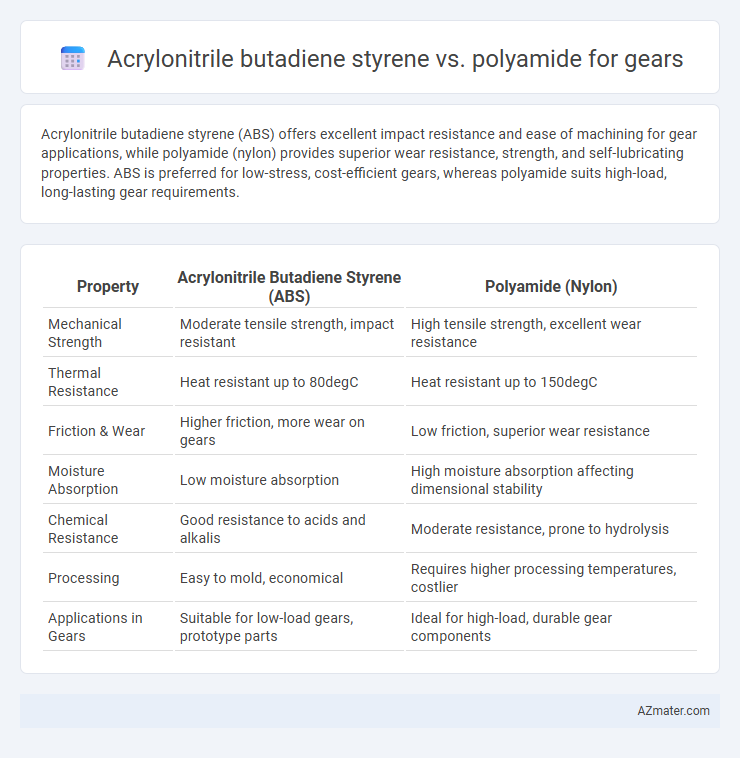
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and ease of machining for gear applications, while polyamide (nylon) provides superior wear resistance, strength, and self-lubricating properties. ABS is preferred for low-stress, cost-efficient gears, whereas polyamide suits high-load, long-lasting gear requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polyamide (Nylon) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength, impact resistant | High tensile strength, excellent wear resistance |
| Thermal Resistance | Heat resistant up to 80degC | Heat resistant up to 150degC |
| Friction & Wear | Higher friction, more wear on gears | Low friction, superior wear resistance |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | High moisture absorption affecting dimensional stability |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Moderate resistance, prone to hydrolysis |
| Processing | Easy to mold, economical | Requires higher processing temperatures, costlier |
| Applications in Gears | Suitable for low-load gears, prototype parts | Ideal for high-load, durable gear components |
Introduction to Gear Material Selection
Gear material selection centers on balancing mechanical strength, wear resistance, and manufacturing feasibility; Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) offers good impact resistance and ease of molding, making it suitable for light-duty gears in consumer applications. Polyamide (nylon) provides superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and self-lubricating properties, ideal for high-stress gear environments with continuous operation. Understanding the specific load, environmental conditions, and required durability guides the choice between ABS and Polyamide for optimal gear performance.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its high impact resistance, toughness, and excellent machinability, making it ideal for manufacturing durable gears. ABS offers superior dimensional stability and resistance to wear and chemical corrosion compared to other plastics, which ensures long-lasting performance in mechanical applications. Its ease of processing through injection molding enhances production efficiency while maintaining consistent mechanical properties suitable for moderate-load gear systems.
Overview of Polyamide (Nylon)
Polyamide (Nylon) exhibits excellent mechanical strength, wear resistance, and low friction properties, making it highly suitable for gear applications requiring durability and reliable performance under dynamic loads. Its inherent resistance to chemicals and moisture absorption enhances gear longevity in various industrial environments. Compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), polyamide offers superior thermal stability and fatigue resistance, ensuring better dimensional stability during operational stress.
Mechanical Strength Comparison: ABS vs Polyamide
Polyamide exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making it more suitable for gears subjected to heavy loads and high stress. Its superior tensile strength, impact resistance, and wear resistance contribute to enhanced durability and longevity in demanding mechanical applications. ABS offers adequate strength for lightweight gears but may suffer deformation and reduced performance under continuous stress.
Wear and Abrasion Resistance in Gear Applications
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate wear and abrasion resistance suitable for low-load gear applications, but its comparatively lower hardness and impact resistance can lead to faster degradation under high stress. Polyamide (PA), especially Nylon 6 and Nylon 66, exhibits superior wear resistance, excellent abrasion properties, and high mechanical strength, making it ideal for gears subjected to continuous friction and load. The intrinsic toughness and self-lubricating nature of polyamide enhance gear durability and reduce maintenance in demanding environments, outperforming ABS in long-term wear performance.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits moderate thermal stability with a heat deflection temperature around 80-100degC, making it suitable for gears operating under low to moderate thermal conditions. Polyamide (PA), commonly known as nylon, offers superior thermal stability and heat resistance, with a glass transition temperature typically between 40-70degC and melting points above 220degC, enabling it to maintain mechanical properties under elevated temperatures. The enhanced thermal resistance of polyamide makes it a preferred choice for gears subjected to high friction and continuous heat exposure.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Suitability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate chemical resistance, particularly effective against acids and alkalis, making it suitable for gears exposed to common industrial chemicals, while polyamide (PA) shows superior resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents, enhancing its durability in harsh chemical environments. In terms of environmental suitability, ABS has better UV and weather resistance, ideal for outdoor gear applications, whereas polyamide's higher moisture absorption can lead to dimensional changes and reduced mechanical performance in humid conditions. Selecting between ABS and polyamide for gears depends on specific chemical exposure and operating environment to optimize gear longevity and functionality.
Noise and Vibration Damping Properties
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate noise and vibration damping properties due to its rubbery butadiene component, making it suitable for gears requiring impact resistance and some noise reduction. Polyamide (PA), particularly nylon variants, exhibits superior vibration absorption and noise dampening capabilities because of its semicrystalline structure and higher inherent damping, enhancing gear performance in high-stress, noisy environments. Selecting polyamide over ABS for gear applications optimizes durability and reduces operational noise and vibration, which is critical in precision machinery and automotive components.
Cost-Effectiveness and Manufacturing Considerations
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior cost-effectiveness for gear production due to its lower material cost and ease of processing through injection molding, resulting in faster cycle times and reduced manufacturing expenses. Polyamide (PA), while more expensive, provides enhanced mechanical strength, wear resistance, and thermal stability, which may justify higher upfront costs in demanding applications. Manufacturing considerations for ABS include excellent dimensional stability and impact resistance, whereas PA requires careful moisture control and longer drying times to prevent defects during molding.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Gear Material
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance, good machinability, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for light to medium-load gears requiring durability and ease of manufacturing. Polyamide (nylon) provides superior wear resistance, higher mechanical strength, and better self-lubrication properties, which ensure enhanced performance and longevity in heavy-duty and high-friction gear applications. For gears exposed to significant mechanical stress and continuous operation, polyamide is the best choice, while ABS is preferred for budget-conscious projects with moderate loading conditions.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polyamide for Gear
 azmater.com
azmater.com