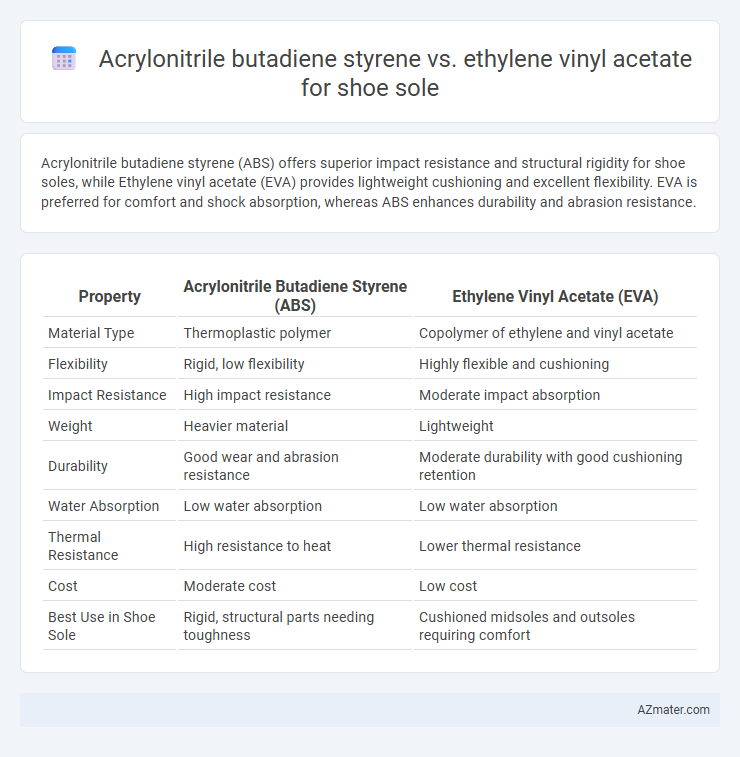
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and structural rigidity for shoe soles, while Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides lightweight cushioning and excellent flexibility. EVA is preferred for comfort and shock absorption, whereas ABS enhances durability and abrasion resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate |
| Flexibility | Rigid, low flexibility | Highly flexible and cushioning |
| Impact Resistance | High impact resistance | Moderate impact absorption |
| Weight | Heavier material | Lightweight |
| Durability | Good wear and abrasion resistance | Moderate durability with good cushioning retention |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption | Low water absorption |
| Thermal Resistance | High resistance to heat | Lower thermal resistance |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Low cost |
| Best Use in Shoe Sole | Rigid, structural parts needing toughness | Cushioned midsoles and outsoles requiring comfort |
Introduction to Shoe Sole Materials
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) are widely used materials in the manufacturing of shoe soles, each offering distinct properties tailored for performance and comfort. ABS provides high impact resistance and toughness, making it suitable for durable and rigid soles, while EVA is prized for its lightweight, flexibility, and superior cushioning characteristics, enhancing shock absorption and comfort in athletic and casual footwear. Selecting between ABS and EVA depends on the specific shoe sole requirements for durability, flexibility, and user comfort in different footwear categories.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its high impact resistance, toughness, and rigidity, making it suitable for durable shoe soles requiring abrasion resistance. ABS offers excellent dimensional stability and chemical resistance, which enhances the lifespan and structural integrity of footwear under various environmental conditions. Compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA), ABS soles are heavier but provide superior strength and impact absorption, ideal for high-performance or work shoes.
Overview of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is a lightweight, flexible, and durable polymer commonly used in shoe soles due to its excellent cushioning and shock absorption properties. Unlike Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), EVA offers superior compression resistance and water resistance, making it ideal for athletic and casual footwear requiring comfort and resilience. Its closed-cell foam structure also provides enhanced thermal insulation and buoyancy, contributing to overall foot comfort and performance.
Mechanical Properties: ABS vs EVA
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits higher tensile strength and impact resistance compared to Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), making it suitable for applications requiring durability and rigidity in shoe soles. EVA offers superior flexibility, cushioning, and shock absorption due to its low density and elastomeric properties, enhancing comfort and reducing fatigue during wear. While ABS provides structural support and wear resistance, EVA excels in energy return and lightweight performance, essential for athletic and casual footwear.
Flexibility and Comfort Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers high rigidity and impact resistance but lacks the flexibility needed for optimal shoe sole comfort, making it less suitable for footwear applications requiring cushioning. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is highly flexible, providing superior shock absorption and cushioning, enhancing overall comfort and reducing foot fatigue during prolonged use. EVA's soft, lightweight properties make it the preferred material for shoe soles where flexibility and comfort are prioritized over rigidity.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior durability and excellent wear resistance due to its high impact strength and rigidity, making it ideal for shoe soles exposed to rough surfaces. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), while lightweight and flexible, provides moderate durability but excels in cushioning and shock absorption, which may wear out faster under heavy abrasion. For long-lasting shoe soles requiring robust abrasion resistance, ABS outperforms EVA in maintaining structural integrity over prolonged use.
Shock Absorption Performance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers moderate shock absorption with high rigidity and impact resistance, making it suitable for durable shoe soles requiring structural support. In contrast, Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides superior shock absorption due to its lightweight, flexible, and cushioning properties, which effectively reduce impact forces during gait. EVA's enhanced energy return and compression resilience make it the preferred material for athletic and casual footwear focused on comfort and shock performance.
Weight and Design Versatility
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers a lightweight composition ideal for reducing overall shoe weight, enhancing comfort during extended wear. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) surpasses ABS in design versatility, allowing for greater flexibility in sole molding and cushioning properties suited for various athletic and casual footwear styles. Weight efficiency of ABS contrasts with EVA's adaptable softness and resilience, influencing material selection based on performance and aesthetic goals in shoe sole manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits high durability and resistance but poses environmental concerns due to its petroleum-based origins and limited recyclability, contributing to long-term landfill waste and carbon emissions. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers enhanced sustainability with its lower density and improved biodegradability under specific conditions, reducing environmental impact and facilitating easier recycling processes. The choice between ABS and EVA for shoe soles critically affects a brand's carbon footprint, waste management, and commitment to sustainable manufacturing practices.
Choosing the Right Material for Shoe Soles
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers high impact resistance, rigidity, and durability, making it ideal for shoe soles requiring structural support and toughness. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) provides excellent cushioning, flexibility, and lightweight comfort, preferred for athletic and casual footwear emphasizing shock absorption and flexibility. Choosing between ABS and EVA depends on the shoe's intended use, balancing durability needs against flexibility and comfort requirements.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Ethylene vinyl acetate for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com