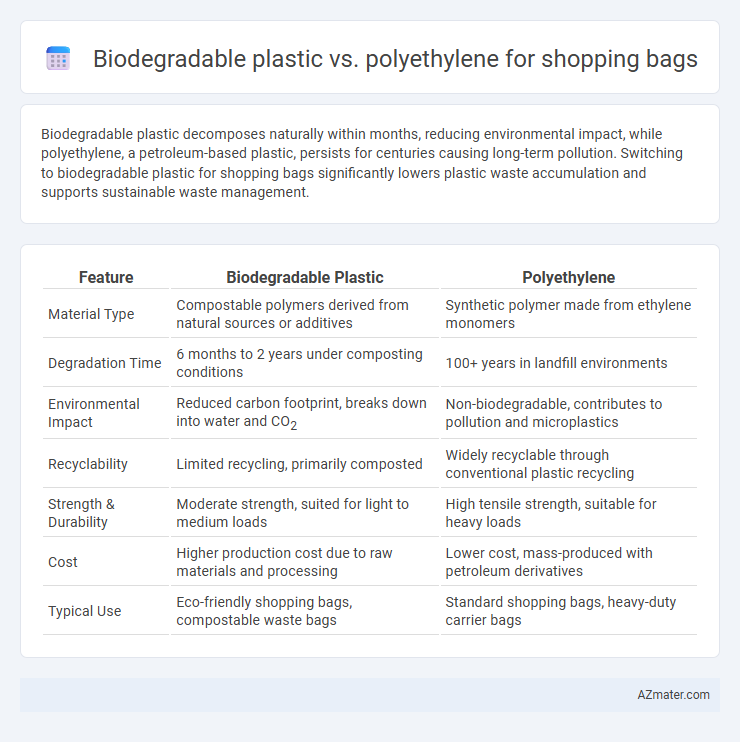
Biodegradable plastic decomposes naturally within months, reducing environmental impact, while polyethylene, a petroleum-based plastic, persists for centuries causing long-term pollution. Switching to biodegradable plastic for shopping bags significantly lowers plastic waste accumulation and supports sustainable waste management.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biodegradable Plastic | Polyethylene |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Compostable polymers derived from natural sources or additives | Synthetic polymer made from ethylene monomers |
| Degradation Time | 6 months to 2 years under composting conditions | 100+ years in landfill environments |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced carbon footprint, breaks down into water and CO2 | Non-biodegradable, contributes to pollution and microplastics |
| Recyclability | Limited recycling, primarily composted | Widely recyclable through conventional plastic recycling |
| Strength & Durability | Moderate strength, suited for light to medium loads | High tensile strength, suitable for heavy loads |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to raw materials and processing | Lower cost, mass-produced with petroleum derivatives |
| Typical Use | Eco-friendly shopping bags, compostable waste bags | Standard shopping bags, heavy-duty carrier bags |
Introduction to Shopping Bag Materials
Biodegradable plastic and polyethylene are two prominent materials used in shopping bag production, each offering distinct environmental and functional properties. Polyethylene, a conventional plastic derived from petroleum, is durable and cost-effective but poses significant environmental concerns due to its non-biodegradable nature and long decomposition time. Biodegradable plastics, often made from renewable resources like cornstarch, break down more rapidly in natural conditions, reducing landfill accumulation and environmental impact, making them a sustainable alternative for eco-conscious consumers and retailers.
What Are Biodegradable Plastics?
Biodegradable plastics are designed to break down through natural processes involving microbes, heat, and moisture, typically decomposing within months to a few years. Unlike traditional polyethylene shopping bags, which can persist in the environment for hundreds of years, biodegradable plastics reduce long-term pollution and landfill burden. These materials are often derived from renewable resources like cornstarch or plant-based polymers, enhancing sustainability in single-use shopping bag applications.
Understanding Polyethylene Bags
Polyethylene bags, widely used for shopping, are made from petroleum-based polymers like high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE), known for their durability, flexibility, and moisture resistance. These characteristics make polyethylene bags cost-effective and suitable for carrying heavy items but contribute significantly to environmental pollution due to their slow degradation rate. Understanding the chemical structure and environmental impact of polyethylene bags highlights the need for improved waste management and development of sustainable alternatives such as biodegradable plastics.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradable Plastic vs Polyethylene
Biodegradable plastic shopping bags break down more quickly under specific conditions, reducing long-term landfill accumulation and decreasing microplastic pollution compared to polyethylene bags, which can persist for hundreds of years in the environment. Polyethylene bags contribute significantly to marine pollution and pose hazards to wildlife due to their non-degradable nature. Although biodegradable plastics offer improved environmental benefits, their effective decomposition requires industrial composting facilities, limiting their impact where such infrastructure is unavailable.
Decomposition Rate and Conditions
Biodegradable plastic shopping bags decompose significantly faster than polyethylene bags, breaking down within months under optimal conditions like industrial composting with high heat and moisture. Polyethylene bags can take up to 500 years to decompose in natural environments due to their stable polymer structure and resistance to microbial activity. The efficiency of biodegradable bags depends heavily on specific conditions, while polyethylene's persistence poses long-term environmental pollution risks.
Manufacturing Process and Resource Consumption
Biodegradable plastic shopping bags are primarily manufactured from renewable plant-based materials such as cornstarch or sugarcane, using processes like fermentation and polymerization that consume less fossil fuel compared to polyethylene production. Polyethylene bags are derived from crude oil through energy-intensive polymerization and extrusion, leading to higher greenhouse gas emissions and non-renewable resource depletion. The resource consumption of biodegradable plastics is generally lower with a smaller carbon footprint due to renewable feedstocks, whereas polyethylene relies heavily on petrochemical resources and extensive energy inputs throughout its manufacturing process.
Strength, Durability, and Usability
Biodegradable plastic shopping bags offer moderate strength and decompose more rapidly in natural environments, reducing long-term pollution compared to polyethylene bags. Polyethylene bags exhibit superior durability and puncture resistance, making them more reliable for carrying heavy or sharp items over extended periods. Usability differs as biodegradable bags may become brittle when exposed to moisture, while polyethylene bags maintain flexibility and consistent performance under various conditions.
Cost Comparison: Biodegradable vs Polyethylene Bags
Biodegradable shopping bags typically cost 20-50% more than polyethylene bags, primarily due to the higher production expenses of biodegradable materials like PLA or PBAT. Polyethylene bags benefit from established manufacturing processes and economies of scale, resulting in a lower average price per unit, often under $0.05 compared to biodegradable bags which may cost $0.07 to $0.10 each. While biodegradable bags offer environmental advantages, their higher upfront cost remains a significant factor for retailers evaluating budget constraints and sustainability goals.
Consumer Perceptions and Market Trends
Consumer perceptions of biodegradable plastic shopping bags highlight environmental benefits such as reduced plastic pollution and faster decomposition compared to traditional polyethylene bags. Market trends indicate a growing demand for sustainable packaging solutions, driven by increasing eco-consciousness and regulatory pressures limiting single-use polyethylene bags. Despite production cost challenges, biodegradable plastics are gaining traction in retail sectors aiming to align with green consumer values and improve brand reputation.
Future Outlook for Sustainable Shopping Bags
Biodegradable plastics, derived from renewable resources such as cornstarch and sugarcane, offer promising solutions for reducing environmental impact compared to traditional polyethylene bags, which are petroleum-based and persist in landfills for centuries. Innovations in compostable biopolymers and enhanced recycling technologies are driving the adoption of biodegradable shopping bags in global markets, supporting circular economy goals. Future outlooks emphasize scalable production of eco-friendly materials and strengthened waste management infrastructure to ensure widespread use and effective degradation of sustainable shopping bags.
Infographic: Biodegradable plastic vs Polyethylene for Shopping bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com