatigue and impact noise effectively. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) flooring, while durable and water-resistant, tends to be stiffer and transmits sound more readily, resulting in lower acoustic performance. Choosing polyurethane enhances both ergonomic comfort and sound dampening in residential and commercial environments.
Installation Methods and Flexibility
Polyurethane flooring offers seamless installation through liquid application methods that cure to form a durable, flexible surface ideal for high-traffic areas. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) flooring typically comes in tiles or sheets, requiring adhesive or click-lock installation, which may be less flexible but allows for easier replacement of damaged sections. Polyurethane's inherent elasticity provides superior flexibility and resistance to cracking compared to the stiffer, more rigid PVC flooring options.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Polyurethane flooring offers superior durability and resistance to stains, making its maintenance and cleaning requirements relatively low compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC). PVC flooring, while cost-effective and water-resistant, tends to accumulate dirt and requires more frequent cleaning with mild detergents to prevent surface degradation. Both materials benefit from regular sweeping and damp mopping, but polyurethane's enhanced scratch and chemical resistance extend the intervals between deep cleanings and refinishing.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Polyurethane flooring typically costs between $5 to $12 per square foot, offering durability and resistance to abrasion, making it a cost-effective option for long-term investment. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) flooring, priced around $2 to $7 per square foot, provides a budget-friendly solution with good water resistance but may require more frequent replacement due to lower durability. Budget considerations should weigh initial installation costs against lifespan and maintenance expenses to determine the most economical choice for specific flooring needs.
Best Applications: Where to Use Polyurethane vs PVC Flooring
Polyurethane flooring excels in high-traffic commercial and industrial spaces due to its exceptional durability, chemical resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for warehouses, garages, and hospitals. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) flooring is best suited for residential and light commercial areas, offering water resistance, easy maintenance, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in kitchens, bathrooms, and retail stores. Choosing between polyurethane and PVC floors depends on the environment's exposure to wear, moisture, and chemicals, tailoring the solution for optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Polyvinyl chloride for Flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com