Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and rigidity compared to polypropylene (PP), making it ideal for syringe components requiring durability and precision. Polypropylene provides excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, which enhances syringe plunger performance and reduces risk of material degradation.
Table of Comparison
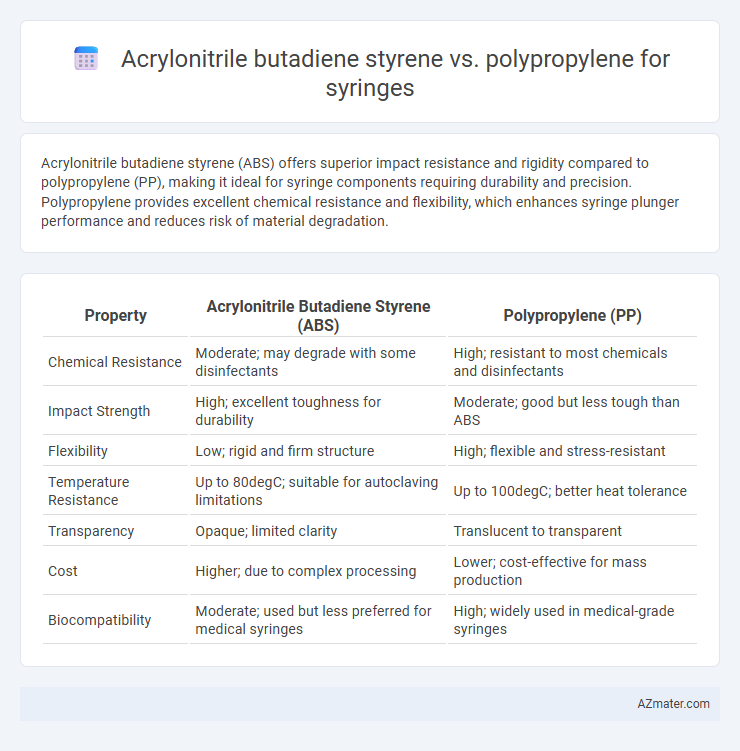
| Property | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate; may degrade with some disinfectants | High; resistant to most chemicals and disinfectants |
| Impact Strength | High; excellent toughness for durability | Moderate; good but less tough than ABS |
| Flexibility | Low; rigid and firm structure | High; flexible and stress-resistant |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 80degC; suitable for autoclaving limitations | Up to 100degC; better heat tolerance |
| Transparency | Opaque; limited clarity | Translucent to transparent |
| Cost | Higher; due to complex processing | Lower; cost-effective for mass production |
| Biocompatibility | Moderate; used but less preferred for medical syringes | High; widely used in medical-grade syringes |
Introduction to Syringe Materials
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and Polypropylene (PP) are commonly used materials in syringe manufacturing due to their distinct physical and chemical properties. ABS offers excellent impact resistance and dimensional stability, making it suitable for rigid syringe barrels and plungers requiring durability. In contrast, Polypropylene provides superior chemical resistance and flexibility, which is ideal for components in contact with diverse pharmaceutical substances and for achieving airtight seals.
Overview of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a durable thermoplastic polymer known for its high impact resistance, toughness, and excellent dimensional stability, making it suitable for precision medical devices like syringes. ABS offers superior resistance to chemicals and heat compared to polypropylene, which enhances its reliability during sterilization processes such as autoclaving. The polymer's rigidity and clarity also support accurate dosage measurements and ease of handling in syringe applications.
Properties of Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) exhibits excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for syringes that require compatibility with a wide range of medications and sterilization processes. Its high tensile strength and flexibility ensure durability and resistance to cracking under pressure or impact, critical for safe medical use. PP's low moisture absorption and clarity also support hygiene and visual inspection of syringe contents, distinguishing it from Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS).
Mechanical Strength Comparison: ABS vs PP
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers higher mechanical strength and impact resistance compared to polypropylene (PP), making it more durable under stress for syringe applications. ABS exhibits better rigidity and toughness, which contributes to resistance against cracking or deformation during handling or injection. Polypropylene is more flexible but has lower tensile strength, which can compromise the syringe's structural integrity under high mechanical loads.
Chemical Resistance Differences
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits moderate chemical resistance, being susceptible to attack by strong acids and bases, which limits its suitability for syringes used with harsh chemicals. Polypropylene (PP) demonstrates superior chemical resistance, particularly against acids, bases, and alcohols, making it more durable and reliable for medical syringes exposed to various chemical sterilants and pharmaceuticals. The enhanced chemical inertness of polypropylene reduces degradation risk, ensuring maintained syringe integrity during storage and use.
Biocompatibility and Safety in Medical Use
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polypropylene (PP) are both commonly utilized in syringe manufacturing, but polypropylene demonstrates superior biocompatibility due to its inert chemical nature and resistance to leaching, making it safer for medical use. Polypropylene exhibits excellent resistance to sterilization processes like autoclaving and gamma radiation, maintaining structural integrity and minimizing patient exposure to contaminants. ABS, while offering good mechanical strength, may release residual monomers and additives, potentially compromising biocompatibility and raising safety concerns in critical medical applications.
Sterilization Suitability for Syringes
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) exhibits excellent dimensional stability and resistance to heat, making it suitable for ethylene oxide and gamma sterilization methods commonly used in syringe manufacturing. Polypropylene (PP) demonstrates superior chemical resistance and can withstand higher autoclave sterilization temperatures without deforming, which is critical for syringes requiring steam sterilization. The choice between ABS and polypropylene for syringes largely depends on the preferred sterilization technique, with polypropylene favored for high-temperature steam processes and ABS suitable for low-temperature sterilization protocols.
Cost-Effectiveness and Manufacturing Efficiency
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers higher impact resistance and better dimensional stability than polypropylene (PP), enhancing manufacturing precision and reducing defect rates in syringe production. Polypropylene is more cost-effective due to its lower raw material price and faster cycle times during injection molding, making it suitable for high-volume syringe manufacturing. Evaluating both materials, ABS provides superior mechanical properties for durable syringes, while PP enables greater manufacturing efficiency and lower overall production costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polypropylene (PP) differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability when used for syringes. PP is favored for its recyclability, lower carbon footprint, and biodegradability compared to ABS, which is less eco-friendly due to its petroleum-based composition and limited recycling options. Selecting polypropylene contributes to sustainable medical waste management by reducing environmental pollution and promoting circular economy practices.
Conclusion: Optimal Material Choice for Syringes
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) offers superior impact resistance and dimensional stability, making it ideal for syringes requiring durability and precision. Polypropylene (PP) excels in chemical resistance and flexibility, enhancing safety in fluid handling and reducing risk of leachables in medical applications. For syringes, polypropylene is typically the optimal choice due to its excellent biocompatibility, cost-effectiveness, and resistance to sterilization processes.
Infographic: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene vs Polypropylene for Syringe
 azmater.com
azmater.com