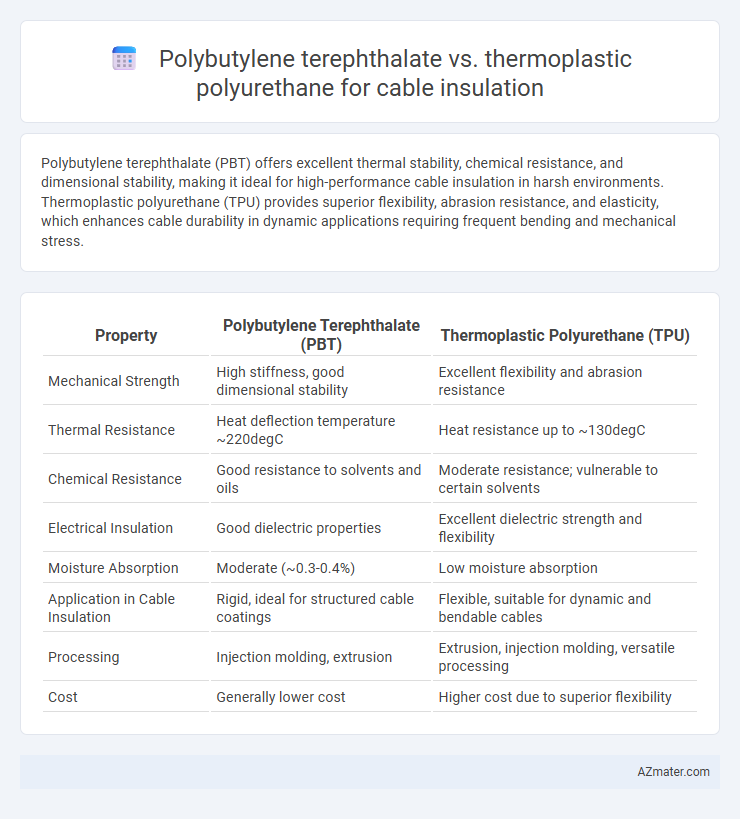
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for high-performance cable insulation in harsh environments. Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) provides superior flexibility, abrasion resistance, and elasticity, which enhances cable durability in dynamic applications requiring frequent bending and mechanical stress.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | High stiffness, good dimensional stability | Excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance |
| Thermal Resistance | Heat deflection temperature ~220degC | Heat resistance up to ~130degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to solvents and oils | Moderate resistance; vulnerable to certain solvents |
| Electrical Insulation | Good dielectric properties | Excellent dielectric strength and flexibility |
| Moisture Absorption | Moderate (~0.3-0.4%) | Low moisture absorption |
| Application in Cable Insulation | Rigid, ideal for structured cable coatings | Flexible, suitable for dynamic and bendable cables |
| Processing | Injection molding, extrusion | Extrusion, injection molding, versatile processing |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to superior flexibility |
Introduction to Cable Insulation Materials
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) and thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) are widely used materials in cable insulation due to their distinct mechanical and chemical properties. PBT offers excellent dimensional stability, high tensile strength, and resistance to heat and chemicals, making it suitable for applications requiring durable and flame-retardant insulation. TPU provides superior flexibility, abrasion resistance, and good elasticity, ideal for cables exposed to dynamic movements and harsh environmental conditions.
Overview of Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) is a semicrystalline thermoplastic polyester known for its excellent electrical insulation properties, high mechanical strength, and resistance to heat and chemicals, making it highly suitable for cable insulation applications. Its low moisture absorption and dimensional stability ensure reliable performance in demanding electrical environments compared to Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU). PBT's inherent flame retardancy and abrasion resistance contribute to enhanced safety and durability in cable insulation systems.
Overview of Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) is a versatile polymer known for its exceptional elasticity, abrasion resistance, and chemical stability, making it highly suitable for cable insulation applications requiring durability and flexibility. TPU offers superior resistance to oils, solvents, and varying temperatures compared to Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT), enhancing cable longevity in harsh environments. Its excellent mechanical properties and ease of processing enable the production of flexible, robust cables ideal for automotive, industrial, and consumer electronics sectors.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers high tensile strength and excellent rigidity, providing superior resistance to deformation and mechanical stress in cable insulation applications. Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) exhibits exceptional elasticity and abrasion resistance, allowing cables to withstand repeated bending and impact without cracking. Comparing both, PBT is preferred for structural durability, while TPU excels in flexibility and wear resistance, making the choice dependent on mechanical performance requirements in different cable environments.
Thermal Resistance and Performance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent thermal resistance with a melting point around 223degC, making it suitable for cable insulation in high-temperature environments. Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) provides good flexibility and abrasion resistance but typically has a lower thermal resistance, with continuous use temperatures around 80-120degC. For applications requiring superior thermal stability and dimensional performance, PBT is preferred, while TPU is chosen for flexibility and mechanical toughness in cable insulation.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Stability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior chemical resistance against oils, solvents, and chemicals, making it highly suitable for cable insulation in harsh industrial environments. Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) offers excellent environmental stability with high resistance to abrasion, UV radiation, and ozone, providing durability in outdoor and flexible cable applications. While PBT excels in chemical robustness, TPU performs better in maintaining flexibility and resilience under environmental stress conditions.
Flexibility and Processability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent dimensional stability and chemical resistance but is less flexible compared to thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), which provides superior elasticity and flexibility ideal for dynamic cable insulation applications. TPU excels in processability due to its lower melting point and can be easily extruded or molded into complex shapes, enhancing manufacturing efficiency for flexible cables. PBT's rigidity and thermal resistance make it suitable for static or semi-flexible cable insulation, whereas TPU's exceptional abrasion resistance and flexibility cater to environments demanding frequent bending and movement.
Cost-Effectiveness and Economic Factors
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers a cost-effective solution for cable insulation due to its lower raw material and processing costs compared to thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU). TPU provides superior flexibility and abrasion resistance but typically involves higher manufacturing expenses, impacting overall project budgets. Evaluating long-term economic factors such as durability and maintenance can further influence the cost-efficiency of selecting PBT or TPU for cable insulation applications.
Application Suitability in Cable Insulation
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and thermal performance, making it suitable for high-voltage and automotive cable insulation where durability under heat and mechanical stress is critical. Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) provides superior flexibility, abrasion resistance, and elasticity, ideal for applications requiring flexible cables in harsh environments or dynamic movements such as robotics and wearable electronics. Selecting between PBT and TPU depends on the specific cable insulation requirements, including mechanical stress, environmental exposure, and thermal conditions.
Choosing Between PBT and TPU for Cable Insulation
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and flame retardancy, making it ideal for cable insulation in harsh industrial environments. Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) provides superior flexibility, abrasion resistance, and elasticity, which enhances cable durability in dynamic applications requiring frequent bending or movement. Choosing between PBT and TPU depends on the application's mechanical demands, environmental exposure, and required thermal properties, with PBT favored for rigidity and thermal stability, while TPU suits flexible, high-wear cables.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Thermoplastic polyurethane for Cable insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com