Polycarbonate eyeglass lenses offer superior impact resistance and lightweight comfort compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which is less durable and heavier. Polycarbonate also provides better UV protection and clarity, making it the preferred choice for eyeglass lenses.
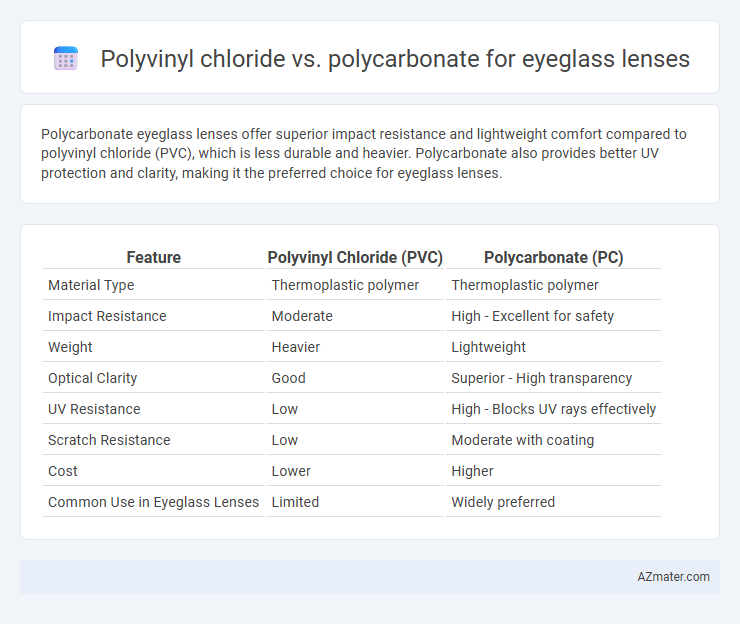
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High - Excellent for safety |
| Weight | Heavier | Lightweight |
| Optical Clarity | Good | Superior - High transparency |
| UV Resistance | Low | High - Blocks UV rays effectively |
| Scratch Resistance | Low | Moderate with coating |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Use in Eyeglass Lenses | Limited | Widely preferred |
Introduction to Eyeglass Lens Materials
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polycarbonate are both used in eyeglass lenses, with polycarbonate being favored for its superior impact resistance and lightweight properties. PVC lenses are less common due to their heavier weight and lower optical clarity compared to polycarbonate, which offers higher shatter resistance and UV protection. Polycarbonate lenses also provide enhanced durability and flexibility, making them a popular choice for safety and everyday eyewear.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Lenses
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) lenses provide a cost-effective and chemically resistant option for eyeglasses, known for their durability and lightweight characteristics. These lenses offer moderate impact resistance and good optical clarity, making them suitable for everyday wear but less ideal for high-impact activities compared to polycarbonate. PVC's inherent rigidity ensures shape retention, although its lower scratch resistance often necessitates additional coatings to enhance lens longevity.
Overview of Polycarbonate Lenses
Polycarbonate lenses are a popular choice for eyeglass lenses due to their high impact resistance and lightweight properties, making them ideal for active lifestyles and children's eyewear. They offer excellent UV protection and superior optical clarity compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) lenses, which are heavier and less durable. Polycarbonate lenses also provide better scratch resistance and can be easily coated with anti-reflective layers, enhancing overall visual comfort.
Optical Clarity Comparison: PVC vs Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate lenses offer superior optical clarity compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) lenses due to their higher light transmittance and reduced chromatic aberration. While PVC lenses tend to suffer from lower transparency and potential yellowing over time, polycarbonate maintains consistent clarity and color accuracy. The refractive index of polycarbonate (approximately 1.58) enhances sharpness and visual performance, making it the preferred material for high-quality eyeglass lenses.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) lenses are less impact-resistant and prone to cracking under stress, making them less durable for eyewear compared to polycarbonate lenses. Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance due to its high toughness and ability to absorb shocks, making it ideal for safety and sports glasses. Durability of polycarbonate also surpasses PVC as it resists shattering and provides longer-lasting optical performance.
Weight and Comfort Considerations
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) lenses are generally heavier than polycarbonate lenses, impacting overall comfort during prolonged wear. Polycarbonate lenses offer exceptional lightweight properties, making them ideal for users seeking reduced pressure on the nose and ears. The superior impact resistance and flexibility of polycarbonate also enhance comfort by minimizing lens breakage and improving fit stability.
UV Protection and Safety Features
Polycarbonate lenses offer superior UV protection by blocking 100% of harmful UVA and UVB rays, making them highly effective for eye safety. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) lenses generally provide lower UV protection, which may expose eyes to greater risk of damage over time. In terms of safety, polycarbonate is impact-resistant and shatterproof, meeting stringent safety standards ideal for active lifestyles, whereas PVC lenses are more brittle and prone to cracking.
Cost and Affordability Analysis
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) eyeglass lenses offer a lower-cost alternative compared to polycarbonate lenses, making them more affordable for budget-conscious consumers. Polycarbonate lenses, although pricier due to their superior impact resistance and optical clarity, provide enhanced durability and lightweight comfort, justifying the higher investment. Cost analysis indicates PVC lenses are suitable for basic eyewear needs, while polycarbonate lenses represent a long-term value with added protective benefits.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polycarbonate differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability for eyeglass lenses. PVC production involves toxic chemicals and generates hazardous waste, complicating recycling and disposal. Polycarbonate, while derived from petroleum, is more durable and recyclable, reducing long-term environmental footprint through extended lens lifespan and efficient recycling processes.
Which Lens Material is Right for You?
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) lenses offer affordability and good chemical resistance but tend to be heavier and less impact-resistant compared to polycarbonate lenses. Polycarbonate lenses excel in impact resistance, lightweight comfort, and UV protection, making them ideal for active lifestyles and safety eyewear. For those prioritizing durability and eye protection, polycarbonate is often the preferred material, while PVC may suit budget-conscious consumers seeking basic vision correction.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride vs Polycarbonate for Eyeglass Lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com