Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to cellulose acetate, enhancing cigarette filter durability and performance. Cellulose acetate remains widely used due to its cost-effectiveness and biodegradability despite lower heat resistance.
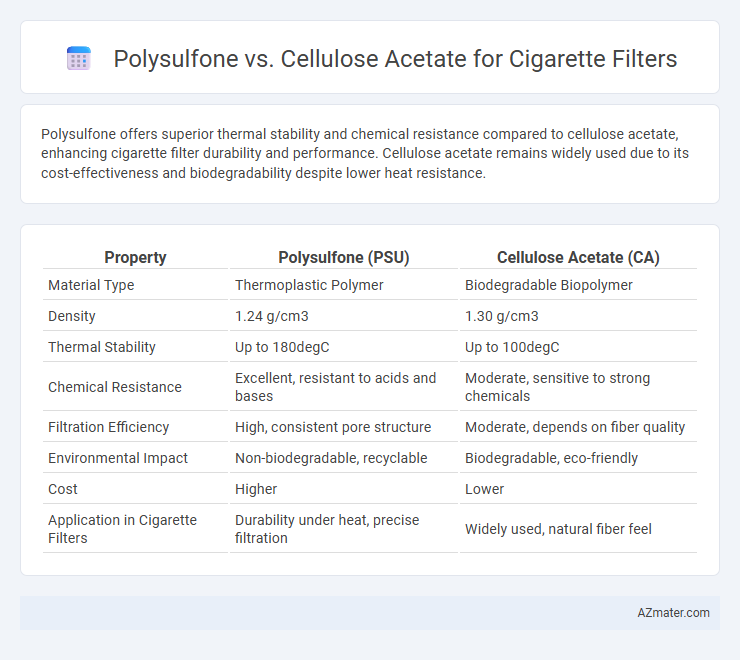
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polysulfone (PSU) | Cellulose Acetate (CA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Biodegradable Biopolymer |
| Density | 1.24 g/cm3 | 1.30 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 180degC | Up to 100degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resistant to acids and bases | Moderate, sensitive to strong chemicals |
| Filtration Efficiency | High, consistent pore structure | Moderate, depends on fiber quality |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable | Biodegradable, eco-friendly |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Application in Cigarette Filters | Durability under heat, precise filtration | Widely used, natural fiber feel |
Introduction to Cigarette Filter Materials
Polysulfone and cellulose acetate are two widely used materials in cigarette filter manufacturing due to their distinct filtration properties and chemical stability. Polysulfone offers high thermal resistance and mechanical strength, making it suitable for advanced filtration, while cellulose acetate remains the industry standard for its biodegradability and efficient particle retention. Understanding the differences in material composition and performance is essential for optimizing cigarette filter effectiveness and environmental impact.
Overview of Polysulfone and Cellulose Acetate
Polysulfone is a high-performance thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making it suitable for advanced filtration applications. Cellulose acetate, derived from cellulose, is a biodegradable polymer widely used in cigarette filters due to its effective filtration properties and affordability. While cellulose acetate is the industry standard for cigarette filters, polysulfone offers enhanced durability and resistance to higher temperatures, potentially improving filter performance and longevity.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polysulfone exhibits a rigid aromatic backbone with sulfone groups, providing high thermal stability and resistance to chemical degradation, which enhances its durability in cigarette filters. Cellulose acetate features ester groups derived from cellulose, offering biodegradability and moderate mechanical strength but lower thermal resistance compared to polysulfone. The distinct chemical structures result in polysulfone's superior chemical resistance and heat tolerance, while cellulose acetate is favored for its environmental friendliness and cost-effectiveness in cigarette filter applications.
Filtration Efficiency: Polysulfone vs Cellulose Acetate
Polysulfone exhibits superior filtration efficiency compared to cellulose acetate in cigarette filters due to its enhanced porosity and chemical resistance, enabling better retention of tar and harmful compounds. Cellulose acetate, while commonly used, tends to have lower filtration performance because of its less uniform fiber structure and lower thermal stability. Consequently, polysulfone filters provide a more effective barrier against toxicants, improving overall smoke filtration quality.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Polysulfone filters, made from synthetic polymers, exhibit limited biodegradability and tend to persist in the environment, contributing to long-term plastic pollution. In contrast, cellulose acetate, derived from natural cellulose, offers partial biodegradability but often contains plasticizers that slow decomposition, resulting in considerable environmental residue. Evaluating cigarette filters for environmental sustainability requires balancing polysulfone's durability against cellulose acetate's incomplete breakdown and pollutant potential.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Polysulfone cigarette filters are produced using a thermoplastic extrusion process that allows precise control over filter porosity and mechanical strength, resulting in consistent performance and durability. Cellulose acetate filters are manufactured through a solvent spinning technique, where cellulose acetate fibers are formed by dissolving the polymer in acetone and then shaping it into tow fibers that are later conjoined into filter plugs. Polysulfone's manufacturing process involves higher temperatures and more complex equipment compared to cellulose acetate, which relies on solution casting and fiber bundling, influencing production speed and cost efficiency.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Polysulfone filters generally incur higher manufacturing costs due to advanced polymer synthesis and processing requirements compared to cellulose acetate, which benefits from established large-scale production and lower raw material expenses. Market availability favors cellulose acetate, dominating the cigarette filter industry with widespread supplier networks and consistent quality standards. Cost-effectiveness and supply chain stability continue to drive cellulose acetate's preference despite polysulfone's superior filtration properties.
Health Implications for Smokers
Polysulfone cigarette filters offer superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to cellulose acetate, potentially reducing the release of harmful byproducts during smoking. Cellulose acetate filters, commonly used in cigarettes, may degrade and release microplastics and toxins, posing additional health risks to smokers and the environment. Choosing polysulfone filters could lower exposure to toxic compounds and improve overall respiratory safety for smokers due to their enhanced filtration efficiency and durability.
Innovations and Future Trends in Filter Materials
Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to cellulose acetate, enabling innovative cigarette filters with enhanced durability and filtration efficiency. Advances in polysulfone composites integrate nanomaterials that improve toxin capture and biodegradability, addressing environmental concerns associated with traditional cellulose acetate filters. Future trends focus on developing sustainable, high-performance filter materials combining polysulfone's robustness with eco-friendly additives to meet increasing regulatory demands and consumer health awareness.
Conclusion: Which Material is Better for Cigarette Filters?
Polysulfone offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to cellulose acetate, making it more durable under prolonged smoking conditions. Cellulose acetate, while cost-effective and widely used, tends to degrade faster and contributes to environmental pollution due to slower biodegradability. For cigarette filters requiring enhanced performance and environmental consideration, polysulfone emerges as the better material choice.
Infographic: Polysulfone vs Cellulose Acetate for Cigarette Filter
 azmater.com
azmater.com