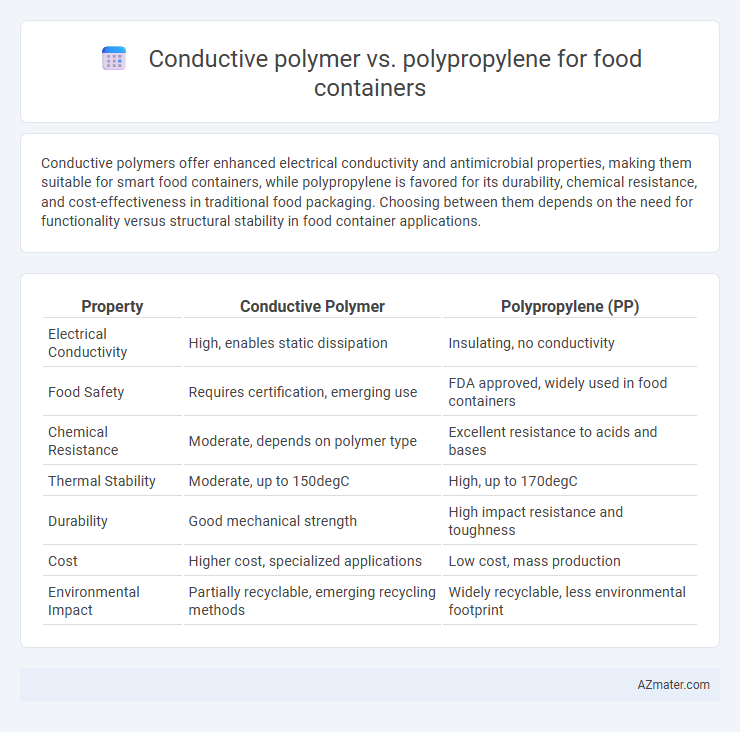
Conductive polymers offer enhanced electrical conductivity and antimicrobial properties, making them suitable for smart food containers, while polypropylene is favored for its durability, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness in traditional food packaging. Choosing between them depends on the need for functionality versus structural stability in food container applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Conductive Polymer | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High, enables static dissipation | Insulating, no conductivity |
| Food Safety | Requires certification, emerging use | FDA approved, widely used in food containers |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate, depends on polymer type | Excellent resistance to acids and bases |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate, up to 150degC | High, up to 170degC |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength | High impact resistance and toughness |
| Cost | Higher cost, specialized applications | Low cost, mass production |
| Environmental Impact | Partially recyclable, emerging recycling methods | Widely recyclable, less environmental footprint |
Introduction to Food Container Materials
Conductive polymers offer unique advantages for food containers by providing antimicrobial properties and static dissipation, enhancing food safety and preservation. Polypropylene remains a widely used food container material due to its lightweight, chemical resistance, and excellent moisture barrier, ensuring durability and food quality. Comparing both materials highlights the potential of conductive polymers to innovate food packaging beyond the traditional, inert properties of polypropylene.
Overview of Conductive Polymers
Conductive polymers are organic materials that combine electrical conductivity with the mechanical properties of conventional polymers, making them ideal for applications requiring static dissipation or electromagnetic interference shielding in food containers. Unlike polypropylene, which is widely used for its chemical resistance, durability, and food safety, conductive polymers offer the added advantage of modulating electrical properties to prevent bacterial growth and enhance packaging functionality. These polymers include polyaniline, polypyrrole, and polythiophene, known for their tunable conductivity, environmental stability, and biocompatibility in food-contact applications.
Properties of Polypropylene in Food Packaging
Polypropylene (PP) is widely used in food packaging due to its excellent chemical resistance, high melting point of approximately 160degC, and strong barrier properties against moisture and oils, ensuring food safety and extended shelf life. Its lightweight and durable nature provide mechanical strength and flexibility, making it ideal for a variety of containers and packaging films. Polypropylene is also microwave-safe and recyclable, enhancing its suitability for modern food packaging applications.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Conductive polymers exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to polypropylene, especially against oils, acids, and solvents commonly encountered in food storage. Polypropylene, while cost-effective and food-safe, tends to degrade or absorb odors and stains when exposed to strong chemicals or prolonged contact with acidic or oily substances. This makes conductive polymers a more durable choice for food containers requiring enhanced resistance to a wide range of chemicals and contaminants.
Thermal Stability and Heat Tolerance
Conductive polymers exhibit superior thermal stability compared to polypropylene, maintaining structural integrity at higher temperatures without significant degradation. Polypropylene typically withstands heat up to 100-110degC before softening, whereas conductive polymers can endure temperatures exceeding 150degC, making them more suitable for applications involving prolonged heat exposure. Their enhanced heat tolerance makes conductive polymers ideal for food containers requiring repeated thermal cycling or microwave heating.
Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Conductive polymers exhibit inherent antimicrobial properties that reduce bacterial contamination risks in food containers, enhancing food safety compared to polypropylene, which lacks such features and may require additives for similar effects. Regulatory compliance for conductive polymers involves rigorous testing under FDA and EFSA guidelines to ensure non-toxicity and chemical stability, while polypropylene is widely approved due to its inertness and established safety profile in food contact applications. The choice between these materials hinges on balancing advanced antimicrobial benefits of conductive polymers with the proven regulatory acceptance and cost-effectiveness of polypropylene for food packaging.
Impact on Food Shelf Life
Conductive polymers in food containers can improve shelf life by providing antimicrobial properties that inhibit bacterial growth, reducing spoilage and contamination. Polypropylene, a widely used food-grade plastic, offers excellent barrier resistance to moisture and gases, helping to maintain food freshness but lacks inherent antimicrobial effects. Combining conductive polymers with polypropylene enhances shelf life through improved preservation and protection against microbial degradation.
Cost Analysis: Conductive Polymer vs Polypropylene
Conductive polymers generally have higher upfront material costs compared to polypropylene due to advanced manufacturing processes and specialized raw materials. Polypropylene remains cost-effective for mass production of food containers because of its widespread availability and well-established processing techniques. However, conductive polymers offer added value in applications requiring anti-static properties or enhanced durability, which can justify their premium pricing in niche markets.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Conductive polymers offer potential for biodegradable and recyclable food containers due to their organic composition and lower environmental footprint compared to traditional plastics. Polypropylene, widely used in food packaging, is durable and cost-effective but poses challenges in biodegradability and contributes to plastic waste accumulation in landfills and oceans. Sustainable alternatives prioritize materials like conductive polymers that reduce carbon emissions and enhance recyclability, addressing critical environmental impact concerns in the food packaging industry.
Future Trends in Food Container Materials
Conductive polymers offer promising applications in smart food containers due to their electrical conductivity and antimicrobial properties, enabling enhanced freshness monitoring and active packaging solutions. Polypropylene remains a staple for food containers owing to its durability, chemical resistance, and recyclability, yet future trends emphasize blending it with advanced materials to improve barrier properties and sustainability. Innovations focus on integrating conductive polymers with polypropylene matrices to create hybrid materials that combine functionality with environmental benefits in next-generation food packaging.
Infographic: Conductive polymer vs Polypropylene for Food container
 azmater.com
azmater.com