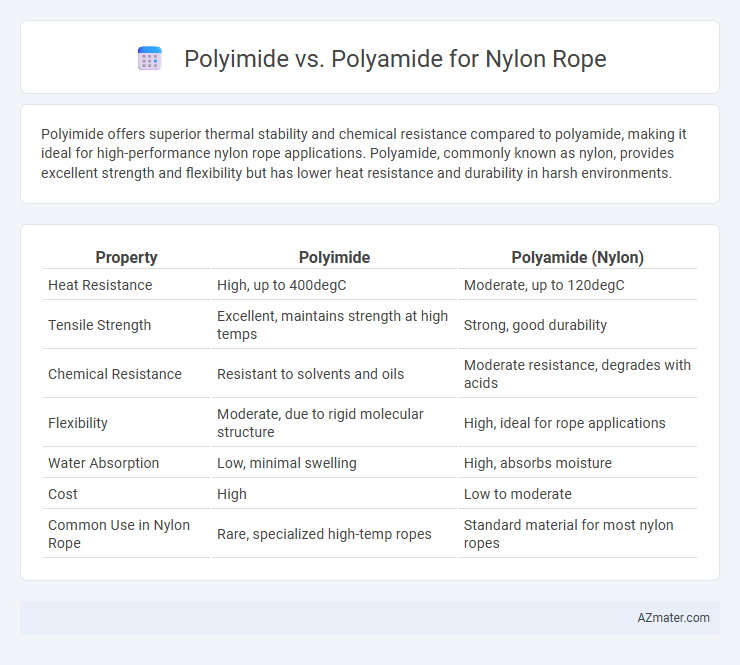
Polyimide offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polyamide, making it ideal for high-performance nylon rope applications. Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, provides excellent strength and flexibility but has lower heat resistance and durability in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyimide | Polyamide (Nylon) |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | High, up to 400degC | Moderate, up to 120degC |
| Tensile Strength | Excellent, maintains strength at high temps | Strong, good durability |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to solvents and oils | Moderate resistance, degrades with acids |
| Flexibility | Moderate, due to rigid molecular structure | High, ideal for rope applications |
| Water Absorption | Low, minimal swelling | High, absorbs moisture |
| Cost | High | Low to moderate |
| Common Use in Nylon Rope | Rare, specialized high-temp ropes | Standard material for most nylon ropes |
Introduction to Polyimide and Polyamide Materials
Polyimide and polyamide are high-performance polymers often compared in the context of nylon rope applications. Polyimides are known for their exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making them ideal for demanding environments. Polyamides, commonly referred to as nylons, offer superior flexibility, abrasion resistance, and moisture absorption properties, which contribute to their widespread use in durable rope manufacturing.
Chemical Structure Comparison: Polyimide vs Polyamide
Polyimides feature rigid aromatic rings and imide groups in their backbone, providing exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polyamides. Polyamides (nylons) contain amide linkages formed by the reaction of diamines and dicarboxylic acids, resulting in flexible chains with strong hydrogen bonding that enhance mechanical strength and moisture absorption. This fundamental chemical structural difference influences the performance of nylon ropes, where polyamide offers superior toughness and elasticity while polyimide provides enhanced heat resistance and chemical durability.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Differences
Polyimide ropes exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to polyamide (nylon) ropes, with higher tensile strength and excellent resistance to wear, heat, and chemicals, making them ideal for extreme environments. Polyamide ropes offer good elasticity and abrasion resistance but have lower thermal stability and UV resistance, which can diminish durability over time. The enhanced durability of polyimide ropes results in longer service life under harsh conditions, whereas polyamide ropes provide cost-effective performance in typical applications.
Thermal Resistance: Which Material Performs Better?
Polyimide exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to polyamide, maintaining stability and strength at temperatures exceeding 400degC, whereas polyamide (nylon) typically degrades above 260degC. This makes polyimide ropes ideal for applications involving extreme heat or continuous high-temperature exposure. Polyamide ropes, while strong and abrasion-resistant, are better suited for moderate temperature environments due to their lower thermal tolerance.
Flexibility and Elasticity in Nylon Rope Applications
Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, exhibits superior flexibility and elasticity, making it ideal for nylon rope applications that require stretch and resilience under load. Polyimide ropes, while offering high thermal stability and chemical resistance, typically lack the same degree of flexibility and elasticity, limiting their use in dynamic or elastic load-bearing scenarios. The inherent molecular structure of polyamide allows for elongation and recovery, enhancing rope durability and performance in marine, climbing, and industrial settings.
Resistance to Chemicals and Environmental Factors
Polyimide offers superior resistance to chemicals and high temperatures, maintaining structural integrity in harsh environments, making it ideal for demanding Nylon rope applications. Polyamide (Nylon) provides good chemical resistance but can degrade when exposed to strong acids, alkalis, or ultraviolet radiation over time. In environments with extreme chemicals or prolonged UV exposure, polyimide-based ropes outperform polyamide by retaining strength and durability longer.
Weight and Density Considerations for Ropes
Polyamide ropes, commonly known as nylon ropes, typically have a density around 1.15 g/cm3, making them heavier but offering excellent strength and elasticity. Polyimide ropes, with densities usually near 1.42 g/cm3, are denser and heavier than nylon, providing superior thermal stability and chemical resistance but potentially increasing overall rope weight. When selecting rope materials, the balance between weight and density influences handling, load capacity, and application suitability, with polyamide favored for lighter, more flexible ropes and polyimide chosen for high-performance, durable applications.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Polyamide, commonly known as Nylon, offers superior cost-effectiveness and widespread availability compared to polyimide for rope manufacturing. Polyamide ropes provide high tensile strength and abrasion resistance at a lower price point, making them ideal for budget-conscious applications. Polyimide ropes, while offering exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, tend to be more expensive and less accessible, limiting their use to specialized industrial environments.
Common Applications in the Rope Industry
Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, dominates the rope industry for applications requiring high strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, such as climbing ropes, marine mooring lines, and industrial lifting slings. Polyimide ropes, while less common, offer superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making them suitable for specialized uses in aerospace, electrical insulation, or high-temperature environments. The choice between polyimide and polyamide ropes depends heavily on specific performance requirements, with polyamide favored for general durability and polyimide for niche, high-performance conditions.
Choosing the Right Material: Polyimide or Polyamide for Your Needs
Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, offers excellent tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for dynamic load applications in rope manufacturing. Polyimide ropes provide superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and durability under extreme temperatures, suitable for specialized industrial uses. Selecting between polyamide and polyimide depends on the specific requirements of strength, temperature tolerance, and environmental exposure for your nylon rope application.
Infographic: Polyimide vs Polyamide for Nylon Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com