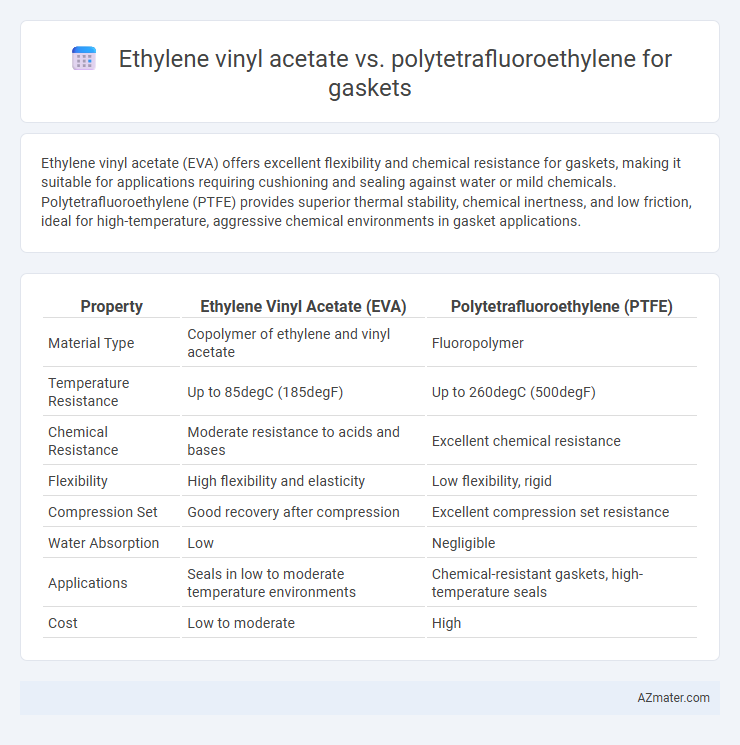
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers excellent flexibility and chemical resistance for gaskets, making it suitable for applications requiring cushioning and sealing against water or mild chemicals. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides superior thermal stability, chemical inertness, and low friction, ideal for high-temperature, aggressive chemical environments in gasket applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate | Fluoropolymer |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 85degC (185degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to acids and bases | Excellent chemical resistance |
| Flexibility | High flexibility and elasticity | Low flexibility, rigid |
| Compression Set | Good recovery after compression | Excellent compression set resistance |
| Water Absorption | Low | Negligible |
| Applications | Seals in low to moderate temperature environments | Chemical-resistant gaskets, high-temperature seals |
| Cost | Low to moderate | High |
Introduction to Gasket Materials
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers excellent flexibility and chemical resistance, making it suitable for low to medium temperature gasket applications where cushioning and resilience are important. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is renowned for its superior chemical inertness, high-temperature tolerance, and low friction, often preferred in harsh environments requiring long-term durability and exceptional sealing performance. When selecting gasket materials, understanding the specific operating conditions and chemical exposure is crucial to optimize sealing effectiveness and longevity.
Overview of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a flexible, rubber-like copolymer known for its excellent cushioning properties, chemical resistance, and low-temperature toughness, making it suitable for gasket applications requiring moderate sealing performance. Unlike Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), EVA offers superior elasticity and compression recovery, enhancing its ability to maintain a seal under varying pressures and temperatures. EVA gaskets are particularly effective in environments with exposure to oils, UV radiation, and mild chemicals, although they do not match the high chemical resistance and temperature tolerance provided by PTFE.
Overview of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer known for its exceptional chemical resistance, high thermal stability up to 260degC, and low coefficient of friction, making it ideal for gasket applications in aggressive chemical environments. Unlike Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), PTFE offers superior non-stick properties and excellent electrical insulation, which enhance gasket performance in demanding industrial settings. Its inert nature and resistance to ultraviolet radiation and weathering contribute to the longevity and reliability of PTFE gaskets in diverse sealing solutions.
Physical Properties: EVA vs PTFE
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) gaskets exhibit excellent flexibility, moderate tensile strength, and low hardness, making them ideal for applications requiring cushioning and shock absorption. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) gaskets offer superior chemical resistance, high melting point (around 327degC), and exceptional dimensional stability under extreme temperatures. While EVA provides good elasticity and compression set resistance, PTFE excels in resistance to chemicals, UV radiation, and temperature extremes, making it suitable for more demanding sealing environments.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers moderate chemical resistance, performing well against acids, bases, and alcohols but is vulnerable to strong solvents and oils. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits exceptional chemical inertness, resisting nearly all chemicals, including strong acids, bases, solvents, and oxidative substances, making it ideal for highly corrosive environments. In gasket applications where chemical resistance is critical, PTFE outperforms EVA by maintaining integrity under aggressive chemical exposure and extreme temperature variations.
Temperature Tolerance and Performance
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) gaskets offer moderate temperature tolerance, typically up to 90degC, making them suitable for low to medium-heat sealing applications. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) gaskets withstand extreme temperatures ranging from -200degC to 260degC, providing superior thermal resistance and chemical inertness. PTFE's high performance under harsh conditions ensures durability and reliability in demanding industrial environments compared to EVA.
Durability and Longevity
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers moderate durability with good flexibility and resistance to cracking, making it suitable for gaskets exposed to moderate temperatures and less aggressive chemicals. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides exceptional longevity due to its outstanding chemical inertness, high temperature resistance up to 260degC, and excellent mechanical strength, ideal for harsh environments and demanding sealing applications. PTFE gaskets outperform EVA in durability under extreme conditions, significantly extending the service life in industrial uses.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) gaskets offer superior cost efficiency due to their lower raw material and manufacturing expenses compared to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) gaskets. EVA's widespread production results in high availability, making it a preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications. Conversely, PTFE gaskets provide enhanced chemical resistance and temperature tolerance but incur higher costs and limited availability in certain regions.
Typical Applications in Gaskets
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) gaskets are commonly used in applications requiring flexibility, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation, such as in automotive seals, waterproofing, and cushioning components. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) gaskets excel in high-temperature, high-pressure environments with aggressive chemical exposure, making them ideal for chemical processing, pharmaceutical, and food industry seals. EVA offers cost-effective sealing with moderate performance, while PTFE provides superior chemical inertness and thermal stability for demanding gasket applications.
Which Material is Best for Your Gasket Needs?
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and cushioning properties, making it suitable for gaskets in applications requiring moderate temperature and pressure tolerance. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) provides superior chemical inertness, high temperature resistance up to 260degC, and low friction, ideal for demanding industrial gasket needs involving aggressive chemicals or high thermal conditions. Selecting the best material depends on the specific operational environment; EVA suits general sealing with less extreme conditions, while PTFE is preferred for harsh chemical exposure and elevated temperatures.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Polytetrafluoroethylene for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com