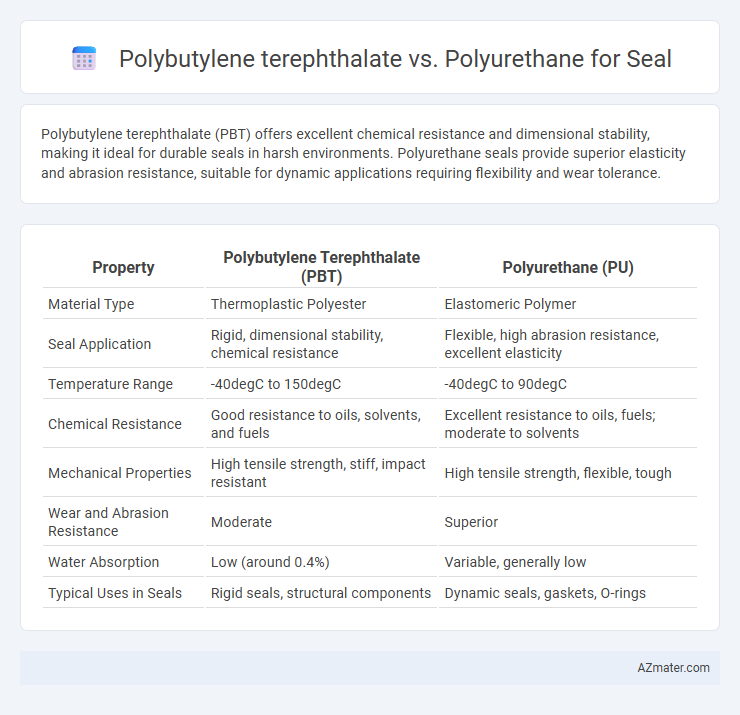
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability, making it ideal for durable seals in harsh environments. Polyurethane seals provide superior elasticity and abrasion resistance, suitable for dynamic applications requiring flexibility and wear tolerance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polyurethane (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Polyester | Elastomeric Polymer |
| Seal Application | Rigid, dimensional stability, chemical resistance | Flexible, high abrasion resistance, excellent elasticity |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC | -40degC to 90degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils, solvents, and fuels | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels; moderate to solvents |
| Mechanical Properties | High tensile strength, stiff, impact resistant | High tensile strength, flexible, tough |
| Wear and Abrasion Resistance | Moderate | Superior |
| Water Absorption | Low (around 0.4%) | Variable, generally low |
| Typical Uses in Seals | Rigid seals, structural components | Dynamic seals, gaskets, O-rings |
Introduction to Seal Materials: PBT vs Polyurethane
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) and polyurethane represent two widely used seal materials distinguished by their mechanical properties and environmental resistance. PBT offers excellent dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and high thermal endurance, making it ideal for automotive and electrical seals exposed to harsh conditions. In contrast, polyurethane excels in flexibility, abrasion resistance, and elasticity, which suits dynamic seals requiring high wear tolerance and resilience under mechanical stress.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic polyester known for its high chemical resistance, excellent dimensional stability, and good mechanical strength, owing to its aromatic ester linkages in the polymer backbone. Polyurethane (PU) consists of segmented block copolymers with urethane linkages formed between diisocyanates and polyols, which grant it superior elasticity, abrasion resistance, and impact strength compared to PBT. PBT offers better resistance to solvents and higher thermal stability, while polyurethane excels in flexibility and resilience, making it suitable for dynamic seal applications requiring elastomeric properties.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits high mechanical strength with excellent rigidity and dimensional stability, making it ideal for seals requiring durability under mechanical stress. Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and abrasion resistance, enabling seals to maintain elasticity and perform well under dynamic strain or varying environmental conditions. The choice between PBT and polyurethane hinges on whether the application demands greater structural strength or enhanced flexibility and resilience.
Resistance to Chemicals and Environmental Factors
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) seals excel in resistance to hydrocarbons, oils, and many acids, maintaining structural integrity in elevated temperatures and humid conditions. Polyurethane seals offer superior wear resistance and flexibility but show vulnerability to strong acids, alkalis, and prolonged UV exposure compared to PBT. Choosing between PBT and polyurethane for seals depends on the specific chemical environment and environmental exposure to ensure optimal durability and performance.
Durability and Lifespan in Seal Applications
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability, making it highly durable in seal applications exposed to oils and solvents. Polyurethane seals exhibit superior abrasion resistance and flexibility, enhancing their lifespan in dynamic environments with high wear and impact. The choice between PBT and polyurethane depends on specific operational conditions, with PBT favored for rigid, chemical-heavy uses and polyurethane preferred for elasticity and wear-intensive sealing tasks.
Temperature Tolerance and Performance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent temperature resistance, maintaining stability between -40degC and 150degC, making it suitable for seals exposed to moderate thermal conditions. Polyurethane seals outperform PBT in flexibility and abrasion resistance but generally tolerate temperatures ranging from -30degC to 80degC, limiting their use in high-temperature environments. When evaluating seal materials for applications requiring durability under elevated temperatures, PBT provides superior thermal performance compared to polyurethane.
Ease of Fabrication and Processing
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior ease of fabrication due to its excellent mold flow characteristics, dimensional stability, and faster cycle times in injection molding compared to polyurethane. PBT's thermoplastic nature allows for efficient reprocessing and consistent quality in high-volume seal manufacturing, whereas polyurethane, being a thermoset elastomer, often requires more complex curing processes and longer production cycles. Processing polyurethane seals involves controlled mixing and curing with precise temperature and timing, making PBT a more straightforward choice for applications demanding rapid fabrication and high repeatability.
Cost Analysis and Economic Efficiency
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) seals typically offer lower material and production costs compared to polyurethane (PU), making them a cost-effective choice for high-volume manufacturing. PBT's resistance to chemicals and high temperatures extends seal longevity, reducing replacement frequency and overall maintenance expenses. Polyurethane seals provide superior elasticity and abrasion resistance but generally incur higher upfront costs and may increase total expenditure in applications with moderate wear.
Industry-Specific Applications and Suitability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability, making it ideal for automotive and electrical seal applications where exposure to oils and solvents is common. Polyurethane seals excel in flexibility and abrasion resistance, suiting heavy-duty industrial settings such as construction machinery and hydraulic systems that require durable, impact-resistant seals. Choosing between PBT and polyurethane depends on specific industry demands, with PBT favored for rigid, high-temperature environments and polyurethane preferred for dynamic, wear-intensive conditions.
Choosing the Right Material: Key Considerations
When choosing between Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) and Polyurethane for seals, key considerations include chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and temperature tolerance. PBT offers excellent dimensional stability and resistance to oils and solvents, making it ideal for automotive and electrical sealing applications. Polyurethane excels in abrasion resistance and flexibility, suitable for dynamic seals exposed to wear and varying pressures.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polyurethane for Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com