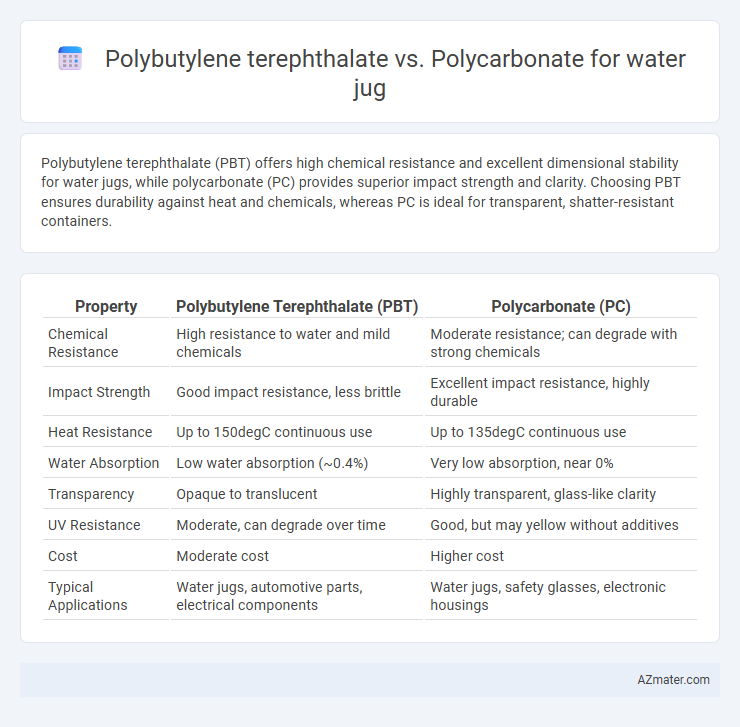
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers high chemical resistance and excellent dimensional stability for water jugs, while polycarbonate (PC) provides superior impact strength and clarity. Choosing PBT ensures durability against heat and chemicals, whereas PC is ideal for transparent, shatter-resistant containers.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to water and mild chemicals | Moderate resistance; can degrade with strong chemicals |
| Impact Strength | Good impact resistance, less brittle | Excellent impact resistance, highly durable |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 150degC continuous use | Up to 135degC continuous use |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption (~0.4%) | Very low absorption, near 0% |
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | Highly transparent, glass-like clarity |
| UV Resistance | Moderate, can degrade over time | Good, but may yellow without additives |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost |
| Typical Applications | Water jugs, automotive parts, electrical components | Water jugs, safety glasses, electronic housings |
Introduction to Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) and Polycarbonate (PC)
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polyester known for its high mechanical strength, excellent chemical resistance, and low moisture absorption, making it suitable for durable water jug fabrication. Polycarbonate (PC) offers outstanding impact resistance, clarity, and thermal stability, often used in transparent water containers requiring toughness and safety. Comparing PBT and PC for water jugs highlights differences in transparency, durability, and resistance to heat and chemicals, guiding material selection based on specific usage and performance needs.
Chemical Structure and Material Properties
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a semicrystalline thermoplastic polyester characterized by ester linkages in its backbone, providing high chemical resistance and dimensional stability, making it suitable for water jugs that require durability and resistance to hydrolysis. Polycarbonate (PC), with its carbonate groups and aromatic rings in the backbone, offers outstanding impact resistance, transparency, and thermal stability but is more susceptible to chemical attack from alkalis and certain solvents. The choice between PBT and PC for water jugs depends on the balance between PBT's superior chemical resistance and PC's superior toughness and clarity.
Mechanical Strength: PBT vs Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate (PC) exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength and impact resistance compared to Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT), making it more suitable for water jugs requiring durability against drops and heavy usage. PBT offers good tensile strength and rigidity but is less resistant to impact and may crack under stress where PC remains intact. The choice between PBT and Polycarbonate for water jugs often hinges on the need for superior toughness and longevity, properties in which PC excels.
Heat Resistance and Temperature Tolerance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent heat resistance with a melting point around 223degC and maintains structural integrity in temperatures up to 150degC, making it suitable for hot water jugs. Polycarbonate (PC) features higher temperature tolerance with a glass transition temperature near 147degC and can withstand continuous use up to 135degC, but its melting point is lower around 155degC compared to PBT. For water jugs requiring consistent exposure to high heat or boiling conditions, PBT generally provides superior thermal stability and durability over polycarbonate.
Durability and Impact Resistance in Water Jugs
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance compared to Polybutylene terephthalate, making it ideal for water jugs prone to drops and rough handling. Polybutylene terephthalate provides good durability with chemical resistance and dimensional stability but is less impact-resistant than polycarbonate. For water jugs requiring maximum toughness and long-term durability, polycarbonate is the preferred material due to its ability to withstand heavy impacts without cracking.
Safety and BPA Concerns
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a BPA-free thermoplastic known for its excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability, making it a safer option for water jugs compared to traditional plastics. Polycarbonate, while durable and transparent, often contains BPA, a chemical linked to health concerns such as endocrine disruption and potential carcinogenic effects. Choosing PBT over polycarbonate minimizes BPA exposure, ensuring safer water storage for consumer health.
Taste and Odor Retention
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) excels in taste and odor retention due to its high chemical resistance and low permeability, making it ideal for water jugs that preserve water purity without leaching flavors. Polycarbonate (PC), while durable and impact-resistant, tends to absorb and retain odors over time, which can subtly alter the taste of stored water. For applications prioritizing minimal taste and odor interference, PBT is the preferred choice over polycarbonate in water jug manufacturing.
Ease of Processing and Manufacturing
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers ease of processing with low moisture absorption and excellent dimensional stability, making it highly suitable for injection molding water jugs. Polycarbonate (PC) provides superior impact resistance but requires more precise temperature control during manufacturing to avoid hydrolytic degradation and ensure consistent quality. PBT's faster crystallization rate contributes to shorter cycle times and higher throughput in production compared to polycarbonate.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers a lower environmental impact due to its biodegradability potential and lower carbon footprint compared to polycarbonate (PC), which relies heavily on bisphenol A (BPA) and petroleum-based processes. PBT is more easily recyclable through standard polyester recycling streams, while polycarbonate recycling faces challenges due to BPA content and more complex chemical structures. Choosing PBT for water jugs supports sustainable manufacturing practices and facilitates material recovery, reducing plastic waste and environmental pollution.
Which is Better: PBT or Polycarbonate for Water Jugs?
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and clarity, making it ideal for durable, transparent water jugs that withstand drops and rough handling. Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) provides excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability, ensuring the jug remains leak-proof and resistant to deformation over time. For water jugs requiring toughness and visual appeal, polycarbonate is better, while PBT suits applications prioritizing chemical durability and structural integrity.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polycarbonate for Water jug
 azmater.com
azmater.com