Polyphenylene oxide offers superior thermal resistance and chemical stability compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for durable, high-performance water bottles. Polyethylene provides excellent flexibility and impact resistance at a lower cost but has limited heat tolerance and chemical durability.
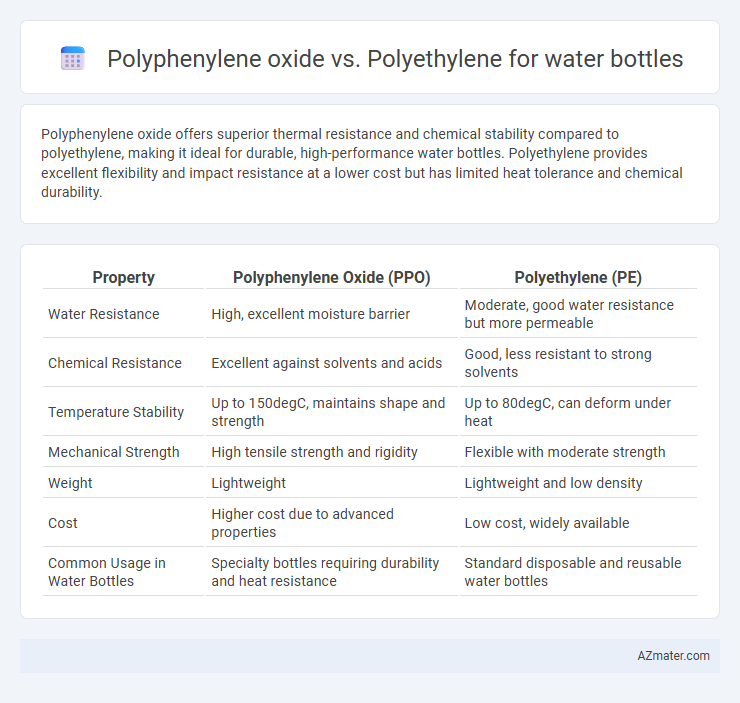
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Water Resistance | High, excellent moisture barrier | Moderate, good water resistance but more permeable |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against solvents and acids | Good, less resistant to strong solvents |
| Temperature Stability | Up to 150degC, maintains shape and strength | Up to 80degC, can deform under heat |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and rigidity | Flexible with moderate strength |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight and low density |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Low cost, widely available |
| Common Usage in Water Bottles | Specialty bottles requiring durability and heat resistance | Standard disposable and reusable water bottles |
Introduction to Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) and Polyethylene (PE)
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and thermal endurance, making it suitable for durable water bottles. Polyethylene (PE), particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE), is widely used in water bottles due to its flexibility, impact resistance, and cost-effectiveness. While PPO offers superior mechanical properties and heat resistance, PE remains popular for its ease of processing and recyclability in beverage containers.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) features an aromatic polymer backbone with repeating phenylene oxide units, providing high thermal stability and chemical resistance crucial for water bottle durability. Polyethylene (PE), composed of long chains of ethylene monomers with a simple hydrocarbon structure, offers flexibility and chemical inertness but lower heat resistance. The rigid, aromatic rings in PPO create enhanced barrier properties against oxygen and moisture compared to the more permeable aliphatic chains of polyethylene.
Key Physical and Mechanical Properties
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and higher impact resistance compared to polyethylene (PE), making it ideal for water bottles requiring durability under heat. PPO exhibits a higher glass transition temperature, around 210degC, versus PE's typical range of -125degC to -80degC, which contributes to better structural integrity in varying temperatures. While polyethylene presents excellent flexibility and chemical resistance, PPO's enhanced rigidity and dimensional stability ensure better long-term performance in reusable water bottles.
Thermal Stability and Temperature Resistance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior thermal stability and temperature resistance compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for water bottles exposed to higher temperatures. PPO maintains structural integrity and resists deformation at temperatures up to 200degC, while polyethylene typically softens around 80-90degC. This enhanced thermal performance of PPO ensures safer use in hot environments and extends the durability of water bottles under thermal stress.
Taste and Odor Neutrality in Water Bottles
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior taste and odor neutrality compared to polyethylene, making it an ideal choice for water bottles aimed at preserving the natural flavor of beverages. PPO's inherent chemical stability prevents leaching of contaminants, ensuring water taste remains unaltered over time, whereas polyethylene can sometimes impart slight plastic odors. Manufacturers prefer PPO for premium water bottles where maintaining pure taste and odor-free storage is critical for consumer satisfaction.
Safety and BPA Concerns
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers enhanced safety for water bottles due to its BPA-free composition and high chemical resistance, reducing the risk of harmful leachates. Polyethylene, also BPA-free, provides excellent durability and low permeability but may have a lower heat tolerance compared to PPO, which can affect long-term safety under high temperatures. Both materials are widely regarded as safe alternatives to BPA-containing plastics, with PPO providing superior structural stability and chemical resistance for extended safe use.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers improved thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polyethylene (PE), reducing leaching and extending water bottle lifespan, which decreases environmental waste. While polyethylene is widely recycled through established systems like HDPE and LDPE streams, PPO recycling is less common due to limited infrastructure despite its potential for chemical recycling. The lower carbon footprint of polyethylene production contrasts with PPO's higher energy-intensive manufacturing, but PPO's durability can offset this by reducing the frequency of bottle replacement.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polyethylene (PE), but it comes at a higher material cost, making PE more budget-friendly for large-scale water bottle production. Manufacturing PPO requires more complex processing parameters such as higher molding temperatures and specialized equipment, while PE benefits from established, cost-effective extrusion and injection molding techniques. The choice between PPO and PE depends on balancing performance needs against manufacturing expenses and production volume constraints.
Durability and Lifespan in Real-World Use
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior durability compared to polyethylene, exhibiting enhanced resistance to heat, chemical degradation, and mechanical stress in water bottle applications. PPO maintains structural integrity over extended periods, resulting in a longer lifespan especially in environments involving repeated washing or exposure to varying temperatures. Polyethylene, while cost-effective and flexible, generally shows quicker wear and potential deformation, limiting its long-term usability for water bottles.
Which Material is Better for Water Bottles?
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polyethylene, making it more durable for reusable water bottles exposed to heat and various liquids. Polyethylene, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE), is lightweight, cost-effective, and widely used for single-use and some reusable bottles due to its excellent impact resistance and flexibility. For longevity and performance under varied conditions, PPO is generally the better choice, while polyethylene remains popular for affordability and ease of manufacturing.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polyethylene for Water Bottle
 azmater.com
azmater.com