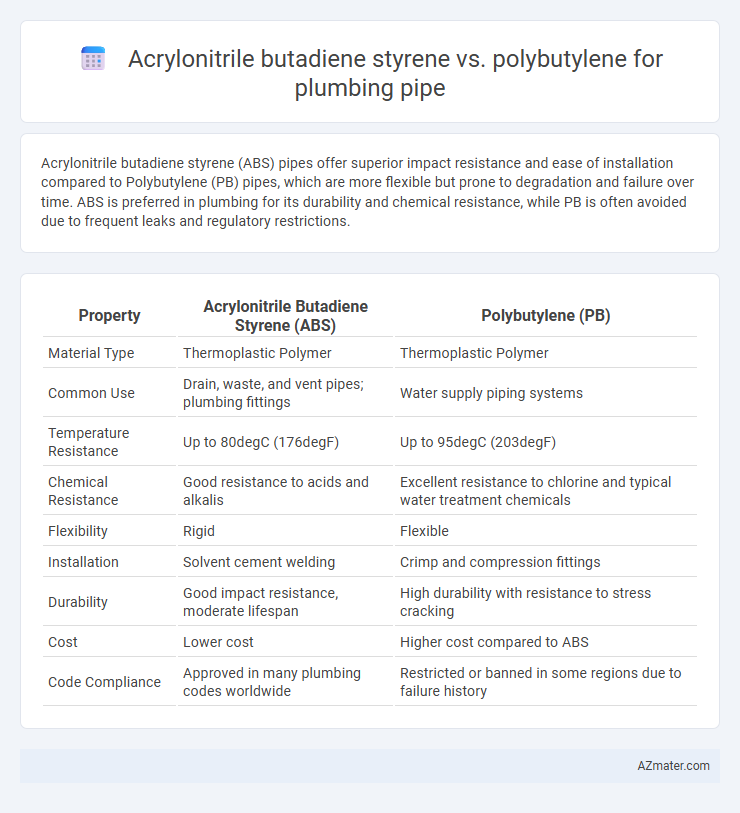
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) pipes offer superior impact resistance and ease of installation compared to Polybutylene (PB) pipes, which are more flexible but prone to degradation and failure over time. ABS is preferred in plumbing for its durability and chemical resistance, while PB is often avoided due to frequent leaks and regulatory restrictions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polybutylene (PB) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polymer | Thermoplastic Polymer |
| Common Use | Drain, waste, and vent pipes; plumbing fittings | Water supply piping systems |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 80degC (176degF) | Up to 95degC (203degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Excellent resistance to chlorine and typical water treatment chemicals |
| Flexibility | Rigid | Flexible |
| Installation | Solvent cement welding | Crimp and compression fittings |
| Durability | Good impact resistance, moderate lifespan | High durability with resistance to stress cracking |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost compared to ABS |
| Code Compliance | Approved in many plumbing codes worldwide | Restricted or banned in some regions due to failure history |
Introduction to ABS and Polybutylene Plumbing Pipes
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) plumbing pipes are known for their rigidity, impact resistance, and ease of installation, commonly used in drain, waste, and vent systems due to their high chemical and temperature tolerance. Polybutylene plumbing pipes, made from a flexible polymer, gained popularity for their corrosion resistance and lower cost but have faced reliability concerns over time, especially related to oxidation and brittle failure. Understanding the material properties and application suitability of ABS versus Polybutylene helps determine the best choice for plumbing installations.
Chemical Composition and Material Properties
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) features a terpolymer composition of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, offering high impact resistance, rigidity, and chemical stability suitable for plumbing pipes exposed to various chemicals. Polybutylene (PB), a semi-crystalline polymer composed of repeating butylene monomers, demonstrates superior flexibility, low-temperature resistance, and resistance to scale and chlorine degradation, making it ideal for hot and cold water supply lines. In terms of chemical resistance, ABS excels against acids and alkalis, while PB provides enhanced durability against chlorinated water and oxidative stress, influencing their specific applications in plumbing systems.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) pipes exhibit high impact resistance and maintain structural integrity under a broad temperature range, making them durable for plumbing applications. Polybutylene (PB) pipes offer flexibility and resistance to scaling but are prone to degradation over time when exposed to chlorinated water, impacting their longevity. ABS generally outperforms PB in long-term durability for plumbing systems, particularly in pressure-resistant and temperature-variable environments.
Installation Process and Requirements
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) plumbing pipes require solvent cement welding, which demands clean, dry surfaces and precise application to ensure strong, leak-proof joints, typically without the need for special tools. Polybutylene (PB) pipes utilize mechanical fittings or compression rings, necessitating skillful fitting and occasionally specialized tools to avoid damage during installation and ensure a durable connection. ABS pipes offer quicker assembly with fewer specialized tools, while PB pipes provide flexibility and require careful handling to prevent stress or cracking during installation.
Cost Differences: ABS vs Polybutylene
ABS pipes typically have a lower initial cost compared to polybutylene, making them more budget-friendly for residential plumbing projects. Polybutylene pipes tend to be more expensive due to their flexible properties and resistance to various chemical reactions. The long-term maintenance costs may be higher for polybutylene, as its susceptibility to degradation over time can lead to leaks and pipe replacements.
Resistance to Corrosion and Chemical Damage
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) pipes exhibit excellent resistance to corrosion and a broad spectrum of chemicals, making them ideal for plumbing systems exposed to harsh substances. Polybutylene (PB) pipes offer good chemical resistance but tend to degrade over time when exposed to chlorine and certain acidic conditions, leading to potential failures. The superior chemical stability of ABS ensures longer-lasting performance in applications where corrosion and chemical damage are critical concerns.
Performance in Varying Water Temperatures
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) pipes offer excellent durability and resistance to impact at low temperatures, maintaining structural integrity in cold water systems. Polybutylene (PB) pipes provide superior flexibility and can handle a wider range of temperatures, including hot water applications up to 180degF (82degC), outperforming ABS in thermal resistance. The thermal expansion rate of PB is higher than ABS, requiring careful installation in varying temperature environments to prevent joint stress or deformation.
Safety Concerns and Health Implications
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) pipes offer excellent impact resistance and chemical stability but emit potentially harmful fumes when burned, raising safety concerns in fire scenarios. Polybutylene (PB) pipes, once popular for ease of installation and flexibility, have been linked to degradation issues and susceptibility to chlorine, leading to increased risk of leaks and water contamination. Regulatory agencies often recommend monitoring the long-term durability of PB in plumbing to mitigate health risks associated with chemical leaching and pipe failure.
Regulatory Standards and Code Compliance
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) pipes typically comply with ASTM D2661 and NSF/ANSI 14 standards, ensuring they meet performance and safety requirements for drainage and vent systems. Polybutylene (PB) pipes, although once popular, have faced regulatory restrictions and are often excluded from current plumbing codes like the Uniform Plumbing Code (UPC) due to documented degradation and failure issues. Building codes prioritize materials with proven long-term durability, making ABS more favorable for regulatory compliance compared to Polybutylene in modern plumbing applications.
Suitability for Residential and Commercial Plumbing
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and higher temperature tolerance, making it suitable for both residential and commercial plumbing systems where durability and thermal stability are critical. Polybutylene (PB), while flexible and easier to install due to its lightweight nature, has faced long-term reliability issues in high-pressure commercial applications, limiting its use primarily to residential water supply and low-pressure systems. The selection between ABS and PB depends on specific requirements such as pressure ratings, temperature exposure, and regulatory approvals for plumbing codes in the intended installation environment.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polybutylene for Plumbing pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com