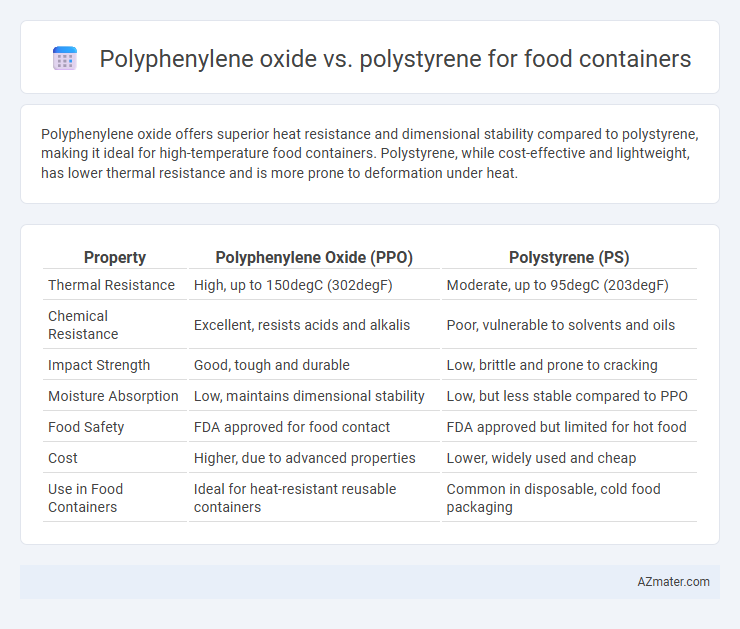
Polyphenylene oxide offers superior heat resistance and dimensional stability compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for high-temperature food containers. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and lightweight, has lower thermal resistance and is more prone to deformation under heat.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | High, up to 150degC (302degF) | Moderate, up to 95degC (203degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resists acids and alkalis | Poor, vulnerable to solvents and oils |
| Impact Strength | Good, tough and durable | Low, brittle and prone to cracking |
| Moisture Absorption | Low, maintains dimensional stability | Low, but less stable compared to PPO |
| Food Safety | FDA approved for food contact | FDA approved but limited for hot food |
| Cost | Higher, due to advanced properties | Lower, widely used and cheap |
| Use in Food Containers | Ideal for heat-resistant reusable containers | Common in disposable, cold food packaging |
Introduction to Polyphenylene Oxide and Polystyrene
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for reusable food containers that require durability and safety. Polystyrene (PS), a cost-effective and lightweight plastic, offers good clarity and ease of molding but has lower heat resistance and brittleness, limiting its use mainly to disposable food packaging. Comparing these polymers highlights PPO's advantage in long-term food storage applications, while PS is preferred for single-use, low-cost options.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) features a rigid aromatic backbone with ether linkages, providing enhanced thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polystyrene (PS), which consists of a polystyrene chain with phenyl side groups. The ether bonds in PPO contribute to greater resistance against oxidation and high temperatures, making it suitable for food containers that require durability and repeated use. In contrast, polystyrene's simpler hydrocarbon structure offers rigidity and clarity but is more susceptible to chemical degradation and less heat-resistant.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) exhibits superior thermal stability compared to polystyrene (PS), maintaining its structural integrity at temperatures up to 210degC, whereas polystyrene typically deforms around 100degC. PPO's heat resistance makes it ideal for food containers used in microwave or dishwasher settings, ensuring no leaching or warping occurs under high heat conditions. Polystyrene's lower heat tolerance restricts its use to cold or room-temperature food storage, limiting its effectiveness in applications requiring heat exposure.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior mechanical strength and durability compared to polystyrene (PS) when used for food containers, with higher impact resistance and tensile strength enabling better performance under stress. PPO exhibits excellent thermal stability and maintains structural integrity during repeated use and exposure to varying temperatures, unlike polystyrene which is more prone to cracking and deformation. These mechanical advantages make PPO a more reliable material for long-term food storage applications requiring repeated handling and washing.
Barrier Properties: Moisture and Gas Permeability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior barrier properties compared to polystyrene (PS), exhibiting significantly lower moisture vapor transmission rates, which helps maintain food freshness and prevents contamination. PPO's molecular structure provides enhanced gas impermeability, effectively reducing oxygen permeation that can lead to oxidation and spoilage, making it ideal for extending shelf life in food packaging. Polystyrene, while cost-effective and rigid, generally shows higher moisture and oxygen permeability, limiting its performance for applications requiring stringent barrier capabilities.
Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior food safety through high thermal stability, chemical resistance, and low moisture absorption, reducing contamination risks compared to polystyrene (PS), which may leach styrene monomers under heat. Regulatory compliance favors PPO as it meets FDA and EU food contact regulations more consistently, while polystyrene faces stricter restrictions due to concerns over styrene migration and environmental impact. Food containers made from PPO ensure longer shelf life and safer food storage, aligning with evolving food safety standards and consumer protection laws.
Impact on Food Taste and Aroma Retention
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior aroma retention compared to polystyrene, minimizing flavor contamination and preserving the original taste of food. PPO's high chemical resistance prevents leaching of plasticizers, ensuring food packaging remains neutral and odor-free. Polystyrene, while cost-effective, is prone to absorbing and transferring odors, which can adversely affect food taste and aroma quality.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and durability compared to polystyrene (PS), making it a more sustainable choice for food containers due to its longer lifespan and reduced material waste. PPO is more readily recyclable through specialized chemical recycling processes, whereas polystyrene recycling is limited and often results in downcycling or landfill disposal, increasing environmental burden. The environmental impact of PPO containers is lower as they produce fewer emissions during recycling and reduce plastic pollution compared to polystyrene, which is prone to fragmentation and persistent microplastic contamination.
Cost Analysis and Commercial Availability
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to polystyrene (PS), but its higher raw material and processing costs result in increased overall expenses for food container production. Polystyrene remains more cost-effective and widely available in commercial markets, benefiting from established supply chains and lower manufacturing costs. The choice between PPO and PS largely depends on the required performance characteristics and budget constraints in food packaging applications.
Applications in Food Packaging: Case Studies
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO) offers superior heat resistance and dimensional stability compared to polystyrene (PS), making it ideal for hot food containers such as coffee cups and microwaveable trays. Case studies reveal that PPO-based packaging maintains structural integrity under high temperatures, reducing leaching risks and preserving food safety, whereas PS often shows deformation and increased chemical migration. Applications in fresh food packaging also highlight PPO's enhanced moisture barrier properties and recyclability, supporting sustainable packaging initiatives over conventional polystyrene.
Infographic: Polyphenylene oxide vs Polystyrene for Food container
 azmater.com
azmater.com