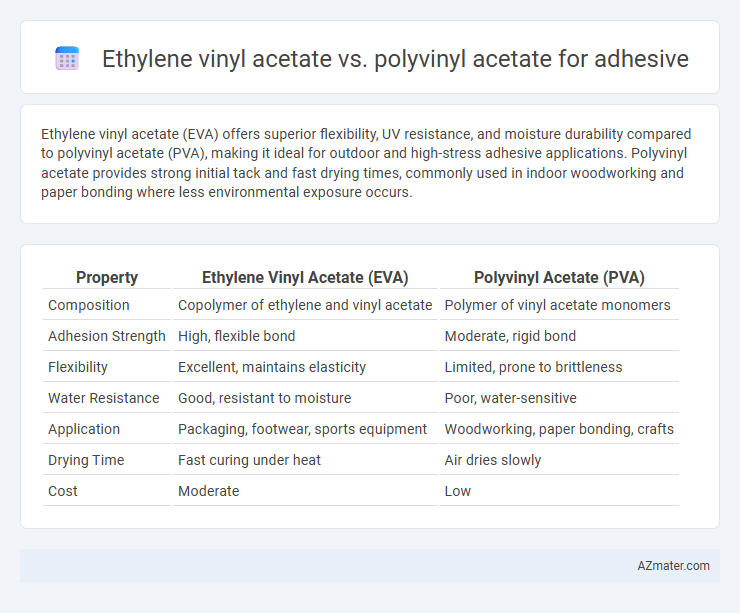
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility, UV resistance, and moisture durability compared to polyvinyl acetate (PVA), making it ideal for outdoor and high-stress adhesive applications. Polyvinyl acetate provides strong initial tack and fast drying times, commonly used in indoor woodworking and paper bonding where less environmental exposure occurs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Polyvinyl Acetate (PVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate | Polymer of vinyl acetate monomers |
| Adhesion Strength | High, flexible bond | Moderate, rigid bond |
| Flexibility | Excellent, maintains elasticity | Limited, prone to brittleness |
| Water Resistance | Good, resistant to moisture | Poor, water-sensitive |
| Application | Packaging, footwear, sports equipment | Woodworking, paper bonding, crafts |
| Drying Time | Fast curing under heat | Air dries slowly |
| Cost | Moderate | Low |
Introduction to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) and Polyvinyl Acetate (PVA)
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is a copolymer commonly used as an adhesive due to its flexibility, strong bonding properties, and resistance to UV radiation and moisture. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) is a synthetic polymer known for its excellent adhesion to porous materials like wood and paper, featuring fast drying times and non-toxic composition. Both EVA and PVA serve critical roles in adhesive applications, with EVA favored for durability and elasticity, while PVA is valued for ease of use and versatility in woodworking and crafts.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) consists of ethylene and vinyl acetate monomers, forming a copolymer with a flexible, semi-crystalline structure that offers enhanced elongation and impact resistance. Polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) is a homopolymer comprised solely of vinyl acetate units, exhibiting a more rigid and glassy structure with strong adhesive properties but limited flexibility. The presence of ethylene in EVA reduces polarity, increasing water resistance and flexibility, while PVAc's higher polarity improves adhesion to porous surfaces yet decreases moisture resistance.
Adhesive Performance and Bonding Strength
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) displays superior adhesive performance and enhanced bonding strength compared to polyvinyl acetate (PVA) due to its greater flexibility, impact resistance, and moisture tolerance. EVA adhesives form strong, durable bonds on diverse substrates such as wood, plastics, and textiles, maintaining elasticity under stress and temperature variations. Conversely, PVA adhesives excel in bonding porous materials like paper and wood but offer lower moisture resistance and reduced bonding strength on non-porous surfaces.
Flexibility and Elasticity Differences
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility and elasticity compared to polyvinyl acetate (PVA), making it ideal for applications requiring high impact resistance and durability under stress. EVA's copolymer structure imparts enhanced elongation and recovery properties, whereas PVA exhibits rigidity and lower stretchability due to its homopolymer composition. These differences make EVA adhesives more suitable for flexible bonding, while PVA is preferred for rigid, less elastic assemblies.
Water Resistance Capabilities
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) exhibits superior water resistance compared to polyvinyl acetate (PVA), making it ideal for applications exposed to moisture. EVA's copolymer structure provides enhanced flexibility and durability in wet environments, whereas PVA tends to degrade and lose adhesive strength when exposed to water. Industries requiring strong bonding under humid or wet conditions commonly prefer EVA adhesives for their long-lasting performance.
Temperature Stability and Thermal Properties
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) exhibits superior temperature stability compared to polyvinyl acetate (PVA), maintaining adhesion performance in temperatures ranging from -40degC to 80degC, whereas PVA typically degrades above 60degC. EVA's enhanced thermal properties include greater flexibility and resistance to thermal aging, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under fluctuating temperatures. PVA, while cost-effective and suitable for indoor use, lacks the thermal resilience necessary for high-temperature environments or prolonged heat exposure.
Suitability for Various Materials and Applications
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility and moisture resistance, making it ideal for bonding plastics, foams, and textiles in packaging and footwear industries. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) excels in wood, paper, and porous surface adhesion due to its strong initial tack and fast drying properties, commonly used in woodworking and paper crafts. EVA's resilience to temperature variations suits outdoor applications, while PVA's biodegradability is preferred for environmentally sensitive products.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) adhesives exhibit lower volatility and reduced emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) compared to polyvinyl acetate (PVA), enhancing indoor air quality and minimizing environmental pollution. EVA's chemical stability and resistance to biodegradation raise concerns about long-term environmental persistence, whereas PVA is more biodegradable but may release formaldehyde-based byproducts during degradation, posing health risks. Safety considerations highlight EVA's reduced flammability and lower toxicity compared to PVA, making EVA preferable for applications requiring stringent human and environmental safety standards.
Cost Effectiveness and Commercial Availability
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior cost-effectiveness due to its lower price point and enhanced flexibility compared to polyvinyl acetate (PVA), making it ideal for a wide range of adhesive applications. EVA adhesives are commercially available in bulk quantities and widely distributed in industrial and consumer markets, ensuring consistent supply and competitive pricing. In contrast, PVA adhesives, though popular for woodworking and paper bonding, tend to be more expensive and less versatile, limiting their cost efficiency and commercial availability for high-demand sectors.
Choosing Between EVA and PVA for Adhesive Uses
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility, water resistance, and UV stability compared to polyvinyl acetate (PVA), making it ideal for outdoor adhesive applications and flexible bonding needs. PVA excels in wood, paper, and porous material adhesion with strong initial tack and fast drying, but lacks the durability and moisture resistance of EVA. Choosing EVA or PVA depends on specific adhesive requirements such as exposure to moisture, flexibility, and substrate type, with EVA preferred for heavy-duty, weather-resistant tasks and PVA suited for indoor, light-duty applications.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Polyvinyl acetate for Adhesive
 azmater.com
azmater.com