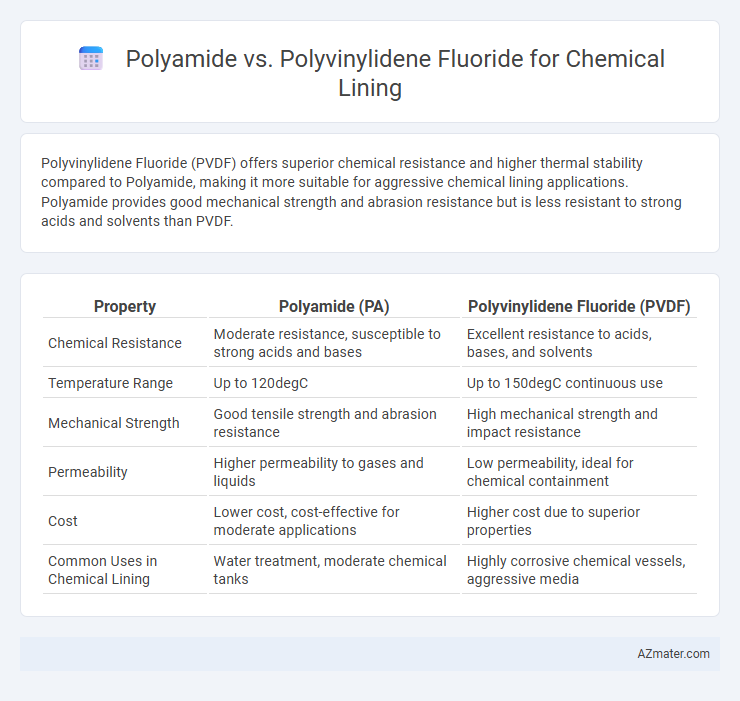
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and higher thermal stability compared to Polyamide, making it more suitable for aggressive chemical lining applications. Polyamide provides good mechanical strength and abrasion resistance but is less resistant to strong acids and solvents than PVDF.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyamide (PA) | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance, susceptible to strong acids and bases | Excellent resistance to acids, bases, and solvents |
| Temperature Range | Up to 120degC | Up to 150degC continuous use |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength and abrasion resistance | High mechanical strength and impact resistance |
| Permeability | Higher permeability to gases and liquids | Low permeability, ideal for chemical containment |
| Cost | Lower cost, cost-effective for moderate applications | Higher cost due to superior properties |
| Common Uses in Chemical Lining | Water treatment, moderate chemical tanks | Highly corrosive chemical vessels, aggressive media |
Introduction to Chemical Lining Materials
Polyamide and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) are prominent chemical lining materials known for their exceptional resistance to corrosion and chemical degradation. Polyamide offers strong mechanical properties and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for dynamic environments, while PVDF provides superior chemical stability, UV resistance, and low permeability, ideal for aggressive chemical processing. Selection between polyamide and PVDF depends on factors like chemical compatibility, temperature tolerance, and mechanical stress requirements in industrial applications.
Overview of Polyamide Properties
Polyamide exhibits excellent mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and flexibility, making it suitable for chemical lining applications that demand durability and impact resistance. Its inherent resistance to oils, fuels, and many solvents ensures long-term stability in aggressive environments. Compared to Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF), polyamide generally offers superior abrasion resistance but lower UV and high-temperature tolerance.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Properties
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) exhibits exceptional chemical resistance, making it ideal for lining applications in aggressive chemical environments such as acids, bases, and solvents. Its high thermal stability allows operation up to 150degC, outperforming polyamide in temperature tolerance and dimensional stability. PVDF offers superior UV resistance and low permeability, ensuring long-lasting protection against corrosive fluids in industrial chemical processing.
Chemical Resistance: Polyamide vs PVDF
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polyamide, making it ideal for harsh chemical lining applications involving strong acids, bases, and solvents. PVDF maintains structural integrity and resists degradation in environments with high temperatures and aggressive chemicals, while polyamide is more susceptible to hydrolysis and chemical attack under similar conditions. For chemical lining requiring durability against a broad spectrum of corrosive substances, PVDF is the preferred choice over polyamide.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyamide exhibits superior mechanical strength with high tensile and impact resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring robust chemical linings under physical stress. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers exceptional chemical resistance and durability against corrosion but generally has lower impact strength compared to polyamide. PVDF's excellent resistance to UV and weathering enhances its longevity in harsh environments, balancing mechanical performance with chemical durability.
Temperature Tolerance in Harsh Environments
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior temperature tolerance compared to Polyamide, maintaining chemical integrity in harsh environments up to 150degC, whereas Polyamide typically withstands temperatures up to 120degC. PVDF's enhanced resistance to thermal degradation and chemical corrosion makes it ideal for high-temperature chemical lining applications in aggressive media. Its stability under thermal stress ensures prolonged service life and reduced maintenance costs in industrial settings demanding reliable chemical protection.
Installation and Fabrication Differences
Polyamide offers greater flexibility during installation, allowing for easier molding and shaping around complex structures, whereas Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) requires more precise welding and specialized fabrication techniques due to its rigid nature. PVDF's higher chemical resistance and thermal stability necessitate careful temperature control during fabrication to prevent degradation, unlike polyamide, which can tolerate a wider range of fabrication conditions. The welding process for PVDF involves hot gas or extrusion welding, demanding skilled technicians, while polyamide installation often benefits from simpler adhesive bonding or thermal methods, speeding up on-site application.
Cost Analysis: Polyamide vs PVDF Linings
Polyamide linings generally offer a lower initial material cost compared to PVDF linings, making them attractive for budget-sensitive applications. However, PVDF linings provide superior chemical resistance and longer service life, which can reduce maintenance and replacement expenses over time. When evaluating total cost of ownership, PVDF linings often prove more cost-effective in aggressive chemical environments despite the higher upfront investment.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
Polyamide offers excellent abrasion resistance and mechanical strength, making it suitable for industrial water treatment and chemical processing plants where durability against mechanical wear is crucial. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, favored in aggressive chemical storage tanks and semiconductor manufacturing where exposure to corrosive acids and solvents is common. Studies in the oil and gas industry reveal polyamide linings improve pipeline longevity under abrasive conditions, while PVDF linings significantly reduce maintenance costs and downtime in high-purity chemical environments.
Selecting the Right Lining: Key Considerations
Polyamide offers excellent abrasion resistance and chemical stability for chemical linings, making it ideal for environments with high mechanical wear and moderate chemical exposure. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) provides superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, suitable for aggressive acids and solvents at elevated temperatures. Selecting the right lining requires evaluating factors such as chemical compatibility, temperature range, mechanical stress, and cost-effectiveness to ensure optimal performance and longevity in industrial applications.
Infographic: Polyamide vs Polyvinylidene Fluoride for Chemical Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com