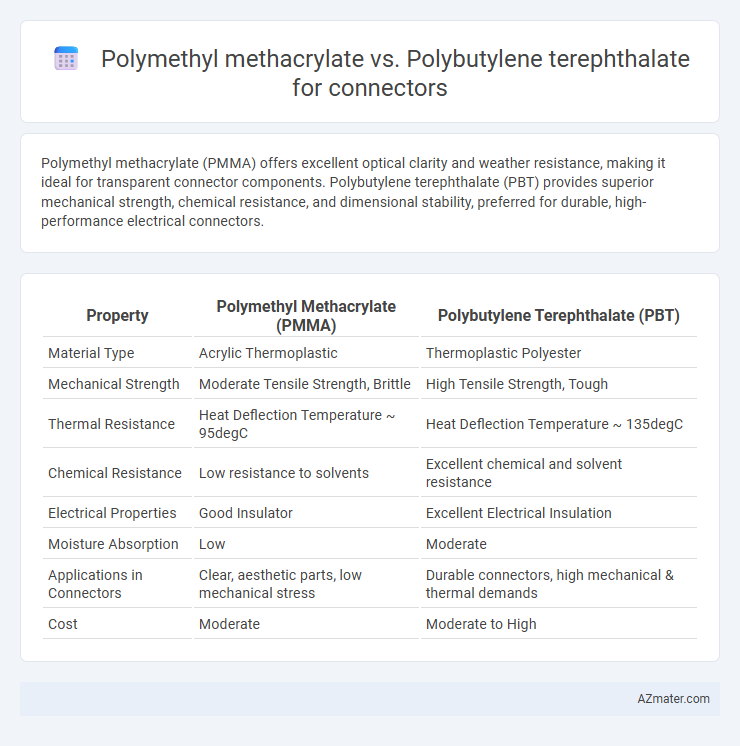
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent optical clarity and weather resistance, making it ideal for transparent connector components. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) provides superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, preferred for durable, high-performance electrical connectors.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Acrylic Thermoplastic | Thermoplastic Polyester |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate Tensile Strength, Brittle | High Tensile Strength, Tough |
| Thermal Resistance | Heat Deflection Temperature ~ 95degC | Heat Deflection Temperature ~ 135degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Low resistance to solvents | Excellent chemical and solvent resistance |
| Electrical Properties | Good Insulator | Excellent Electrical Insulation |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | Moderate |
| Applications in Connectors | Clear, aesthetic parts, low mechanical stress | Durable connectors, high mechanical & thermal demands |
| Cost | Moderate | Moderate to High |
Introduction to Connector Materials
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) serve distinct roles in connector materials due to their unique properties. PMMA offers superior optical clarity and weather resistance, making it ideal for connectors requiring transparency and aesthetic appeal. In contrast, PBT provides excellent mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, which ensures durable performance in harsh electrical environments.
Overview of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a transparent thermoplastic often used in connectors for its excellent optical clarity and high UV resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring light transmission and durability. PMMA offers superior rigidity and weather resistance compared to Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), though it has lower impact resistance and thermal stability. Its chemical resistance to dilute alkalis and acids supports longevity in connector housings exposed to environmental stress.
Overview of Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polyester known for its excellent mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for electrical connectors. Its higher heat resistance and low moisture absorption outperform polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) in environments requiring durability and long-term reliability. PBT also offers superior electrical insulation properties and is commonly used in automotive and electronic connector manufacturing due to its toughness and resistance to solvents.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent rigidity and high tensile strength, making it suitable for connectors requiring good structural stability and resistance to deformation under load. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior impact resistance, higher flexibility, and better fatigue endurance, which enhances connector durability in dynamic or vibration-prone environments. PBT also provides improved thermal resistance and dimensional stability compared to PMMA, crucial for connectors used in fluctuating temperature conditions.
Thermal Performance: PMMA vs PBT
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) has a lower heat deflection temperature, typically around 90degC, making it less suitable for high-temperature connector applications compared to Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), which exhibits heat deflection temperatures between 120degC and 150degC. PBT's superior thermal stability and resistance to thermal degradation ensure reliable performance in harsh environments where temperature fluctuations occur. PMMA offers good clarity but lacks the thermal endurance required for connectors exposed to elevated temperatures, whereas PBT provides a balanced combination of mechanical strength and thermal resistance for durable connector manufacturing.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent electrical insulation due to its high volume resistivity and excellent dielectric strength, making it suitable for connectors requiring reliable insulation under low to moderate voltage conditions. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) provides superior thermal stability and enhanced tracking resistance, which improves electrical insulation performance in high-temperature and high-humidity environments. For connectors, PBT's better resistance to electrical tracking and lower moisture absorption makes it preferable in demanding electrical insulation applications.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Stability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) exhibits excellent chemical resistance to dilute acids and alkalis but is vulnerable to organic solvents, limiting its use in harsh chemical environments. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior chemical resistance against fuels, oils, and many solvents, ensuring enhanced durability for connector applications exposed to aggressive chemicals. PBT also provides outstanding environmental stability, with higher resistance to UV radiation and moisture absorption compared to PMMA, making it ideal for outdoor or high-humidity connector environments.
Processing and Manufacturing Differences
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent clarity and ease of machining, making it suitable for optical connectors, but it requires precise temperature control during injection molding to avoid degradation. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) provides superior chemical resistance and mechanical strength, with a higher melting point that demands specialized processing equipment and longer cycle times in manufacturing. The manufacturing of PMMA connectors typically allows faster prototyping due to its lower melting temperature, whereas PBT connectors benefit from enhanced durability in harsh environments, justifying its more complex processing requirements.
Cost-Effectiveness and Market Availability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior optical clarity and cost-effectiveness in low to medium volume production of connectors, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency and aesthetic appeal. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) provides enhanced mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and durability, resulting in higher initial costs but long-term value in demanding environments and large-scale manufacturing. Market availability of PMMA connectors is widespread due to their popularity in consumer electronics, while PBT connectors dominate automotive and industrial sectors, reflecting specialized supply chains and material sourcing.
Application Suitability: Choosing PMMA or PBT for Connectors
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers excellent optical clarity and weather resistance, making it suitable for connectors in applications requiring high transparency and UV stability. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) provides superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for connectors exposed to high temperatures, mechanical stress, and harsh chemical environments. Selecting PMMA or PBT depends on whether the connector prioritizes optical properties or durability and thermal resistance in its specific application.
Infographic: Polymethyl methacrylate vs Polybutylene terephthalate for Connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com