Fluoropolymers offer superior chemical resistance and durability for toys, while Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides excellent impact strength and ease of molding. ABS is widely used in toy manufacturing due to its toughness and cost-effectiveness, whereas fluoropolymers are preferred for high-performance applications requiring non-stick and weather-resistant properties.
Table of Comparison
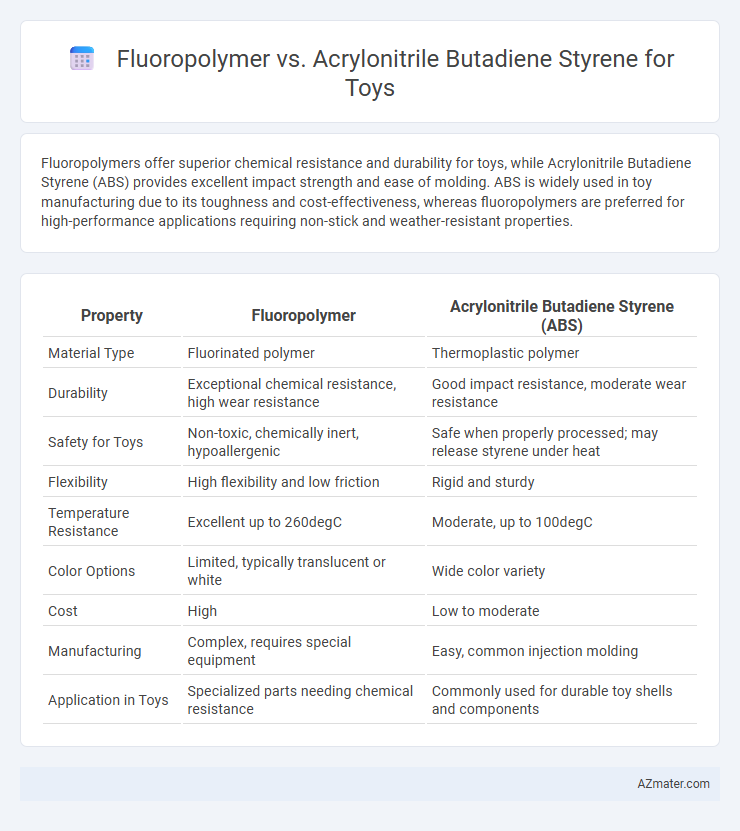
| Property | Fluoropolymer | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Fluorinated polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Durability | Exceptional chemical resistance, high wear resistance | Good impact resistance, moderate wear resistance |
| Safety for Toys | Non-toxic, chemically inert, hypoallergenic | Safe when properly processed; may release styrene under heat |
| Flexibility | High flexibility and low friction | Rigid and sturdy |
| Temperature Resistance | Excellent up to 260degC | Moderate, up to 100degC |
| Color Options | Limited, typically translucent or white | Wide color variety |
| Cost | High | Low to moderate |
| Manufacturing | Complex, requires special equipment | Easy, common injection molding |
| Application in Toys | Specialized parts needing chemical resistance | Commonly used for durable toy shells and components |
Introduction to Toy Material Selection
Fluoropolymers offer exceptional chemical resistance, low friction, and high durability, making them ideal for toys requiring long-lasting performance and safety under harsh conditions. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides excellent impact resistance, toughness, and ease of molding, which supports intricate designs and vibrant colors in toy manufacturing. Selecting between fluoropolymers and ABS depends on factors such as mechanical stress, environmental exposure, and regulatory compliance for non-toxicity in children's products.
Overview of Fluoropolymer Properties
Fluoropolymers exhibit exceptional chemical resistance, high thermal stability up to 260degC, and low surface energy, making them highly durable and resistant to staining or degradation in toy applications. Their non-stick and anti-corrosive properties enable safe, long-lasting use under repeated handling and exposure to various environmental conditions. Compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), which offers good impact resistance and ease of processing, fluoropolymers provide superior performance in extreme temperatures and chemical exposure, ideal for specialized toy components requiring enhanced safety and longevity.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Key Characteristics
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is renowned for its high impact resistance, toughness, and excellent rigidity, making it a preferred material for durable toy manufacturing. With superior dimensional stability and ease of processing through injection molding, ABS allows for precise, complex shapes and vibrant color retention. Unlike fluoropolymers, ABS offers cost-effective production and superior surface finish, essential qualities for safe, visually appealing toys.
Safety Concerns: Fluoropolymer vs ABS in Toys
Fluoropolymers offer superior chemical resistance and low toxicity, making them highly safe for toy applications where exposure to harsh chemicals or UV light occurs. ABS, while widely used for its impact resistance and ease of molding, can release harmful additives like BPA or phthalates when degraded, posing potential toxicological risks in children's toys. Selecting fluoropolymers over ABS significantly reduces concerns related to chemical off-gassing and long-term safety under repeated use or stress.
Durability and Impact Resistance Comparison
Fluoropolymers exhibit superior chemical resistance, thermal stability, and exceptional durability, making them highly resistant to wear and environmental degradation in toy applications. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) offers excellent impact resistance and toughness, providing effective shock absorption and structural integrity under mechanical stress. While ABS is favored for its cost-effectiveness and strength, fluoropolymers deliver enhanced longevity and resilience in harsh conditions, ideal for long-lasting, high-performance toys.
Cost Analysis: Fluoropolymer vs ABS
Fluoropolymers typically incur higher material and processing costs compared to Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), making ABS a more cost-effective choice for toy manufacturing. The raw material price per kilogram of fluoropolymers can be up to 5 times greater than ABS, which directly impacts production budgets and retail pricing. ABS offers a balanced trade-off between durability, ease of manufacturing, and affordability, which is critical for high-volume toy production.
Manufacturing and Processing Differences
Fluoropolymers and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) differ significantly in manufacturing and processing for toy applications. Fluoropolymers require high-temperature processing due to their high melting points and chemical resistance, often necessitating specialized extrusion and molding equipment to maintain material integrity. In contrast, ABS offers easier injection molding with lower processing temperatures, faster cycle times, and greater dimensional stability, making it a cost-effective and versatile option for mass production of detailed toy components.
Color, Finish, and Aesthetic Capabilities
Fluoropolymers provide exceptional color stability and resistance to UV degradation, making them ideal for vibrant and long-lasting toy finishes, while Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) offers a broader palette with excellent gloss and smooth surface finish possibilities. The color retention in fluoropolymers supports extended outdoor use without fading, whereas ABS is known for its ease of painting and dyeing, enabling diverse aesthetic customization. Both materials balance durability and visual appeal, but fluoropolymers excel in high-performance color endurance, and ABS is preferred for intricate molding with consistent surface texture.
Environmental Impact and Recycling Considerations
Fluoropolymers, known for their chemical resistance and durability, pose significant environmental challenges due to their persistent nature and difficulty in recycling, often leading to long-term ecological accumulation. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), widely used in toys, offers better recyclability and a more established recycling infrastructure, reducing its overall environmental footprint compared to fluoropolymers. The choice between these materials significantly impacts sustainability, with ABS being the preferred option for minimizing environmental harm and facilitating circular economy practices in toy manufacturing.
Best Use Cases for Fluoropolymer and ABS in Toy Manufacturing
Fluoropolymers excel in toy manufacturing where chemical resistance, non-toxicity, and durability are paramount, making them ideal for components exposed to harsh cleaning agents or outdoor environments. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is preferred for its excellent impact resistance, ease of molding, and cost-effectiveness, thus dominating in creating intricate, high-detail toy parts and durable casings. Fluoropolymers are best suited for specialty toys requiring high-performance materials, while ABS is optimal for mass-produced, visually appealing, and safe toys.
Infographic: Fluoropolymer vs Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene for Toy
 azmater.com
azmater.com