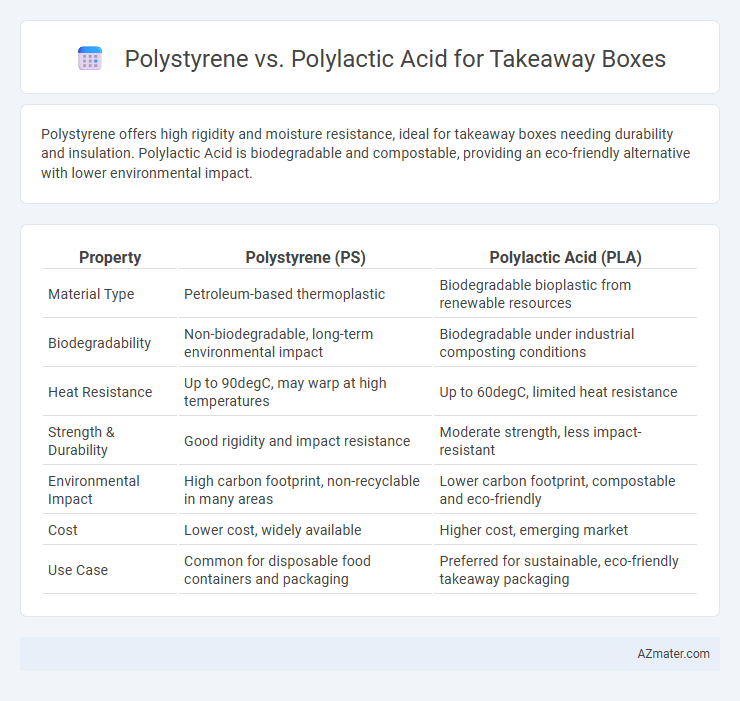
Polystyrene offers high rigidity and moisture resistance, ideal for takeaway boxes needing durability and insulation. Polylactic Acid is biodegradable and compostable, providing an eco-friendly alternative with lower environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polystyrene (PS) | Polylactic Acid (PLA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Petroleum-based thermoplastic | Biodegradable bioplastic from renewable resources |
| Biodegradability | Non-biodegradable, long-term environmental impact | Biodegradable under industrial composting conditions |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 90degC, may warp at high temperatures | Up to 60degC, limited heat resistance |
| Strength & Durability | Good rigidity and impact resistance | Moderate strength, less impact-resistant |
| Environmental Impact | High carbon footprint, non-recyclable in many areas | Lower carbon footprint, compostable and eco-friendly |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, emerging market |
| Use Case | Common for disposable food containers and packaging | Preferred for sustainable, eco-friendly takeaway packaging |
Introduction to Takeaway Containers: Polystyrene and Polylactic Acid
Polystyrene and polylactic acid (PLA) are two common materials used in takeaway containers, each with distinct properties influencing their environmental impact and usability. Polystyrene offers lightweight durability and excellent insulation but poses significant challenges in biodegradability and recycling, contributing to environmental pollution. In contrast, PLA is a biodegradable polymer derived from renewable resources like corn starch, providing a more sustainable option with compostable features suitable for eco-friendly food packaging.
Material Composition and Source Comparison
Polystyrene (PS) is a petroleum-based synthetic polymer derived from styrene monomers, offering high durability and thermal insulation but contributing to environmental pollution due to its non-biodegradable nature. In contrast, Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic sourced from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, promoting sustainability in takeaway packaging through its compostability and reduced carbon footprint. The material composition of PLA ensures lower environmental impact, while PS provides superior mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness, making the choice dependent on prioritizing ecological benefits versus performance and price.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradability and Sustainability
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers superior environmental benefits compared to polystyrene (PS) due to its biodegradability and renewable sourcing from corn starch or sugarcane, which reduces dependence on fossil fuels. Polystyrene, derived from petroleum, is non-biodegradable and contributes significantly to plastic pollution and landfill accumulation. PLA breaks down under industrial composting conditions within months, enhancing waste management sustainability, whereas polystyrene can persist for hundreds of years, posing long-term ecological risks.
Food Safety and Health Considerations
Polylactic Acid (PLA) takeaway boxes are preferred for food safety due to their biodegradable nature and reduced chemical leaching compared to Polystyrene (PS), which may release styrene, a potential carcinogen, when exposed to heat. PLA is derived from renewable resources like corn starch, making it a safer, environmentally friendly option that poses fewer health risks during use. Polystyrene containers, while inexpensive and effective for insulation, raise health concerns related to chemical exposure and environmental persistence.
Thermal Insulation and Heat Resistance
Polystyrene offers superior thermal insulation and heat resistance for takeaway boxes, maintaining food temperature longer due to its low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.033 W/m*K. Polylactic Acid (PLA), biodegradable and derived from renewable resources, has a higher thermal conductivity, approximately 0.13 W/m*K, resulting in less effective insulation and lower heat resistance, usually withstanding temperatures up to 60degC before deformation. For applications requiring sustained heat retention and resistance to hot food, polystyrene is more suitable, whereas PLA is favored for eco-friendly, short-term thermal needs.
Cost Analysis for Businesses
Polystyrene takeaway boxes typically cost less per unit compared to polylactic acid (PLA) options, making them attractive for businesses aiming to minimize upfront expenses. However, PLA boxes, derived from renewable resources, may entail higher initial costs but can reduce long-term waste disposal fees due to their compostability. Factoring in environmental regulations and customer demand for sustainable packaging, businesses evaluating cost analysis must balance the immediate savings of polystyrene against potential future benefits and market positioning offered by PLA.
User Experience: Strength, Weight, and Convenience
Polystyrene takeaway boxes offer high strength and durability, making them resistant to crushing and leakage during transport, but they tend to be heavier, potentially reducing portability. Polylactic Acid (PLA) boxes are lightweight and environmentally friendly, enhancing convenience for users who prioritize easy carrying and disposal, though their strength may vary depending on temperature and moisture exposure. Choosing between the two depends on balancing the need for sturdy packaging against the desire for eco-friendly, lightweight options that enhance overall user experience.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Polystyrene takeaway boxes often face strict regulatory scrutiny due to concerns about environmental persistence and potential health risks associated with styrene monomers, leading to bans or restrictions in multiple regions such as the EU and California. Polylactic Acid (PLA), derived from renewable resources, complies more easily with global biodegradability and compostability standards like ASTM D6400 and EN 13432, making it preferable under evolving sustainability regulations. Compliance with these standards ensures PLA takeaway boxes meet the growing demand for eco-friendly packaging and qualify for certifications that enhance market acceptance.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Polystyrene remains prevalent in the takeaway box market due to its low cost and excellent insulation properties, driving steady demand despite growing environmental concerns. Polylactic acid (PLA) is rapidly gaining consumer preference aligned with increasing eco-consciousness, supported by rising regulations favoring biodegradable and compostable materials in food packaging. Market trends indicate a significant shift towards sustainable alternatives like PLA, as major foodservice brands and retailers adopt green packaging solutions to meet evolving consumer expectations and legislative mandates.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Takeaway Boxes
Polylactic Acid (PLA) offers a biodegradable and compostable alternative to traditional Polystyrene, making it ideal for environmentally conscious takeaway packaging. Polystyrene provides superior insulation and cost-effectiveness, but its environmental impact and non-biodegradability pose significant sustainability challenges. Selecting PLA supports eco-friendly initiatives and reduces landfill waste, while Polystyrene remains suitable for applications prioritizing durability and thermal protection.
Infographic: Polystyrene vs Polylactic Acid for Takeaway Box
 azmater.com
azmater.com