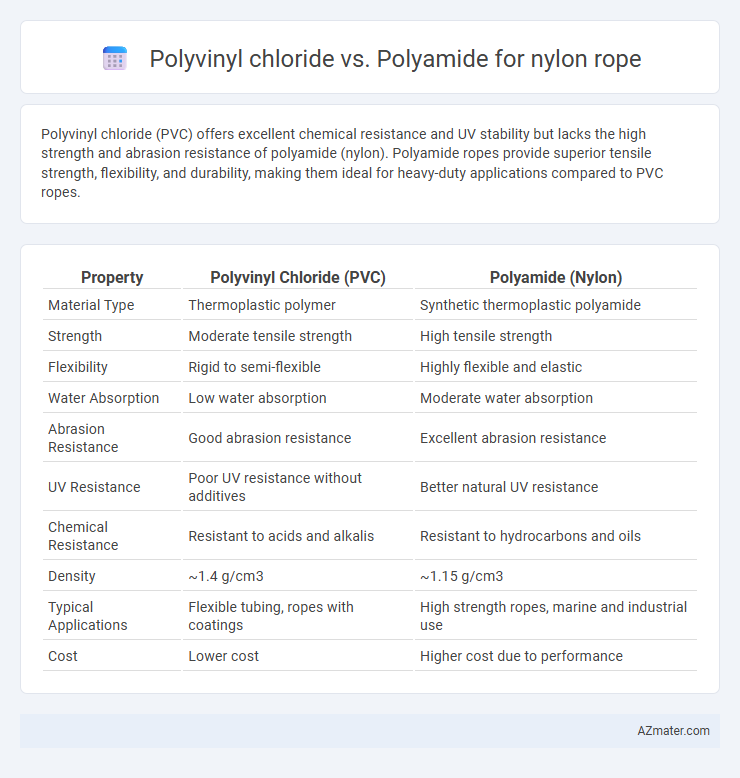
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers excellent chemical resistance and UV stability but lacks the high strength and abrasion resistance of polyamide (nylon). Polyamide ropes provide superior tensile strength, flexibility, and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications compared to PVC ropes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Polyamide (Nylon) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Synthetic thermoplastic polyamide |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength |
| Flexibility | Rigid to semi-flexible | Highly flexible and elastic |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption | Moderate water absorption |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good abrasion resistance | Excellent abrasion resistance |
| UV Resistance | Poor UV resistance without additives | Better natural UV resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids and alkalis | Resistant to hydrocarbons and oils |
| Density | ~1.4 g/cm3 | ~1.15 g/cm3 |
| Typical Applications | Flexible tubing, ropes with coatings | High strength ropes, marine and industrial use |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to performance |
Introduction to Polyvinyl Chloride and Polyamide
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a durable synthetic polymer widely used in rope manufacturing for its excellent resistance to chemicals, weathering, and abrasion. Polyamide, commonly known as Nylon, offers superior tensile strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for dynamic load applications. Comparing these materials, PVC ropes are favored for static, low-stretch uses, while Nylon ropes excel in strength and flexibility for demanding environments.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a synthetic polymer consisting of repeating vinyl chloride monomers, characterized by a rigid backbone with chlorine atoms that impart chemical resistance and durability. Polyamide, commonly known as Nylon, is a synthetic polymer made from repeating units linked by amide bonds, providing high tensile strength and flexibility due to its hydrogen-bonded molecular structure. The chlorine atoms in PVC contribute to its rigidity and flame retardance, while the amide linkages in Nylon enable superior elasticity and abrasion resistance, making them distinct in chemical composition and performance for rope applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polyamide (Nylon) ropes exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) ropes, with tensile strengths typically ranging from 75 to 100 MPa for Nylon, while PVC ropes often max out around 40 to 60 MPa. Nylon's high tensile strength and excellent elasticity contribute to greater load-bearing capacity and resistance to abrasion and impact, making it a preferred choice for industrial and marine applications. In contrast, PVC ropes are less durable under heavy mechanical stress and tend to degrade faster when exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Polyamide, commonly known as Nylon, offers superior durability and wear resistance compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) when used in rope applications. Nylon ropes exhibit excellent abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and better elasticity, making them ideal for heavy-duty and dynamic loads. In contrast, PVC ropes tend to be less resistant to wear and environmental stress, leading to quicker degradation over time.
Flexibility and Handling Characteristics
Polyamide (nylon) ropes offer superior flexibility and elasticity compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) ropes, allowing for easier handling and better shock absorption in dynamic applications. PVC ropes tend to be stiffer and less pliable, which can limit their ease of knotting and manipulation during use. The inherent flexibility of polyamide fibers enhances grip and reduces hand fatigue, making nylon ropes the preferred choice in demanding marine and climbing environments.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Polyamide (nylon) ropes exhibit superior resistance to abrasion, UV radiation, and chemicals compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) ropes, making them more durable in harsh outdoor environments. PVC ropes tend to degrade faster under prolonged sun exposure and extreme weather conditions due to their lower UV resistance and susceptibility to cracking. Nylon's inherent elasticity and moisture resistance further enhance its performance for marine and industrial applications where environmental stress is significant.
Cost and Availability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) ropes are generally more cost-effective and widely available than polyamide (nylon) ropes, making them a preferred choice for budget-conscious applications. Nylon ropes offer superior strength and elasticity but come at a higher price point due to more complex manufacturing processes and limited production scale. The availability of PVC ropes in various thicknesses and colors contributes to their widespread use, while nylon ropes are often specialized for high-performance needs.
Applications in Nylon Rope Manufacturing
Polyamides, commonly known as nylon, exhibit superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and elasticity, making them ideal for high-performance rope applications such as climbing, marine, and industrial lifting. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) coatings are often applied to nylon ropes to enhance UV resistance, waterproofing, and surface durability without compromising flexibility. Nylon ropes with PVC coatings are prevalent in outdoor environments where enhanced weather resistance and longevity are critical.
Safety and Environmental Impact
Polyamide (nylon) ropes offer high tensile strength and abrasion resistance but can release harmful chemicals like nitrous oxides during degradation, posing environmental risks. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) ropes are less prone to UV damage and chemical degradation but contain plasticizers and chlorine, which may leach toxic substances and produce dioxins when burned. Choosing between PVC and polyamide ropes requires balancing mechanical performance with environmental safety, emphasizing proper disposal and potential ecological impact.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Nylon Rope
Polyamide, commonly known as Nylon, offers superior strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it the preferred choice for high-performance ropes. PVC ropes, while more affordable and resistant to chemicals and UV radiation, lack the durability and flexibility essential for demanding applications. Selecting Nylon ensures enhanced load-bearing capacity and longevity, critical for industrial and marine environments requiring reliable rope performance.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride vs Polyamide for Nylon rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com