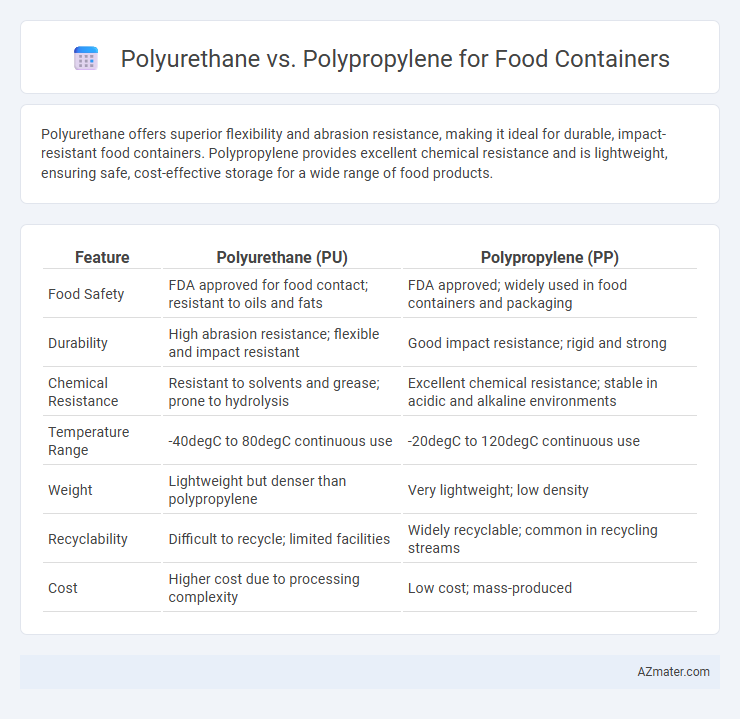
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for durable, impact-resistant food containers. Polypropylene provides excellent chemical resistance and is lightweight, ensuring safe, cost-effective storage for a wide range of food products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyurethane (PU) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Food Safety | FDA approved for food contact; resistant to oils and fats | FDA approved; widely used in food containers and packaging |
| Durability | High abrasion resistance; flexible and impact resistant | Good impact resistance; rigid and strong |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to solvents and grease; prone to hydrolysis | Excellent chemical resistance; stable in acidic and alkaline environments |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 80degC continuous use | -20degC to 120degC continuous use |
| Weight | Lightweight but denser than polypropylene | Very lightweight; low density |
| Recyclability | Difficult to recycle; limited facilities | Widely recyclable; common in recycling streams |
| Cost | Higher cost due to processing complexity | Low cost; mass-produced |
Introduction to Polyurethane and Polypropylene in Food Packaging
Polyurethane offers excellent flexibility and durability, making it ideal for food containers that require impact resistance and airtight seals. Polypropylene is widely used in food packaging due to its chemical resistance, lightweight nature, and ability to withstand high temperatures during sterilization processes. Both polymers meet food safety standards, but polypropylene is more commonly chosen for disposable containers, while polyurethane suits reusable and heavy-duty food storage solutions.
Material Composition: Polyurethane vs Polypropylene
Polyurethane, composed of organic polymers with urethane linkages, offers excellent flexibility and thermal resistance, making it suitable for durable food containers. Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer made from propylene monomers, known for its high chemical resistance, low density, and food-safe properties. Material composition impacts performance, with polyurethane providing superior elasticity and polypropylene favored for lightweight, rigid containers.
Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Polyurethane and polypropylene differ significantly in food safety and regulatory compliance, with polypropylene being widely approved by agencies like the FDA and EFSA for direct food contact due to its non-toxic, BPA-free properties. Polyurethane, while offering excellent durability and flexibility, often contains additives or curing agents that may not be fully approved for food contact, limiting its use in food container applications. Manufacturers prioritize polypropylene for food containers to meet stringent safety standards, ensuring no harmful chemical migration into food products.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Polyurethane food containers offer superior durability due to their high resistance to abrasion, impact, and chemical degradation, making them ideal for heavy-duty food storage applications. Polypropylene containers exhibit excellent lifespan with strong resistance to heat, moisture, and repeated sterilization, but they are more prone to cracking under extreme stress or prolonged exposure to UV light. When comparing durability and lifespan, polyurethane containers generally outperform polypropylene in toughness and longevity, especially in industrial or high-wear environments.
Temperature Resistance and Performance
Polypropylene offers excellent temperature resistance, withstanding temperatures from -20degC to 120degC, making it ideal for both refrigeration and microwave use in food containers. Polyurethane, while providing superior flexibility and impact resistance, generally has a narrower temperature range, typically between -40degC and 80degC, which limits its performance under high-heat conditions. Polypropylene's chemical resistance and durability ensure safer food storage and reheating, whereas polyurethane containers excel in cushioning but may degrade or deform under prolonged heat exposure.
Chemical Resistance in Food Storage Applications
Polypropylene exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polyurethane in food storage applications, effectively withstanding acids, bases, and fats without degrading or leaching harmful substances. Polyurethane, while offering flexibility and durability, is more prone to chemical breakdown when exposed to certain solvents and oils, making it less ideal for long-term food contact. Food containers made from polypropylene ensure safer storage by maintaining integrity and preventing contamination from reactive food components.
Impact on Food Freshness and Taste
Polyurethane offers superior sealing properties that help maintain food freshness by preventing moisture and air infiltration, which significantly preserves taste and aroma. Polypropylene, while more cost-effective and resistant to chemical leaching, allows slightly more air exchange, potentially impacting long-term food flavor retention. Choosing polyurethane containers ensures enhanced protection for delicate flavors, making them ideal for storing perishable and aromatic foods.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane and polypropylene differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability when used for food containers. Polypropylene is more widely recycled and has a lower carbon footprint during production, making it a preferred choice for eco-friendly packaging. Polyurethane, while versatile and durable, often involves toxic chemicals and is less recyclable, posing greater environmental challenges.
Cost Analysis: Polyurethane vs Polypropylene Food Containers
Polypropylene food containers generally offer a lower cost compared to polyurethane due to their widespread availability and easier manufacturing process. Polyurethane containers tend to be more expensive but provide superior durability and resistance to heat and chemicals, which can result in longer product life. Choosing between polyurethane and polypropylene depends on balancing initial investment with long-term value and specific food storage requirements.
Best Use Cases and Recommendations
Polypropylene offers excellent chemical resistance and durability, making it ideal for microwave-safe and dishwasher-safe food containers, especially for acidic or oily foods. Polyurethane provides superior flexibility and impact resistance, best suited for reusable, airtight containers designed for cold or dry food storage. For prolonged exposure to heat or moisture, polypropylene containers are recommended due to their stability and resistance to leaching.
Infographic: Polyurethane vs Polypropylene for Food Container
 azmater.com
azmater.com