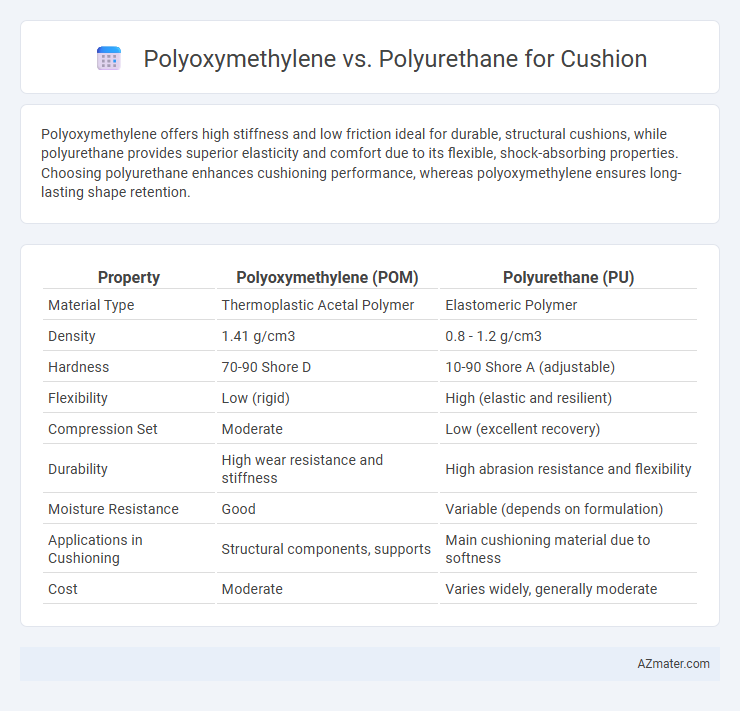
Polyoxymethylene offers high stiffness and low friction ideal for durable, structural cushions, while polyurethane provides superior elasticity and comfort due to its flexible, shock-absorbing properties. Choosing polyurethane enhances cushioning performance, whereas polyoxymethylene ensures long-lasting shape retention.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyoxymethylene (POM) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Acetal Polymer | Elastomeric Polymer |
| Density | 1.41 g/cm3 | 0.8 - 1.2 g/cm3 |
| Hardness | 70-90 Shore D | 10-90 Shore A (adjustable) |
| Flexibility | Low (rigid) | High (elastic and resilient) |
| Compression Set | Moderate | Low (excellent recovery) |
| Durability | High wear resistance and stiffness | High abrasion resistance and flexibility |
| Moisture Resistance | Good | Variable (depends on formulation) |
| Applications in Cushioning | Structural components, supports | Main cushioning material due to softness |
| Cost | Moderate | Varies widely, generally moderate |
Introduction to Polyoxymethylene and Polyurethane
Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, is a high-performance thermoplastic renowned for its exceptional stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for precision cushion components requiring durability and wear resistance. Polyurethane (PU) is a versatile polymer characterized by its superior flexibility, high resilience, and strong cushioning properties, widely used in applications needing comfort and impact absorption. Comparing POM and PU for cushion applications highlights the trade-off between POM's rigidity and strength versus PU's elasticity and cushioning effectiveness.
Material Composition and Structure
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is a crystalline thermoplastic characterized by its high stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability, making it suitable for structural cushion components requiring durability. Polyurethane (PU) is a versatile polymer elastomer composed of flexible chains linked by urethane bonds, offering superior elasticity, cushioning, and energy absorption ideal for comfort and impact resistance in cushions. The rigid, crystalline structure of POM contrasts with the soft, open-cell or closed-cell foam morphology of PU, leading to different performance profiles in cushioning applications.
Cushioning Performance: Comfort and Support
Polyurethane foam outperforms polyoxymethylene in cushioning performance due to its superior elasticity and ability to absorb impact, providing enhanced comfort and long-lasting support. Polyoxymethylene, while rigid and durable, lacks the flexibility needed for effective pressure distribution and shock absorption in cushions. For comfort-centric applications, polyurethane remains the preferred material, offering a balanced combination of softness and structural support.
Durability and Lifespan
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers exceptional durability due to its high tensile strength and resistance to wear, making it ideal for cushions subjected to frequent pressure and impact. Polyurethane provides excellent elasticity and shock absorption, but its lifespan may be shorter as it can degrade from UV exposure and repeated compression over time. Choosing POM ensures longer-lasting structural integrity, while polyurethane excels in comfort but may require more frequent replacement.
Resistance to Wear and Tear
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits superior resistance to wear and tear due to its high stiffness, low friction coefficient, and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for cushions subjected to repeated mechanical stress. Polyurethane offers moderate wear resistance but excels in flexibility and cushioning comfort, though it tends to degrade faster under abrasive conditions compared to POM. For applications demanding long-term durability and minimal surface degradation, polyoxymethylene outperforms polyurethane in wear resistance and structural integrity.
Applications in Cushion Manufacturing
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers exceptional rigidity and wear resistance, making it ideal for structural components in cushion manufacturing where durability is critical. Polyurethane excels in flexibility and cushioning properties, commonly used for foam padding and comfort layers due to its superior shock absorption and resilience. Manufacturers often select polyurethane for seat cushions and mattresses, while POM is favored for supporting framework and mechanical parts within the cushion assembly.
Cost Comparison and Economic Factors
Polyoxymethylene (POM) cushions generally cost more upfront due to higher material and manufacturing expenses, whereas polyurethane (PU) cushions offer a more budget-friendly option with lower initial investment. PU cushions benefit from widespread availability and efficient production methods that reduce overall expenses, making them economically advantageous for large-scale or cost-sensitive projects. Long-term economic factors such as durability and maintenance costs also favor PU cushions, as their flexibility and resilience lower replacement frequency compared to POM's rigid but costly properties.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is a durable thermoplastic with limited biodegradability and challenging recycling processes, often relying on energy-intensive methods which contribute to a higher carbon footprint compared to more sustainable materials. Polyurethane (PU), widely used in cushions, varies in environmental impact depending on its formulation, with bio-based and water-blown variants offering improved sustainability through reduced reliance on petroleum and lower emissions. The biodegradability and recyclability of both materials remain concerns, but innovations in bio-based polyurethanes provide a more eco-friendly alternative to conventional polyoxymethylene in cushion manufacturing.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Polyoxymethylene cushions require minimal maintenance due to their resistance to moisture and chemical degradation, enabling easy cleaning with mild detergents and water. Polyurethane cushions demand more frequent attention as they are prone to absorb oils and stains, necessitating specialized cleaning agents and periodic conditioning to maintain flexibility and appearance. Both materials benefit from routine dusting, but polyurethane's susceptibility to wear highlights the need for careful maintenance to extend its lifespan.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Cushions
Polyurethane offers superior cushioning comfort, durability, and elasticity, making it ideal for mattresses and seating applications where softness and resilience are essential. Polyoxymethylene provides excellent structural rigidity and wear resistance but lacks the flexibility and softness required for effective cushioning. Selecting polyurethane ensures optimal comfort and longevity in cushions, while polyoxymethylene is better suited for rigid components rather than flexible padding.
Infographic: Polyoxymethylene vs Polyurethane for Cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com