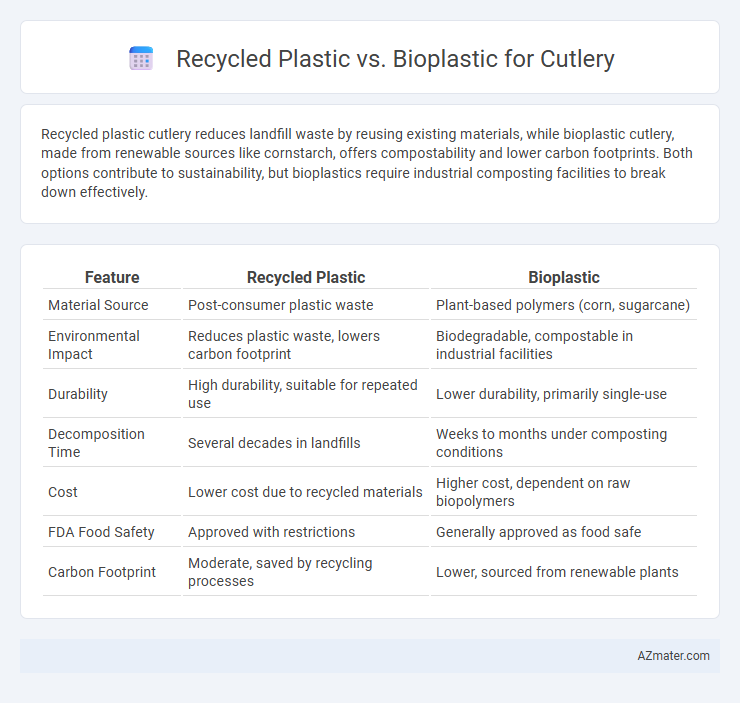
Recycled plastic cutlery reduces landfill waste by reusing existing materials, while bioplastic cutlery, made from renewable sources like cornstarch, offers compostability and lower carbon footprints. Both options contribute to sustainability, but bioplastics require industrial composting facilities to break down effectively.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Plastic | Bioplastic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Post-consumer plastic waste | Plant-based polymers (corn, sugarcane) |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces plastic waste, lowers carbon footprint | Biodegradable, compostable in industrial facilities |
| Durability | High durability, suitable for repeated use | Lower durability, primarily single-use |
| Decomposition Time | Several decades in landfills | Weeks to months under composting conditions |
| Cost | Lower cost due to recycled materials | Higher cost, dependent on raw biopolymers |
| FDA Food Safety | Approved with restrictions | Generally approved as food safe |
| Carbon Footprint | Moderate, saved by recycling processes | Lower, sourced from renewable plants |
Introduction: The Need for Sustainable Cutlery Alternatives
Recycled plastic cutlery utilizes post-consumer waste to reduce landfill accumulation and lower environmental impact by reprocessing existing materials. Bioplastic cutlery, derived from renewable plant-based sources like cornstarch or sugarcane, offers biodegradability and decreased reliance on fossil fuels. Both options address the urgent demand for sustainable cutlery alternatives that minimize plastic pollution and support circular economy principles.
What is Recycled Plastic Cutlery?
Recycled plastic cutlery is made from plastic materials that have been collected, processed, and reformed from post-consumer or post-industrial plastic waste, primarily polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or high-density polyethylene (HDPE). This type of cutlery reduces environmental impact by diverting plastic from landfills and oceans while conserving raw materials and energy compared to producing virgin plastic. Although not biodegradable, recycled plastic cutlery supports circular economy initiatives by promoting reuse of existing plastic resources.
Understanding Bioplastic Cutlery
Bioplastic cutlery is derived from renewable biomass sources such as cornstarch, sugarcane, or potato starch, offering a compostable alternative to traditional plastics. Unlike recycled plastic cutlery, which reuses existing plastic materials, bioplastics break down more rapidly under industrial composting conditions, reducing landfill impact. Consumer preference is shifting toward bioplastic cutlery due to its reduced carbon footprint and alignment with sustainable waste management practices.
Comparing Environmental Impacts
Recycled plastic cutlery reduces landfill waste and conserves resources by reusing existing materials, but still relies on fossil fuel-based polymers. Bioplastic cutlery, derived from renewable biomass such as corn or sugarcane, offers lower carbon emissions during production and biodegrades more easily under industrial composting conditions. However, bioplastics may compete with food crops for land use and require specific composting infrastructures to achieve environmental benefits compared to recycled plastics.
Durability and Performance: Recycled Plastic vs Bioplastic
Recycled plastic cutlery offers high durability and strength, making it suitable for repeated use and resistant to breakage under pressure. Bioplastic cutlery, often derived from cornstarch or PLA, tends to be less robust and can soften or deform when exposed to heat or moisture. For performance demands requiring sturdy, long-lasting utensils, recycled plastic typically outperforms bioplastic alternatives.
Compostability and End-of-Life Scenarios
Recycled plastic cutlery typically cannot be composted and often ends up in landfills or incineration facilities, limiting its environmental benefits. Bioplastic cutlery, made from renewable resources like cornstarch, offers compostability under industrial conditions, breaking down into natural elements within weeks. End-of-life scenarios favor bioplastics for reducing landfill waste and supporting circular economies, though proper composting infrastructure is crucial for effectiveness.
Cost Analysis for Businesses and Consumers
Recycled plastic cutlery offers lower material and production costs, making it a cost-effective choice for businesses aiming to minimize expenses while supporting sustainability goals. Bioplastic cutlery typically incurs higher costs due to raw material sourcing, such as corn starch or sugarcane, and more complex manufacturing processes, which can lead to increased prices for consumers. Businesses must balance the affordability of recycled plastic with the environmental benefits of bioplastics when considering budget constraints and consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
Regulatory and Certification Considerations
Recycled plastic cutlery must comply with regulations such as the FDA's food contact substance requirements and often requires certifications like NSF or FDA approval to ensure safety and hygiene. Bioplastic cutlery is subject to standards like ASTM D6400 or EN 13432, certifying compostability and biodegradability, which are critical for compliance with environmental regulations. Both materials face evolving regulatory landscapes focused on sustainability, mandating transparent labeling and proof of environmental impact reduction.
Consumer Perceptions and Market Trends
Consumer perceptions increasingly favor bioplastic cutlery due to its association with sustainability and biodegradability, despite recycled plastic cutlery offering strong durability and cost-effectiveness. Market trends indicate a growing demand for bioplastic products driven by environmental regulations and eco-conscious consumers, while recycled plastic cutlery maintains relevance in value-oriented segments. Innovations in bioplastic formulations and improved recycling technologies for plastic waste are shaping the competitive landscape in disposable cutlery.
The Future of Eco-Friendly Cutlery Choices
Recycled plastic cutlery reduces waste by repurposing existing materials, lowering the demand for virgin plastic and minimizing landfill impact. Bioplastic cutlery, derived from renewable resources like cornstarch or sugarcane, offers compostability and a smaller carbon footprint but requires specific industrial composting conditions. Future eco-friendly cutlery choices will likely balance durability and environmental impact, integrating advances in material science to optimize performance and sustainability.
Infographic: Recycled plastic vs Bioplastic for Cutlery
 azmater.com
azmater.com