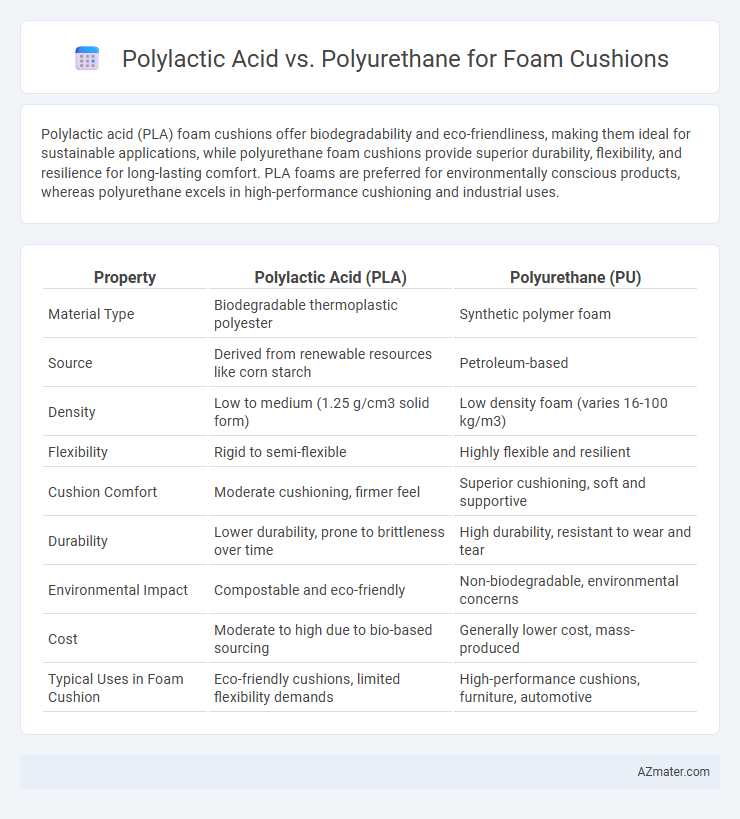
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam cushions offer biodegradability and eco-friendliness, making them ideal for sustainable applications, while polyurethane foam cushions provide superior durability, flexibility, and resilience for long-lasting comfort. PLA foams are preferred for environmentally conscious products, whereas polyurethane excels in high-performance cushioning and industrial uses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biodegradable thermoplastic polyester | Synthetic polymer foam |
| Source | Derived from renewable resources like corn starch | Petroleum-based |
| Density | Low to medium (1.25 g/cm3 solid form) | Low density foam (varies 16-100 kg/m3) |
| Flexibility | Rigid to semi-flexible | Highly flexible and resilient |
| Cushion Comfort | Moderate cushioning, firmer feel | Superior cushioning, soft and supportive |
| Durability | Lower durability, prone to brittleness over time | High durability, resistant to wear and tear |
| Environmental Impact | Compostable and eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, environmental concerns |
| Cost | Moderate to high due to bio-based sourcing | Generally lower cost, mass-produced |
| Typical Uses in Foam Cushion | Eco-friendly cushions, limited flexibility demands | High-performance cushions, furniture, automotive |
Introduction to Foam Cushion Materials
Polylactic acid (PLA) and polyurethane (PU) are prominent materials used in foam cushions, each offering distinct properties tailored to comfort and durability. PLA, a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources, provides an eco-friendly alternative with moderate cushioning and firmness suitable for sustainable products. Polyurethane foam, known for its excellent elasticity, resilience, and shock absorption, remains the industry standard for high-performance cushioning in furniture and automotive seating.
Overview of Polylactic Acid (PLA) Foam
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam is a biodegradable material derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, commonly used in foam cushions for its eco-friendly properties. PLA foam offers good cushioning, lightweight characteristics, and excellent breathability, making it suitable for sustainable furniture and packaging applications. Compared to polyurethane foam, PLA foam provides a lower environmental impact due to its compostability and reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
Overview of Polyurethane (PU) Foam
Polyurethane (PU) foam is a versatile material widely used in foam cushions due to its exceptional flexibility, durability, and cushioning properties. It offers excellent support and resilience, making it ideal for furniture and bedding applications where long-term comfort is essential. PU foam also provides superior load-bearing capacity and resistance to wear compared to alternatives like polylactic acid-based foams.
Production Processes: PLA vs Polyurethane
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam cushions are produced through fermentation of renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, followed by a polymerization process that yields a biodegradable polymer suitable for environmentally friendly foams. Polyurethane foam production involves the chemical reaction between polyols and isocyanates, creating a versatile and durable material typically synthesized from petroleum-based feedstocks. PLA production emphasizes sustainable bio-based raw materials and lower carbon footprint, while polyurethane prioritizes mechanical performance and cost efficiency through established petrochemical processes.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam cushions exhibit higher stiffness and lower elongation at break compared to polyurethane (PU) foams, indicating greater rigidity but less flexibility. Polyurethane foams demonstrate superior tensile strength and excellent resilience, making them more durable under repeated compressive stress. PLA's mechanical properties are suitable for applications requiring eco-friendly, biodegradable materials, while PU foams outperform in cushioning performance and long-term mechanical stability.
Comfort and Performance Analysis
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam cushions offer superior breathability and biodegradability, making them ideal for eco-conscious users seeking firm yet breathable comfort. Polyurethane foam cushions provide enhanced durability, higher resilience, and better pressure distribution, resulting in improved long-term support and cushioning performance. Performance analysis reveals that polyurethane excels in energy absorption and load-bearing capacity, while PLA offers moderate cushioning with environmental sustainability advantages.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam cushions are derived from renewable biomass sources like corn starch, making them biodegradable and compostable, thereby reducing landfill waste and lowering carbon footprint compared to traditional petroleum-based polyurethane (PU) foam. Polyurethane foam, while durable and versatile, relies on non-renewable fossil fuels and presents significant challenges in recycling and degradation, contributing to long-term environmental pollution. Advances in bio-based PU and recycling techniques aim to improve sustainability, but PLA currently offers superior environmental benefits through its renewable origins and end-of-life compostability.
Durability and Lifespan Differences
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam cushions offer biodegradability but have lower durability and a shorter lifespan compared to polyurethane foam, which excels in resilience and long-term performance. Polyurethane foam maintains its cushioning ability and structural integrity over extended use, making it ideal for high-traffic furniture and automotive applications. PLA foam tends to degrade faster under stress and environmental factors, limiting its lifespan in demanding use cases.
Cost and Market Availability
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam cushions typically have higher production costs due to bio-based raw materials and less mature manufacturing processes, limiting widespread market availability compared to polyurethane (PU) foams. Polyurethane foam remains the industry standard for cushions because of its low material cost, efficient mass production, and extensive supplier networks, resulting in broader market presence. Market trends indicate growing interest in PLA foams for sustainable applications, but PU dominance persists due to affordability and large-scale availability.
Applications and Future Trends
Polylactic acid (PLA) foam cushions are increasingly favored in eco-friendly packaging and biomedical applications due to their biodegradability and renewable sourcing, while polyurethane (PU) foams dominate furniture and automotive industries because of their superior durability and cushioning properties. Emerging trends indicate growing research into enhancing PLA's mechanical strength and thermal stability to expand its use in flexible cushioning applications traditionally held by PU. Future developments in bio-based PU and hybrid PLA-PU composites aim to combine environmental sustainability with high-performance comfort and resilience in foam cushions.
Infographic: Polylactic acid vs Polyurethane for Foam cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com