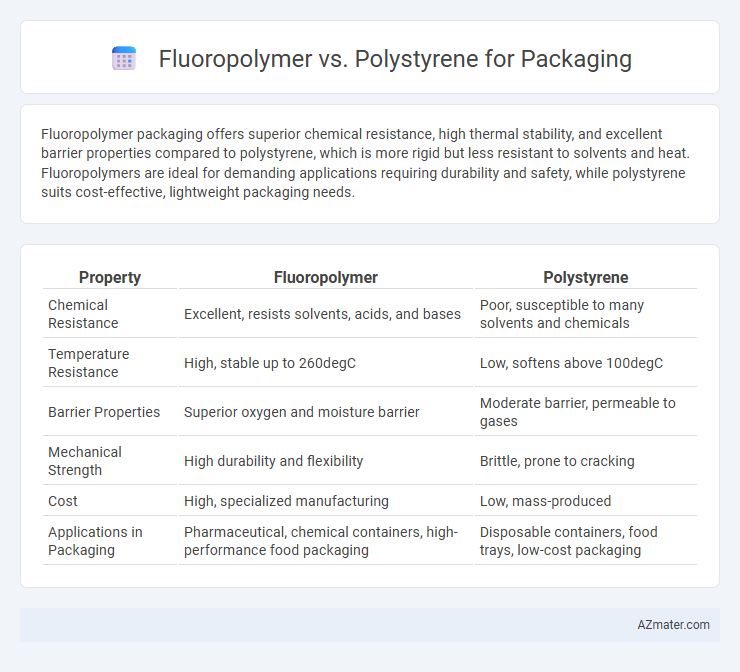
Fluoropolymer packaging offers superior chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and excellent barrier properties compared to polystyrene, which is more rigid but less resistant to solvents and heat. Fluoropolymers are ideal for demanding applications requiring durability and safety, while polystyrene suits cost-effective, lightweight packaging needs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fluoropolymer | Polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resists solvents, acids, and bases | Poor, susceptible to many solvents and chemicals |
| Temperature Resistance | High, stable up to 260degC | Low, softens above 100degC |
| Barrier Properties | Superior oxygen and moisture barrier | Moderate barrier, permeable to gases |
| Mechanical Strength | High durability and flexibility | Brittle, prone to cracking |
| Cost | High, specialized manufacturing | Low, mass-produced |
| Applications in Packaging | Pharmaceutical, chemical containers, high-performance food packaging | Disposable containers, food trays, low-cost packaging |
Introduction to Packaging Materials
Fluoropolymer and polystyrene are widely used materials in packaging, each offering distinct properties for different applications. Fluoropolymers provide exceptional chemical resistance, low surface energy, and durability, making them ideal for packaging sensitive or reactive products. Polystyrene is valued for its rigidity, clarity, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in disposable containers, insulation, and food packaging.
Overview of Fluoropolymers
Fluoropolymers are high-performance polymers known for their exceptional chemical resistance, low friction, and excellent barrier properties, making them ideal for advanced packaging applications. Their molecular structure imparts outstanding thermal stability and non-reactivity, which protects sensitive products from contamination and extends shelf life. These characteristics differentiate fluoropolymers significantly from polystyrene, particularly in environments requiring enhanced durability and chemical inertness.
Overview of Polystyrene
Polystyrene is a versatile thermoplastic polymer widely used in packaging due to its lightweight, rigidity, and clarity. It offers excellent insulation properties and is cost-effective for producing disposable containers, trays, and protective packaging materials. Despite its advantages, polystyrene is less chemically resistant and less flexible compared to fluoropolymers, limiting its use in applications requiring high chemical durability and thermal stability.
Barrier Properties: Fluoropolymer vs Polystyrene
Fluoropolymers exhibit superior barrier properties compared to polystyrene, effectively resisting gases, moisture, and chemicals, which significantly extends the shelf life of packaged goods. Polystyrene's barrier performance is limited, allowing higher permeability to oxygen and water vapor, making it less suitable for sensitive or perishable products. These enhanced barrier properties make fluoropolymers the preferred choice in high-performance packaging applications requiring robust protection against environmental factors.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Fluoropolymers exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to polystyrene, withstanding harsh solvents, acids, and bases without degradation. Polystyrene tends to swell, crack, or dissolve when exposed to organic solvents such as acetone or ethanol, limiting its use in chemically aggressive environments. The high molecular stability and low surface energy of fluoropolymers make them ideal for packaging applications requiring durability against corrosive chemicals.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fluoropolymer packaging offers superior chemical resistance and durability but poses significant environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradability and difficulty in recycling, contributing to persistent plastic pollution. Polystyrene, while easier to recycle and more biodegradable than fluoropolymers, still generates substantial waste and emits toxic chemicals during production and degradation, impacting human health and ecosystems. Sustainable packaging efforts increasingly favor biodegradable materials and improved recycling technologies to mitigate the environmental footprint of both fluoropolymers and polystyrene.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
Fluoropolymer packaging materials typically incur higher upfront costs compared to polystyrene due to their advanced chemical resistance and durability, which may justify investment in specialized applications requiring enhanced barrier properties. Polystyrene remains economically feasible for mass-market packaging because of its low production costs and widespread availability, meeting cost-sensitive demands despite lower chemical resistance and environmental sustainability. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including lifecycle expenses and potential regulatory compliance, is essential for determining the most cost-effective option between fluoropolymers and polystyrene in packaging solutions.
Applications in Packaging Industries
Fluoropolymers offer exceptional chemical resistance, moisture barrier properties, and high thermal stability, making them ideal for packaging aggressive chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and foods requiring extended shelf life. Polystyrene is favored for its rigidity, clarity, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in disposable food containers, trays, and protective packaging for electronics. Fluoropolymers excel in high-performance, specialty packaging applications, whereas polystyrene dominates in standard, everyday packaging solutions.
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
Fluoropolymers in packaging offer superior chemical resistance and comply with stringent FDA and EU food contact regulations, ensuring minimal risk of contaminant migration. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and widely used, faces stricter scrutiny due to potential styrene monomer migration and associated health concerns under REACH and EPA guidelines. Selecting fluoropolymer packaging enhances regulatory compliance and consumer safety in applications requiring high barrier properties and chemical inertness.
Choosing the Right Material for Packaging Needs
Fluoropolymer offers superior chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and excellent barrier properties, making it ideal for packaging sensitive or reactive products such as pharmaceuticals and food items requiring extended shelf life. Polystyrene provides a cost-effective, lightweight option with good rigidity and clarity but lacks the durability and resistance to solvents and gases found in fluoropolymers. Selecting between fluoropolymer and polystyrene depends on the specific packaging requirements, including chemical compatibility, environmental exposure, and budget constraints to ensure product integrity and safety.
Infographic: Fluoropolymer vs Polystyrene for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com